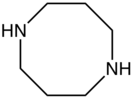
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,5-Diazocane | |
| Other names
DACO, octahydro-1,5-diazocine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14N2 | |
| Molar mass | 114.192 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Boiling point | 78–80 °C (172–176 °F; 351–353 K) 16 Torr |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
1,5-Diazacyclooctane is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2CH2NH)2. It is a colorless oil. 1,5-Diazacyclooctane is a cyclic diamine.[1]
Synthesis and reactions
It is prepared in low yield by the alkylation of ammonia with 1,3-dibromopropane.[2]
The N-H centers can be replaced with many other groups. As a bis secondary amine, it condenses with aldehydes to give bicyclic derivatives.[3] When treated with transition metal salts, it serves as a chelating ligand.[1]
Related compounds
References
- 1 2 Musker, W. Kenneth (1992). "Coordination Chemistry of Bidentate Medium Ring Ligands (Mesocycles)". Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 117: 133–57. doi:10.1016/0010-8545(92)80022-J.
- ↑ Daniel K. Mills; Ivan Font; Patrick J. Farmer; et al. (1998). "1,5-Diazacyclooctane, Pendant Arm Thiolato Derivatives and [ N,N′ -Bis(2-Mercaptoethyl)-1,5-Diazacyclooctanato]Nickel(II)". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 32. pp. 89–98. doi:10.1002/9780470132630.ch15. ISBN 9780471249214.
- ↑ Billman, John H.; Dorman, Linneaus C. (1962). "Reaction of 1,5-Diazacyclooctane with Aldehydes". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 27 (7): 2419–22. doi:10.1021/jo01054a033.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.