| 1932 presidential election | |
  Nominees Hoover and Curtis | |
| Convention | |
|---|---|
| Date(s) | June 14–16, 1932 |
| City | Chicago, Illinois |
| Venue | Chicago Stadium |
| Candidates | |
| Presidential nominee | Herbert C. Hoover of California |
| Vice presidential nominee | Charles Curtis of Kansas |
| Results (president) | Herbert Hoover (CA): 1126.5 (98.5%) John J. Blaine: 13 Calvin Coolidge: 4.5 Joseph Irwin France: 4 James W. Wadsworth: 1 |
The 1932 Republican National Convention was held at Chicago Stadium in Chicago, Illinois, from June 14 to June 16, 1932. It nominated President Herbert Hoover and Vice President Charles Curtis for reelection.[1]
Hoover was virtually unopposed for the nomination. Despite the ongoing situation facing the Republican Party, the convention praised Hoover and pledged itself to maintain a balanced budget.
Presidential nomination
Presidential candidates
_(cropped1).jpg.webp)
Republicans gloomily gathered in Chicago for the 20th Republican National Convention. Los Angeles attorney Joseph Scott delivered President Hoover's nominating address, praising him as the man who taught the nation to resist the temptations of governmental paternalism. Hoover was re-nominated on the first ballot without significant opposition. To have repudiated the incumbent would have destroyed what little chance of victory the party had amid the worst economic depression in U.S. history.
Former senator Joseph I. France of Maryland attempted to engineer a draft-Coolidge movement, but the former president expressed no interest in the nomination.
| Presidential Ballot | ||
|---|---|---|
| Candidate | 1st | Unanimous |
| Hoover | 1,126.5 | 1,154 |
| Blaine | 13 | |
| Coolidge | 4.5 | |
| France | 4 | |
| Dawes | 1 | |
| Wadsworth | 1 | |
| Not Voting | 3 | |
| Absent | 1 | |
Presidential Balloting / 3rd Day of Convention (June 16, 1932)
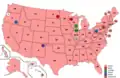 1st Presidential Ballot
1st Presidential Ballot
Vice Presidential nomination
Vice Presidential candidates
Vice President Curtis experienced more difficulties than President Hoover in securing his party's re-nomination. It took the fervid appeals of Hoover's cabinet members to keep the Illinois delegation from nominating former Vice President Charles Dawes for his old office. Curtis nonetheless still had to fight for his re-nomination despite the disorganization of his opposition by the advance refusal of Dawes to accept the nomination for second place. Ambassador Hanford MacNider and RCA Chairman James Harbord, both military professionals, were the primary beneficiaries of the opposition to Curtis.[2]
The initial roll call revealed Curtis to be 18 votes shy of securing re-nomination. At this point, Pennsylvania switched its 75 votes from favorite son Edward Martin to Curtis. After Curtis had secured the vice presidential nomination, the delegates moved to make his re-nomination unanimous.[2]
| Vice Presidential Ballot | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Candidate | 1st (Before Shifts) | 1st (After Shifts) | Unanimous |
| Curtis | 559.25 | 634.25 | 1,154 |
| MacNider | 178.75 | 178.75 | |
| Harbord | 161.75 | 161.75 | |
| Martin | 75 | 0 | |
| Fuller | 57 | 57 | |
| Snell | 56 | 56 | |
| Replogle | 23.75 | 23.75 | |
| Couzens | 11 | 11 | |
| Dawes | 9.75 | 9.75 | |
| Ingalls | 5 | 5 | |
| Hurley | 2 | 2 | |
| Kenyon | 2 | 2 | |
| Bingham | 1 | 1 | |
| Morgan | 1 | 1 | |
| Not Voting | 9.75 | 9.75 | |
| Absent | 1 | 1 | |
Vice Presidential Balloting / 3rd Day of Convention (June 16, 1932)
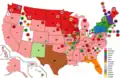 1st
1st
Vice Presidential Ballot
(Before Shifts)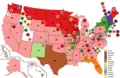 1st
1st
Vice Presidential Ballot
(After Shifts)
See also
References
- ↑ Shi & Tindall 2010, p. 1081.
- 1 2 Kalb, Deborah (ed.). CQ Press Guide to U.S. Elections (seventh ed.). Washington, DC: CQ Press. p. 227. ISBN 978-1-4833-8038-4 – via Google Books.
Bibliography
- Pietrusza, David 1932: The Rise of Hitler & FDR: Two Tales of Politics, Betrayal and Unlikely Destiny Lyons Press Guilford, CT 2015.
- Shi, David E.; Tindall, George Brown (2010). Jon Durbin (ed.). America: A Narrative History. Vol. 1 (8th ed.). New York: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-11700-4.
External links
- Republican Party platform of 1932 at The American Presidency Project
- Hoover acceptance address at The American Presidency Project
- Hoover acceptance letter at The American Presidency Project
| Preceded by 1928 Kansas City, Missouri |
Republican National Conventions | Succeeded by 1936 Cleveland, Ohio |









.jpg.webp)
