 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.574 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
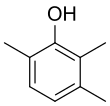
| C9H12O | |
| Molar mass | 136.194 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 72 °C (162 °F; 345 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
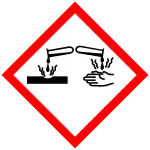  | |
| Danger | |
| H315, H318 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P271, P272, P280, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P332+P313, P333+P313, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2,3,6-Trimethylphenol is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3C6H2OH. As a precursor to vitamin E, it is the most widely used of the several isomers of trimethylphenol.
2,3,6-Trimethylphenol is produced industrially by the methylation of m-cresol with methanol in the presence of a solid acid.[2]
References
- ↑ "2,3,6-Trimethylphenol". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ↑ Fiege, Helmut; Voges, Heinz-Werner; Hamamoto, Toshikazu; Umemura, Sumio; Iwata, Tadao; Miki, Hisaya; Fujita, Yasuhiro; Buysch, Hans-Josef; Garbe (2000). "Phenol Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_313. ISBN 978-3527306732.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.