 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
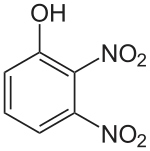
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,3-Dinitrophenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.571 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1599 1320 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H4N2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 184.107 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.683 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 108 °C (226 °F; 381 K) |
| Boiling point | 113 °C (235 °F; 386 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   | |
| Danger | |
| H301, H311, H331, H373, H411 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P311, P312, P314, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Legal status | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2,3-Dinitrophenol (2,3-DNP) is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H3(NO2)2.[2] 2,3-Dinitrophenol is not planar due to rotation of nitro groups, and is acidic.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Anvisa (2023-07-24). "RDC Nº 804 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-07-25). Archived from the original on 2023-08-27. Retrieved 2023-08-27.
- ↑ Markwell, Roger E. (1979). "Novel cine substitution in the reaction of 2,3-dinitrophenol with secondary amines". Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications (9): 428. doi:10.1039/C39790000428.
- ↑ Abraham, Michael H.; Du, Chau My; Platts, James A. (1 October 2000). "Lipophilicity of the Nitrophenols". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 65 (21): 7114–7118. doi:10.1021/jo000840w. PMID 11031037.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
