 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
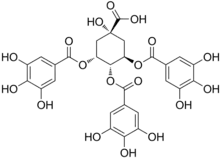
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1S,3R,4S,5R)-1-Hydroxy-3,4,5-tris[(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy]cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
TGQA (3R,5R)-1-Hydroxy-3,4,5-tris(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenylcarbonyloxy)cyclohexanecarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H24O18 | |
| Molar mass | 648.482 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.98g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 1,114.4 °C (2,037.9 °F; 1,387.6 K) at 760mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 364.6 °C (688.3 °F; 637.8 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
3,4,5-Tri-O-galloylquinic acid is a hydrolysable tannin found in Lepidobotrys staudtii,[1] in Guiera senegalensis[2] or in the resurrection plant (Myrothamnus flabellifolius).[3]
It is classified as a natural product with anti-HIV activity[1] and a DNA polymerase inhibitor.[4]
References
- 1 2 "3,4,5-tri-O-galloylquinic acid on home.ncifcrf.gov". Archived from the original on 2011-07-16. Retrieved 2010-07-05.
- ↑ Bouchet, N.; Levesque, J. L.; Bodo, B.; Pousset, J. L. (1998). "3,4,5-Tri-O-Galloylquinic Acid Ethyl Ester from Guiera senegalensis". Pharmaceutical Biology. 36: 63–65. doi:10.1076/phbi.36.1.63.4624.
- ↑ Westall, K. L.; Moore, J. P.; Ravenscroft, N.; Farrant, J. M.; Lindsey, G. G.; Brandt, W. F. (2005). "The predominant polyphenol in the leaves of the resurrection plant Myrothamnus flabellifolius, 3,4,5 tri-O-galloylquinic acid, protects membranes against desiccation and free radical-induced oxidation". Biochemical Journal. 385 (Pt 1): 301–308. doi:10.1042/BJ20040499. PMC 1134698. PMID 15355309.
- ↑ CID 127406 from PubChem
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.