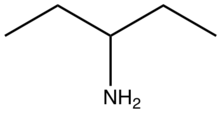
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pentan-3-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.520 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H13N | |
| Molar mass | 87.166 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.7479 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 89 °C (192 °F; 362 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 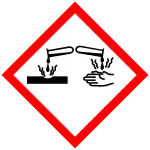 | |
| Danger | |
| H225, H314 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P370+P378, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
3-Aminopentane is the organic compound with the formula (CH3CH2)2CHNH2. It is a colorless liquid. It is of interest for producing soluble imides and imines without introducing a chiral center.[1]
Safety
The LD50 (rat, oral or dermal) for primary alkylamines is 100-1 mg/kg.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Demmig, Stefan; Langhals, Heinz (1988). "Very soluble and Photostable perylene Fluorescent Dyes". Chemische Berichte. 121: 225–30. doi:10.1002/cber.19881210205.
- ↑ Eller, Karsten; Henkes, Erhard; Rossbacher, Roland; Höke, Hartmut (2005). "Amines, Aliphatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001. ISBN 978-3527306732.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.