Antonio Cabral de Melo y Carbajal | |
|---|---|
 Enlazando ganado en las pampas by Fernando Brambila | |
| Accionero del Ganado Vacuno of Buenos Aires Province | |
| Personal details | |
| Born | Antonio Román Cabral de Melo Alpoim y Carbajal de Salas.[1] 1646 Buenos Aires, Argentina |
| Died | c.1717 Buenos Aires, Argentina |
| Nationality | Spanish |
| Spouse | Leonor de Morales |
| Occupation | landowner cattle merchant |
| Profession | Militia Officer |
| Signature | 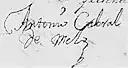 |
| Military service | |
| Allegiance | |
| Branch/service | Spanish Army |
| Years of service | c.1670-c.1700 |
| Rank | Captain |
| Unit | Fuerte de Buenos Aires |
| Commands | Milicias Provinciales de Buenos Aires |
Antonio Cabral de Melo (1646-c.1717) was a Spanish landowner and Captain of provincial militias.[2] He dedicated himself to the raising of cattle and agriculture, later obtaining the position of Accionero (Vaquería (caza)) of the Río de la Plata, with permission for the slaughter of the cattle cimarron.[3]
Biography

Antonio Román Cabral de Melo y Carbajal was born in Buenos Aires, the son of Cristóbal Cabral de Melo, a nobleman born in Vila do Porto, and María de Carbajal, belonging to a distinguished family.[4] He was baptized on March 11, 1646, being his godparents the Captain Diego Gutiérrez de Humanes and Leonor Carbajal.[5]
He was married to Leonor Morales, daughter of Pedro Morales y Mercado and Mariana de Manzanares. The wedding was celebrated on July 13, 1671, in the Cathedral Mayor, and attended by godparents Juan Báez de Alpoim and Gerónima Cabral, relatives of the groom.[6]
He possibly completed his studies at the age of 18 or 20 at the Jesuit College of the City. He dedicated himself to raising livestock, horses, and pigs. He also devoted himself to agriculture and viticulture.[7] He owned a large number of haciendas, one of which was located in the center of Buenos Aires Province.[8]
Like most of his relatives, he had active participation in the provincial militias belonging to the Fort of Buenos Aires. He took part in some military expeditions against the Pampas tribes. He held the position of Maestre de Campo, in charge of the provincial militias of the Spanish Army. Towards 1690 the town council authorized him to carry out the slaughter of the wild cattle that were in the jurisdiction of the province of Buenos Aires.[9]
The "accioneros" of the cattle of the Río de la Plata, supplied meat and leather to the city during the 17th and 18th century, and were also in charge of the export of leather through the Compañía de Guinea de Francia and Asiento de Inglaterra until 1740.[10] The right to the title of "accionero" was inheritable.[11] In 1668, Cabral de Melo requested the Ayuntamiento for permission to hunt 3000 head of cattle in the area of Luján, belonging to his mother Doña María de Carbajal.[12] After the death of Antonio Cabral de Melo, the right to hunt cattle cimarron passed to his son-in-law Don Miguel Gerónimo de Esparza.[13]
After the extinction of cattle cimarron of Buenos Aires Province, the accioneros were dedicated entirely to the raising of cattle in their haciendas, trading their products with the Compañía Guipuzcoana[14] and Compañía de Filipinas.[15]
In 1707, Antonio Cabral de Melo was granted the power to make his testament to Miguel de Riglos, a personal friend of the Cabral de Melo family. He was the nephew of Manuel Cabral de Alpoim, a prominent rancher and military leader of Portuguese origin, who had an outstanding performance in the Río de la Plata, where he served as Mayor and Lieutenant of Governor of Corrientes.[16] His maternal grandfather was General Gonzalo Carbajal, who held various honorary positions in Buenos Aires.[17]
References
- ↑ Revista patriótica del pasado argentino, Volumen 1, Pedro de Montenegro, 1888
- ↑ Historia de Zárate, 1689-1909, by Vicente Raúl Botta, 1948
- ↑ Acuerdos del extinguido Cabildo de Buenos Aires (1719-1721), Archivo General de la Nación, archived from the original on 2018-08-05, retrieved 2018-03-29
- ↑ Hombres del coloniaje, Casa Oucinde, 1932, 1932
- ↑ Bautismos 1635-1636, 1640, Nuestra Señora de La Merced
- ↑ Matrimonios 1656-1762, Nuestra Señora de La Merced
- ↑ Anuario del Instituto de Historia Argentina, Issues 5-6, Editorial de la Universidad Nacional de La Plata, 2006
- ↑ El Fuerte 25 [i.e. veinticinco] de Mayo en Cruz de Guerra, Dirección de Impresiones Oficiales, 1949, 1949
- ↑ Acuerdos del extinguido Cabildo de Buenos Aires, Volumen 13, by Buenos Aires. Cabildo, José Juan Biedma, Augusto S. Mallié, Héctor C. Quesada, Eugenio Corbet France, 1914
- ↑ Evolución económica de la Banda Oriental, Volume 1, Lucía Sala de Touron, Julio C. Rodríguez, Nelson de la Torre, 1968
- ↑ Nueva revista de Buenos Aires, Volume 4, C. Casavalle, 1882, 1882
- ↑ Acuerdos del Extinguido Cabildo de Buenos Aires (1668-1672), Archivo General de la Nación, archived from the original on 2018-04-02, retrieved 2018-04-02
- ↑ Acuerdos del extinguido Cabildo de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires (Argentina). Cabildo, 1927
- ↑ Resumen de la historia de Venezuela, Rafael María Baralt, Ramón Díaz, 1841
- ↑ El Virreinato Rioplatense en las vistas fiscales de José Márquez de la Plata, Volume 2, Universidad del Museo Social Argentino, 1988
- ↑ Why Have You Come Here? : The Jesuits and the First Evangelization of Native ..., State University of New York, 3 August 2006, ISBN 9780195307566
- ↑ Nupcias patricias: descendencia de los fundadores de la ciudad, siglos XVII-XVIII-XIX-XX, by Alberto A. Wildner-Fox, 1987
External links
- Antonio Cabral de Melo - Genealogía Familiar Archived 2018-08-05 at the Wayback Machine