 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
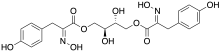
[(2S,3R)-2,3-Dihydroxy-4-[(2Z)-2-hydroxyimino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]oxybutyl] (2Z)-2-hydroxyimino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H24N2O10 | |
| Molar mass | 476.438 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Aspergillusol A is an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor isolated from marine Aspergillus.[2] Structurally, it consists of an erythritol group in the center, with two hydroxyimino-phenylpropanoyl groups attached to it from either side. It was synthesized in 2010 by researchers from King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, starting with 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde.[3]
References
- ↑ "KNApSAcK Metabolite Information - C00047738". www.knapsackfamily.com.
- ↑ Ingavat, N; Dobereiner, J; Wiyakrutta, S; Mahidol, C; Ruchirawat, S; Kittakoop, P (2009). "Aspergillusol A, an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus aculeatus". Journal of Natural Products. 72 (11): 2049–52. doi:10.1021/np9003883. PMID 19824618.
- ↑ Ullah, N.; Haladu, S. A. (2010). "The first total synthesis of aspergillusol A, an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor". Natural Product Communications. 5 (7): 1077–1080. doi:10.1177/1934578X1000500719. PMID 20734944. S2CID 29175958.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.