
The atmospheric carbon cycle accounts for the exchange of gaseous carbon compounds, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), between Earth's atmosphere, the oceans, and the terrestrial biosphere. It is one of the faster components of the planet's overall carbon cycle, supporting the exchange of more than 200 billion tons of carbon (i.e. gigatons carbon or GtC) in and out of the atmosphere throughout the course of each year.[1] Atmospheric concentrations of CO2 remain stable over longer timescales only when there exists a balance between these two flows. Methane (CH4), Carbon monoxide (CO), and other man-made compounds are present in smaller concentrations and are also part of the atmospheric carbon cycle.[2]
Human activities, primarily the extraction and burning of fossil carbon from Earth's lithosphere starting with the industrial revolution, have disturbed the previous balance of the atmospheric carbon cycle and have been mostly responsible for the ongoing rapid growth in CO2 and CH4 concentrations.[3] As of year 2019, annual emissions grew to 10 GtC/year, with a cumulative total of about 450 GtC injected into the cycle.[4] The terrestrial and ocean sinks have thus far absorbed half of the added carbon, and half has remained in the atmosphere primarily as CO2. Assuming the growth trend in emissions continues, the CO2 concentration is on a path to at least double by the latter half of this century.[5]
The atmospheric carbon cycle also strongly influences Earth's energy balance through the greenhouse effect, and affects the acidity or alkalinity of the planet's surface waters and soils. Despite comprising less than 0.05% of all atmospheric gases by mole fraction,[6] the recent rise in carbon concentrations has caused substantial global heating and ocean acidification.[7] Such effects are generally projected to accelerate further until net emissions are stabilized and reduced.[5]
Relevant gases
| Part of a series on the |
| Carbon cycle |
|---|
 |
|
The atmosphere is one of the Earth's major carbon reservoirs and holds approximately 720 gigatons of carbon as of year 2000.[1] The concentration of mostly carbon-based greenhouse gases has increased dramatically since the onset of the industrial era. This makes an understanding of the carbon component of the atmosphere highly important. The two main carbon greenhouse gases are methane and carbon dioxide.[9]
Methane
Methane (CH4) is one of the more potent greenhouse gases and is mainly produced by the digestion or decay of biological organisms. It is considered the second most important greenhouse gas,[9] yet the methane cycle in the atmosphere is currently only poorly understood.[10] The amount of methane produced and absorbed yearly varies widely.[9]
Large stores of methane can be found in the form of methane ice under permafrost and on continental shelves. Additional methane is produced by the anaerobic decay of organic material and is produced in organisms' digestive tracts, soil, etc. Natural methane production accounts 10-30% of global methane sources.[11]
Anthropogenic methane is produced in various ways, e.g. by raising cattle or through the decay of trash in landfills. It is also produced by several industrial sources, including the mining and distribution of fossil fuels.[10] More than 70% of atmospheric methane comes from biogenic sources. Methane levels have risen gradually since the onset of the industrial era,[12] from ~700 ppb in 1750 to ~1775 ppb in 2005.[9]
Methane can be removed from the atmosphere through a reaction of the photochemically produced hydroxyl free radical (OH).[13][14] It can also leave the atmosphere by entering the stratosphere, where it is destroyed, or by being absorbed into soil sinks.[15] Because methane reacts fairly quickly with other compounds, it does not stay in the atmosphere as long as many other greenhouse gases, e.g. carbon dioxide. It has an atmospheric lifetime of about eight years.[12] This keeps the concentration of methane in the atmosphere relatively low and is the reason that it currently plays a secondary role in the greenhouse effect to carbon dioxide, despite the fact that it produces a much more powerful greenhouse effect per volume.[10]
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (CO2) has a large warming effect on global temperatures through the greenhouse effect. Although individual CO2 molecules have a short residence time in the atmosphere, it takes an extremely long time for carbon dioxide levels to sink after sudden rises, due to e.g. volcanic eruptions or human activity[16] and among the many long-lasting greenhouse gases, it is the most important because it makes up the largest fraction of the atmosphere.[9] Since the industrial revolution, the CO2 concentration in the atmosphere has risen from about 280 ppm to almost 400 ppm.[6] Although the amount of CO2 introduced makes up only a small portion of the global carbon cycle, carbon dioxide's long residence time makes these emissions relevant for the total carbon balance. The increased carbon dioxide concentration strengthens the greenhouse effect, causing changes to the global climate. Of the increased amounts of carbon dioxide that are introduced to the atmosphere each year, approximately 80% are from the combustion of fossil fuels and cement production. The other ~20% originate from land use change and deforestation.[17] Because gaseous carbon dioxide does not react quickly with other chemicals, the main processes that change the carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere involve exchanges with the earth's other carbon reservoirs, as explained in the following sections.
Interactions with other systems
| Part of a series on |
| Biogeochemical cycles |
|---|
 |
|
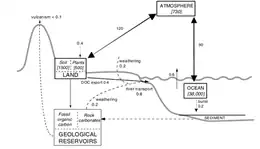
Atmospheric carbon is exchanged quickly between the oceans and the terrestrial biosphere. This means that at times the atmosphere acts as a sink, and at other times as a source of carbon.[1] The following section introduces exchanges between the atmospheric and other components of the global carbon cycle.
Terrestrial biosphere
Carbon is exchanged with varying speed with the terrestrial biosphere. It is absorbed in the form of carbon dioxide by autotrophs and converted into organic compounds. Carbon is also released from the biosphere into the atmosphere in the course of biological processes. Aerobic respiration converts organic carbon into carbon dioxide and a particular type of anaerobic respiration converts it into methane. After respiration, both carbon dioxide and methane are typically emitted into the atmosphere. Organic carbon is also released into the atmosphere during burning.[18]
The residence time of carbon in the terrestrial biosphere varies and is dependent on a large number of factors. The uptake of carbon into the biosphere occurs on various time scales. Carbon is absorbed primarily during plant growth. A pattern of increased carbon uptake is observable both over the course of the day (less carbon is absorbed at night) and over the course of the year (less carbon is absorbed in winter).[9] While organic matter in animals generally decays quickly, releasing much of its carbon into the atmosphere through respiration, carbon stored as dead plant matter can stay in the biosphere for as much as a decade or more. Different plant types of plant matter decay at different rates - for example, woody substances retain their carbon longer than soft, leafy material.[19] Active carbon in soils can stay sequestered for up to a thousand years, while inert carbon in soils can stay sequestered for more than a millennium.[18]
Oceans
Each year, the ocean and atmosphere exchange large amounts of carbon. A major controlling factor in oceanic-atmospheric carbon exchange is thermohaline circulation. In regions of ocean upwelling, carbon-rich water from the deep ocean comes to the surface and releases carbon into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. Large amounts of carbon dioxide are dissolved in cold water in higher latitudes. This water sinks down and brings the carbon into the deeper ocean levels, where it can stay for anywhere between decades and several centuries.[1] Ocean circulation events cause this process to be variable. For example, during El Nino events there is less deep ocean upwelling, leading to lower outgassing of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.[17]
Biological processes also lead to ocean-atmosphere carbon exchange. Carbon dioxide equilibrates between the atmosphere and the ocean's surface layers. As autotrophs add or subtract carbon dioxide from the water through photosynthesis or respiration, they modify this balance, allowing the water to absorb more carbon dioxide or causing it to emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.[1]
Geosphere
Carbon is generally exchanged very slowly between the atmosphere and geosphere. Two exceptions are volcanic eruptions and the combustion of fossil fuels, both of which release high amounts carbon into the atmosphere very quickly.[20] Fresh silicate rock that is exposed through geological processes absorbs carbon from the atmosphere when it is exposed to air by the processes of weathering and erosion.
Anthropogenic sources


Human activities change the amount of carbon in the atmosphere directly through the burning of fossil fuels and other organic material, thus oxidizing the organic carbon and producing carbon dioxide.[21][22] Another human-caused source of carbon dioxide is cement production. The burning of fossil fuels and cement production are the main reasons for the increase in atmospheric CO2 since the beginning of the industrial era.[9]
Other human-caused changes in the atmospheric carbon cycle are due to anthropogenic changes to carbon reservoirs. Deforestation, for example, decreases the biosphere's ability to absorb carbon, thus increasing the amount of carbon in the atmosphere.[23]
As the industrial use of carbon by humans is a very new dynamic on a geologic scale, it is important to be able to track sources and sinks of carbon in the atmosphere. One way of doing so is by observing the proportion of stable carbon isotopes present in the atmosphere. The two main carbon isotopes are 12C and 13C. Plants absorb the lighter isotope, 12C, more readily than 13C.[24] Because fossil fuels originate mainly from plant matter, the 13C/12C ratio in the atmosphere falls when large amounts of fossil fuels are burned, releasing 12C. Conversely, an increase in the 13C/12C in the atmosphere suggests a higher biospheric carbon uptake.[18] The ratio of the annual increase in atmospheric CO2 compared to CO2 emissions from fossil fuel and cement manufactured is called the "airborne fraction.".[25] The airborne fraction has been around 60% since the 1950s, indicating that about 60% of the new carbon dioxide in the atmosphere each year originated from human sources.[9] For clarity, this is not meant to suggest that 60% of the uptake of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere comes from human activity. It means that the atmosphere exchanges around 210 gigatonnes of carbon annually, but absorbs between 6 and 10 gigatonnes more than it loses. Of this net gain, about 60% is attributable to the burning of fossil fuels.
Gallery
 Atmospheric CO2 concentrations over the last 800,000 years as measured from ice cores (blue/green) and directly (black).
Atmospheric CO2 concentrations over the last 800,000 years as measured from ice cores (blue/green) and directly (black). Ocean and land sinks have taken up about half of fossil carbon emissions into the atmosphere. It's uncertain how long this will continue.[26]
Ocean and land sinks have taken up about half of fossil carbon emissions into the atmosphere. It's uncertain how long this will continue.[26] CO2 flows from human activity (left) into atmosphere, land, and ocean sinks (right).[4]
CO2 flows from human activity (left) into atmosphere, land, and ocean sinks (right).[4]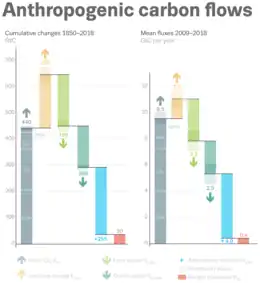 Anthropogenic carbon flows during years 1850-2018 (left) and 2009-2018 (right).[4]
Anthropogenic carbon flows during years 1850-2018 (left) and 2009-2018 (right).[4]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Falkowski, P.; Scholes, R. J.; Boyle, E.; Canadell, J.; Canfield, D.; Elser, J.; Gruber, N.; Hibbard, K.; Högberg, P.; Linder, S.; MacKenzie, F. T.; Moore III, B.; Pedersen, T.; Rosenthal, Y.; Seitzinger, S.; Smetacek, V.; Steffen, W. (2000). "The Global Carbon Cycle: A Test of Our Knowledge of Earth as a System". Science. 290 (5490): 291–296. Bibcode:2000Sci...290..291F. doi:10.1126/science.290.5490.291. PMID 11030643.
- ↑ Riebeek, Holli (16 June 2011). "The Carbon Cycle". Earth Observatory. NASA. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 5 April 2018.
- ↑ Heede, R. (2014). "Tracing anthropogenic carbon dioxide and methane emissions to fossil fuel and cement producers, 1854–2010". Climatic Change. 122 (1–2): 229–241. Bibcode:2014ClCh..122..229H. doi:10.1007/s10584-013-0986-y.
- 1 2 3 Friedlingstein, P., Jones, M., O'Sullivan, M., Andrew, R., Hauck, J., Peters, G., Peters, W., Pongratz, J., Sitch, S., Le Quéré, C. and 66 others (2019) "Global carbon budget 2019". Earth System Science Data, 11(4): 1783–1838. doi:10.5194/essd-11-1783-2019.
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Material was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. - 1 2 Masson-Delmotte, Valérie; Zhai, Panmao; Pirani, Anna; Connors, Sarah L.; Péan, Clotilde; Berger, Sophie; Caud, Nada; Chen, Yang; Goldfarb, Leah; Gomis, Melissa I.; Huang, Mengtian; Leitzell, Katherine; Lonnoy, Elisabeth; Matthews, J. B. Robin; Maycock, Tom K.; Waterfield, Tim; Yelekçi, Ozge; Yu, Rong; Zhou, Baiquan, eds. (2021-08-09). "Summary for Policymakers". Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (PDF). IPCC / Cambridge University Press. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-08-13. Retrieved 2021-08-09.
- 1 2 Tans, Pieter; Keeling, Ralph. "Trends in Carbon Dioxide". NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory.
- ↑ "What is Ocean Acidification?". National Ocean Service, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2020-10-30.
- ↑ A Year In The Life Of Earth’s CO2 NASA: Goddard Space Flight Center, 17 November 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Forster, P.; Ramawamy, V.; Artaxo, P.; Berntsen, T.; Betts, R.; Fahey, D.W.; Haywood, J.; Lean, J.; Lowe, D.C.; Myhre, G.; Nganga, J.; Prinn, R.; Raga, G.; Schulz, M.; Van Dorland, R. (2007), "Changes in atmospheric constituents and in radiative forcing", Climate Change 2007: The Physical Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
- 1 2 3 Prather, M.; et al. (2001), "Atmospheric chemistry and greenhouse gases", Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
- ↑ Keppler, F.; Hamilton, J. T. G.; Brass, M.; Röckmann, T. (2006). "Methane emissions from terrestrial plants under aerobic conditions". Nature. 439 (7073): 187–191. Bibcode:2006Natur.439..187K. doi:10.1038/nature04420. PMID 16407949. S2CID 2870347.
- 1 2 Global Observing Systems Information Center (2011). "GCOS Atmospheric Composition ECV: Methane (CH4) and other Long-Lived Green House Gases". Archived from the original on 2012-03-08. Retrieved 2012-06-04.
- ↑ Platt, U.; Allan, W.; Lowe, D. (2004). "Hemispheric average Cl atom concentration from 13C/12C ratios in atmospheric methane". Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics. 4 (9/10): 2393. Bibcode:2004ACP.....4.2393P. doi:10.5194/acp-4-2393-2004.
- ↑ Allan, W.; Lowe, D. C.; Gomez, A. J.; Struthers, H.; Brailsford, G. W. (2005). "Interannual variation of 13C in tropospheric methane: Implications for a possible atomic chlorine sink in the marine boundary layer". Journal of Geophysical Research. 110 (D11): D11306. Bibcode:2005JGRD..11011306A. doi:10.1029/2004JD005650.
- ↑ Born, M.; Dorr, H.; Levin, I. (1990). "Methane consumption in aerated soils of the temperate zone". Tellus B. 42 (1): 2–8. Bibcode:1990TellB..42....2B. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0889.1990.00002.x.
- ↑ Inman, M. (2008). "Carbon is forever". Nature Reports Climate Change. 1 (812): 156–158. doi:10.1038/climate.2008.122.
- 1 2 Denman, Kenneth; Brasseur, Guy; Chidthaisong, A.; Ciais, P.; Cox, P.; Dickinson, R..; Hauglustaine, D.; Heinze, C.; Holland, E.; Jacob, D.; Lohmann, U.; Ramachandran, S.; da Silva Dias, P.; Wofsy, S.; Zhang, X. (2007), "Couplings between changes in the climate system and biogeochemistry", Climate Change 2007: The Physical Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
- 1 2 3 4 Prentice, I. C.; et al. (2001). "The carbon cycle and atmospheric carbon dioxide" (PDF). Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: 184–238. Retrieved 2020-06-20.
- ↑ Concise Environmental Engineering. Bookboon. ISBN 978-87-403-0197-7.
- ↑ "Carbon Cycle and Atmospheric CO2 | Earth 530: The Critical Zone". www.e-education.psu.edu. Retrieved 2023-10-08.
- ↑ Van Der Werf, G. R.; Randerson, J. T.; Collatz, G. J.; Giglio, L.; Kasibhatla, P. S.; Arellano Jr, A. F.; Olsen, S. C.; Kasischke, E. S. (2004). "Continental-Scale Partitioning of Fire Emissions During the 1997 to 2001 El Nino/La Nina Period" (PDF). Science. 303 (5654): 73–76. Bibcode:2004Sci...303...73V. doi:10.1126/science.1090753. PMID 14704424. S2CID 21618974.
- ↑ Andreae, M. O.; Merlet, P. (2001). "Emission of trace gases and aerosols from biomass burning". Global Biogeochemical Cycles. 15 (4): 955. Bibcode:2001GBioC..15..955A. doi:10.1029/2000GB001382.
- ↑ Houghton, R. A. (2003). "Revised estimates of the annual net flux of carbon to the atmosphere from changes in land use and land management 1850-2000". Tellus B. 55 (2): 378–390. Bibcode:2003TellB..55..378H. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0889.2003.01450.x.
- ↑ Nakazawa, T.; Morimoto, S.; Aoki, S.; Tanaka, M. (1997). "Temporal and spatial variations of the carbon isotopic ratio of atmospheric carbon dioxide in the western Pacific region". Journal of Geophysical Research. 102 (D1): 1271–1285. Bibcode:1997JGR...102.1271N. doi:10.1029/96JD02720.
- ↑ Keeling, C. D.; Whorf, T. P.; Wahlen, M.; Van Der Plichtt, J. (1995). "Interannual extremes in the rate of rise of atmospheric carbon dioxide since 1980". Nature. 375 (6533): 666. Bibcode:1995Natur.375..666K. doi:10.1038/375666a0. S2CID 4238247.
- ↑ Lynch, Patrick (12 November 2015). "GMS: Carbon and Climate Briefing - 12 November 2015". National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Goddard Media Studios. Retrieved 7 November 2018.