Native name: Белый остров | |
|---|---|
 Bely Island, Kara Sea | |
 Bely Island Bely Island, Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug (Russia) | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Kara Sea |
| Coordinates | 73°11′N 71°17′E / 73.183°N 71.283°E |
| Area | 1,810 km2 (700 sq mi) |
| Length | 63 km (39.1 mi) |
| Width | 41 km (25.5 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 12 m (39 ft) |
| Highest point | Bely HP |
| Administration | |
Russia | |
| Oblast | Tyumen Oblast |
| Okrug | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug |
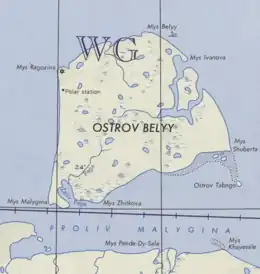
Bely Island (also spelled as Belyy and Beliy, Russian: Белый остров) is a relatively large island in the Kara Sea off the tip of the Yamal Peninsula, Siberia, Russia.[1] Close to the island's northwest tip, there is the Russian Experiment Station (Polyarnaya Stantsiya) Popov Station.
Geography
Bely Island covers an area of 1,810 square kilometres (700 sq mi). It is covered by tundra, but some lichens, grasses, and dwarf willow shrubs (Salix purpurea) grow during the warmer seasons.[2][3] It is separated from the mainland by the Malygina Strait, an 8 to 10 km wide sound which is frozen most of the year. The land is rather flat, going only 12m above sea level, and the island is dotted by small lakes and ponds. Since it is in the Arctic Circle, winters are long and frigid, the average annual temperature is a mere -10.6°C. In February, temperatures average -24.2°C reaching a record low of -59°C. The summers are characterized by fog, with an average temperature of +5.3°C. The area is subject to polar lows and general cyclonic activity.[3]
This island belongs to the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug which is the northern part of the Tyumen Oblast administrative division of Russia.
 Popov Polar Station. |
Adjacent islands
Within Bely Island's wide eastern bay there is a 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) long island called Bezymyannyy. Ostrov Tabango and Ostrov Tyubtsyango are located 20 kilometres (12 mi) to the south of Bely Island's SE corner.
Scientific research
Bely Island has been the site of arctic research for its remote and unsettled nature. Research stations here are used to investigate changes in the Arctic Circle due to climate change and the effects of the Russian petroleum industry, where its unaffected soil is used to measure trace elements in comparison to soil on the mainland.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Staalesen, Atle (26 August 2016). "Cleanup of Bely Island completed". The Independent Barents Observer. Retrieved 26 April 2018.
- ↑ Marie Gilbert; Julie K. Jackson (1 May 2007). "UAF Newsroom: Feature Story: Greening of the Arctic". web.archive.org. Retrieved 30 December 2023.
- 1 2 3 Abakumov E, Shamilishviliy G, Yurtaev A (2017). "Soil polychemical contamination on Beliy Island as key background and reference plot for Yamal region". www.czasopisma.pan.pl. Retrieved 30 December 2023.
- Satellite Views of Russian Experiment station Polyarnaya Stantsiya Belyy: www.satelliteviews.net
External links
- Photograph of polar station Archived 2006-10-07 at the Wayback Machine