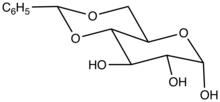
Structure of the benzylidene acetal of glucose.
In organic chemistry, a benzylidene acetal is the functional group with the structural formula C6H5CH(OR)2 (R = alkyl, aryl). Benzylidene acetals are used as protecting groups in glycochemistry.[1][2] These compounds can also be oxidized to carboxylic acids in order to open important biological molecules, such as glycosaminoglycans, to other routes of synthesis.[3] They arise from the reaction of a 1,2- or 1,3-diols with benzaldehyde. Other aromatic aldehydes are also used.[4]
References
- ↑ David Crich (2010). "Mechanism of a Chemical Glycosylation Reaction". Acc. Chem. Res. 43 (8): 1144–1153. doi:10.1021/ar100035r. PMID 20496888.
- ↑ S. Hanessian (1987). "6-Bromo-6-deoxy Hexose Derivatives By Ring Opening Of Benzylidene Acetals With N-bromosuccinimide: Methyl 4-o-benzoyl-6-bromo-6-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranoside". Org. Synth. 65: 243. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.065.0243.
- ↑ Banerjee, Amit; Senthilkumar, Soundararasu; Baskaran, Sundarababu (2015-12-07). "Benzylidene Acetal Protecting Group as Carboxylic Acid Surrogate: Synthesis of Functionalized Uronic Acids and Sugar Amino Acids". Chemistry - A European Journal. 22 (3): 902–906. doi:10.1002/chem.201503998. ISSN 0947-6539. PMID 26572799.
- ↑ Hiroyuki Osajima; Hideto Fujiwara; Kentaro Okano; Hidetoshi Tokuyama; Tohru Fukuyama (2009). "Protection Of Diols With 4-(Tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy)benzylidene Acetal And Its Deprotection". Org. Synth. 86: 130. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.086.0130.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.