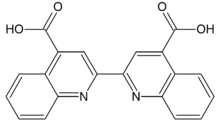 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
[2,2′-Biquinoline]-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Bicinchoninic acid 4,4′-Dicarboxy-2,2′-biquinoline 2,2'-Biquinoline-4,4'-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.628 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H12N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 344.326 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Cream colored powder |
| Odor | Characteristic odor |
| Melting point | 352 °C (666 °F; 625 K) decomposes |
| Partially soluble in cold water, hot water | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Will irritate eyes and mucous membranes. |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Bicinchoninic acid /baɪsɪnkɔːnɪnɪk/ is a weak acid composed of two carboxylated quinoline rings.
Bicinchoninic is an organic compound with the formula (C9H5NCO2H)2. The molecule consists of a pair of quinoline rings, each bearing a carboxylic acid group. Its sodium salt forms a purple complex with cuprous ions.[1][2][3]
Bicinchoninic acid is most commonly employed in the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay, which is used to determine the total level of protein in a solution. Bicinchoninic acid is used to detect the presence of cuprous ions, due to its purple coloration via a biuret reaction. In this assay, two molecules of bicinchoninic acid chelate a single Cu+ ion, forming a purple water-soluble complex that strongly absorbs light at 562 nm.[4]
References
- ↑ Smith, P.K.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.T.; Mallia, A.K.; Gartner, F.H.; Provenzano, M.D.; Fujimoto, E.K.; Goeke, N.M.; Olson, B.J.; Klenk, D.C. (1985). "Measurement of Protein Using Bicinchoninic Acid". Analytical Biochemistry. 150 (1): 76–85. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. PMID 3843705.
- ↑ Brown, Rhoderick E.; Jarvis, Kari L.; Hyland, Kristi J. (1989). "Protein measurement using bicinchoninic acid: Elimination of interfering substances". Analytical Biochemistry. 180 (1): 136–139. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(89)90101-2. PMID 2817336.
- ↑ Noble, James E.; Bailey, Marc J.A. (2009). "Chapter 8 Quantitation of Protein". Guide to Protein Purification, 2nd Edition. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 463. pp. 73–95. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(09)63008-1. ISBN 9780123745361. PMID 19892168.
- ↑ Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit
