Bullworker is a product and fitness company that specializes in isometric exercise, that is the static contraction of a muscle without any visible movement. The original portable home fitness device was invented by Gert F. Kölbel in 1962.
The product enjoyed widespread popularity in the 1960s and 1970s during the personal fitness craze, but its popularity fell off in the 1980s when personal gyms became readily available. New models have been made available, and Bullworker is still marketed worldwide by different holders.
The devices before the Bullworker
Arthur Aubriot Pons

The original device was patented in 1912 by Arthur A. Pons from Brooklyn.[1] The device looked quite like the first bullworker to come (without strings). It consisted of three sleeved, spring-loaded, telescopic cylinders in the center, with two hand grips affixed at the outermost ends.
The patent states:
"The invention consists essentially in the novel construction and arrangement of parts whereby spring controlled telescopic members are embodied in an exercising apparatus in a special manner more particularly described hereinafter. The objects of the invention are to devise a portable exercising apparatus particularly for the development of the chest and arm muscles, suitable for both old and young persons by reason of the interchangeability of the resilient member and generally to provide an exercising apparatus to be operated by the hands and arms, simple in construction, cheap to manufacture, durable and interchangeable as to its parts".[2]
Arthur William Chapman
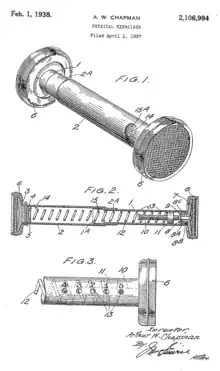
A second device, invented in 1937 by Arthur William Chapman would be used to create the Bullworker.
The patent states:
The invention relates to physical exercisers for human use, and seeks to provide in a single device means whereby a large variety of beneficial exercises for the body and limbs may be carried out. An object of the invention is to provide an exerciser usable by compression between the hands or parts of the body or limbs. A further object is to provide such an exerciser with a degree of adjustability so that as the user's physique improves the effort he has to exert may be increased. Again, an object is to provide simple means Whereby the adjustment at the time being may readily be observed. A minor object is to provide locking means for transport or storage of the device, and other objects will become apparent, more especially in relation to economical and convenient constructional features.[3]
Isometric exercises
In the 1950s, German scientists Dr. Erich Albert Müller[4] and Theodor Hettinger[5] "observed that contractions involving less than about one third of maximum strength do not train the muscle. If the contraction of a muscle exceeds one third of its maximum strength, its mass grows and hence also its strength".[6] Furthermore, it is said that he concluded that muscle growth can be attained by exerting 60% of existing muscle strength against a superior resistance for only seven seconds once a day, a fitness technique known as isometrics. The study at the Max Planck Institute consisted of over 200 experiments over a ten-year period. Theodor Hettinger published his book Physiology of Strength.[7] They both developed a training program based on isometrics exercise.[8]
In the 1960s, professor James A. Baley put isometrics to the test with a class of 104 college students at the University of Connecticut. The Bullworker manual claimed that study resulted in the isometric training group improving three times faster than the sports training group on tests measuring increases in strength, endurance, coordination, and agility. However, the original article is far more complex even if it showed significant gains after a 4 week program of isometric exercises.[9]
The Tensolator and the first Bullworker device

In the early 1960s, Gert F. Kölbel used and enhanced the devices of Pons and Chapman to create the Tensolator which became the Bullworker, a portable home fitness device and the seven second isometric exercise principle for the fastest strength gains, using both contraction and extension movements involving range of motion for all the major muscle groups, into one lightweight and compact fitness tool at a price everyone could afford.
The US patent states:
The invention relates to physical exercisers, and more particularly to a device for human use by which a large variety of physical exercisers for training and strengthening the muscular system of the body may be carried out. It is an object of the invention to provide an exerciser usable by compression, pull and expansion. Another object is to provide an exerciser of simple and robust construction which is safe against accidents. A further object is to provide an exerciser which the user may manipulate with his hands and feet and may also support against the floor, wall or ceiling of a room.[10]
The original Bullworker device consists of two sleeved, spring-loaded, telescopic cylinders in the center, with two hand grips affixed at the outermost ends. Two opposing cables are attached to the hand grips at each end of the device. The original Bullworker exercise apparatus weighs about four pounds (1.8 kilograms). Exercises are performed by pushing inwards on the contractible cylinders, by pulling the cables outwards away from the cylinders, or any variation of these. The resultant compression of the internal spring creates the desired resistance.[11] The Bullworker will return to its original position when pressure is released. A range of up to 150 pounds (68 kilograms) or more of resistance is possible in the Bullworker exercise routines.
Reception and fame of the device
Bullworker enjoyed widespread popularity in Europe and the United States in the 1960s and 1970s during the personal fitness craze. Various charts were then introduced, proposing different work to exercise and develop the muscles.
Later Bullworker versions
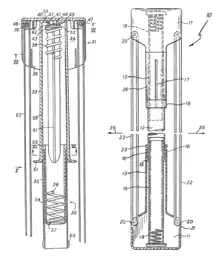
Since the original Bullworker fitness device was made available for purchase and use by the general public in the 1960s, a number of modified and improved different versions of the original Bullworker have been made available since its introduction, particularly Bullworker 2, Bullworker Deluxe, and Bullworker X5. However, the Bullworker's functional isometric concepts to improve physical fitness remained the same. The major improvement was the X5 model, which had been patented.
The patent of the X5 describes it as:
a spring type exerciser involving a telescopic arrangement including a spring so that as the telescopic system is collapsed the spring is placed under compression; also an endless rope is connected to the handles at the ends of the telescopic system so that as two runs of the rope are pulled apart the spring is again placed under compression. In use certain exercises comprise squeezing the spring by applying force to the handles at each end and certain exercises comprise pulling the two runs of rope apart and again placing the spring under compression. In this way the exercises bring into play different muscles involving forces of both compression and tension while at the same time the work by the person using the exerciser always acts on the spring to place it under compression. An object of the present invention is to provide a physical exerciser of the type described in [the] U.S. Pat. No. 3,268,225 which is simplified in construction and allows the user the possibility of carrying out a wider range of exercises. It is another object of the invention to provide an exerciser which gives a greater amount of contraction for the same initial length of telescopic system. It is a still further object of the invention to produce an exerciser which allows the user to vary the movement distance during an exercise and to vary the strength required to move the tension elements during exercise.[12]
Current versions

Though Bullworker's popularity fell off in the 1980s when personal gyms became readily available, new models had been created by Hughes Marketing, LLC: the Bullworker Bow Classic and the Bullworker Steel-Bow.
- The Bow Classic is 910 mm (36 in) long, and is the Bullworker 'barbell' equivalent, specializing in powerful holds and greater range of motion.
- The Steel-Bow is 510 mm (20 in) long and is the Bullworker dumbbell specializing in versatility for muscle targeting and travel. Both Bullworker models have interchangeable springs to easily change resistance levels, ranging from approximately 0–60 kg (0-130 lbs) of resistance.
The original Bullworker suggested 26 individual exercises. While isometrics was the emphasis, the instructions included isotonic, cardio, resiliency and endurance routines. The emphasis on these additional functions greatly expanded the number of exercises available. An additional fitness routine of Iso-Motion has since been added. Bullworkers are well built and very durable; many early units remain in regular fitness use decades later.
The trademark
According to the World Intellectual Property Organization, Bullworker is still marketed worldwide by different holder depending on the country, among them:
- WOA World of Accessories GmbH in Germany (the oldest holder)
- Reeves international limited
- Flo Fitness, LLC
- Fukuhatsu Metal in Japon
Examples of training
- Bullworker 2 training program
- Bullworker X5 training program Archived 2020-01-31 at the Wayback Machine
- Bullworker New training program Archived 2022-01-25 at the Wayback Machine
- Bullworker X5 chart
The Bullworker in popular culture
- In the movie Never Say Never Again, James Bond uses a Bullworker as a weapon against Lippe.
- The biographical page of Gert F. Kölbel claims that among famous users were: Franz Beckenbauer, Konrad Adenauer and Muhammad Ali.[13]
- A photograph exists showing a Bullworker behind Bruce Lee. [14]
- Dave Prowse, who played Darth Vader, used to be a commercial consultant to sell the Bullworker in the United Kingdom.[15]
References
- ↑ Patent : US1023756A
- ↑ US1023756A
- ↑ Patent of the "Physical exerciser" by Arthur William Chapman
- ↑ Erich A. Mueller, "The Regulation of Muscular Strength", Journal of the Association for Physical and Mental Rehabilitation, 11 (March–April, 1957): 41-47.
- ↑ Hettinger, T., & Müller, E. A. (1953). Muskelleistung und muskeltraining. Arbeitsphysiologie, 15(2), 111-126.
- ↑ "Sweating in the Service of Science, Occupational Physiology" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-06-28. Retrieved 2020-08-02.
- ↑ Physiology of Strength. Theodor Hettinger, M.D. Edited by M. H. Thurwell. Springfield, Illinois, Charles C. Thomas, 1961
- ↑ Crakes, J. G. (1957). An analysis of some aspects of an exercise and training program developed by Hettinger and Mueller. Unpublished master's thesis, University of Oregon.
- ↑ Effects of Isometric Exercises Done with a Belt upon the Physical Fitness Status of Students in Required Physical Education Classes, Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, Volume 37, 1966 - Issue 3.
- ↑ United States Patent Office, SPRING TYPE PHYSICAL EXERCISER Gert F. Kölbel
- ↑ United States Patent Office, SPRING TYPE PHYSICAL EXERCISER Gert F. Kölbel
- ↑ Patent of the Bullworker X5.
- ↑ Mehr über Gert F. Koelbel
- ↑ "Isometrics for martial arts: how you can get really strong – Dojo Mart". dojomart.com. Retrieved 2023-04-01.
- ↑ Prowse, Dave. Straight from the Force's Mouth: The Autobiography of Dave Prowse. MBE. 2016. ISBN 1785384759