Bussigny | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Bussigny | |
 Bussigny  Bussigny | |
| Coordinates: 46°33′N 06°33′E / 46.550°N 6.550°E | |
| Country | Switzerland |
| Canton | Vaud |
| District | Ouest Lausannois |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Syndic Michel Wehrli |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4.82 km2 (1.86 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 415 m (1,362 ft) |
| Population (31 December 2018)[2] | |
| • Total | 8,736 |
| • Density | 1,800/km2 (4,700/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (Central European Time) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (Central European Summer Time) |
| Postal code(s) | 1030 |
| SFOS number | 5624 |
| Surrounded by | Aclens, Bremblens, Crissier, Échandens, Écublens, Mex, Villars-Sainte-Croix, Vufflens-la-Ville |
| Website | www Profile (in French), SFSO statistics |
Bussigny (until 2014 Bussigny-près-Lausanne) is a municipality in the Swiss canton of Vaud, located in the district of Ouest Lausannois.
History
Bussigny is first mentioned in 1358 as Bussignye.[3]
Geography

Bussigny has an area, as of 2009, of 4.8 square kilometers (1.9 sq mi). Of this area, 1.6 km2 (0.62 sq mi) or 33.2% is used for agricultural purposes, while 0.83 km2 (0.32 sq mi) or 17.2% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 2.32 km2 (0.90 sq mi) or 48.1% is settled (buildings or roads), 0.03 km2 (7.4 acres) or 0.6% is either rivers or lakes.[4]
Of the built up area, industrial buildings made up 11.0% of the total area while housing and buildings made up 17.6% and transportation infrastructure made up 14.1%. Power and water infrastructure as well as other special developed areas made up 1.9% of the area while parks, green belts and sports fields made up 3.5%. Out of the forested land, all of the forested land area is covered with heavy forests. Of the agricultural land, 30.9% is used for growing crops and 1.5% is pastures. All the water in the municipality is flowing water.[4]
The municipality was part of the Morges District until it was dissolved on 31 August 2006, and Bussigny-près-Lausanne became part of the new district of Ouest Lausannois.[5] On 1 May 2014, the official name changed from Bussigny-près-Lausanne to Bussigny.[5]
The municipality is located west of Lausanne and near the Venoge river. It consists of the villages of Bussigny-près-Lausanne and Saint-Germain.
Coat of arms
The blazon of the municipal coat of arms is Per fess, argent and gules, a rooster sable, lined argent, beaked, crowned and "bearded" gules.[6]
Demographics
Bussigny has a population (as of December 2020) of 9,603.[7] As of 2008, 32.0% of the population are resident foreign nationals.[8] Over the last 10 years (1999–2009), the population has changed at a rate of 9.9%, of which 3.2% was due to migration and 7.2% due to births and deaths.[9]
Most of the population (as of 2000) speaks French (6,308 or 84.1%), with Italian being second most common (336 or 4.5%) and German being third (272 or 3.6%). Three people speak Romansh.[10]
Of the population in the municipality, 1,462 or about 19.5% were born in Bussigny and lived there in 2000. There were 2,673 or 35.6% who were born in the same canton, while 1,146 or 15.3% were born somewhere else in Switzerland, and 2,020 or 26.9% were born outside of Switzerland.[10]
In 2008, there were 64 live births to Swiss citizens and 27 births to non-Swiss citizens, and in same time span there were 35 deaths of Swiss citizens and six non-Swiss citizen deaths. Ignoring immigration and emigration, the population of Swiss citizens increased by 29 while the foreign population increased by 21. There were 6 Swiss men who emigrated from Switzerland. At the same time, there were 92 non-Swiss men and 73 non-Swiss women who immigrated from another country to Switzerland. The total Swiss population change in 2008 (from all sources, including moves across municipal borders) was an increase of 85 and the non-Swiss population increased by 131 people. This represents a population growth rate of 2.8%.[8]
The age distribution, as of 2009, in Bussigny is; 889 children or 11.1% of the population are 9 years old or younger and 1,006 children or 12.5% are between 10 and 19. Of the adult population, 1,116 people or 13.9% of the population are between 20 and 29 years old, 1,282 people or 16.0% are between 30 and 39, 1,336 people or 16.6% are between 40 and 49, and 1,031 people or 12.8% are between 50 and 59. The senior population distribution is 802 people or 10.0% of the population are between 60 and 69 years old, 384 people or 4.8% are between 70 and 79, 159 people or 2.0% who are between 80 and 89, and there are 28 people or 0.3% who are 90 and older.[11]
As of 2000, there were 3,194 people who were single and never married in the municipality. There were 3,612 married individuals, 259 widows or widowers and 433 individuals who are divorced.[10]
As of 2000, there were 3,062 private households in the municipality, and an average of 2.4 persons per household.[9] There were 901 households that consisted of only one person and 199 households with five or more people. Out of a total of 3,114 households that answered this question, 28.9% were households made up of just one person and there were eight adults who lived with their parents. Of the rest of the households, there are 836 married couples without children, 1,048 married couples with children, and 218 single parents with a child or children. There were 51 households that were made up of unrelated people and 52 households that were made up of some sort of institution or another collective housing.[10]
In 2000, there were 571 single-family homes (or 58.1% of the total) out of a total of 983 inhabited buildings. There were 269 multi-family buildings (27.4%), along with 96 multi-purpose buildings that were mostly used for housing (9.8%) and 47 other use buildings (commercial or industrial) that also had some housing (4.8%). Of the single-family homes, 44 were built before 1919, while 119 were built between 1990 and 2000. The greatest number of single-family homes (168) were built between 1971 and 1980. The most multi-family homes (64) were built between 1981 and 1990 and the next most (48) were built between 1971 and 1980. There were six multi-family houses built between 1996 and 2000.[12]
In 2000, there were 3,249 apartments in the municipality. The most common apartment size was three rooms of which there were 1,128. There were 171 single room apartments and 580 apartments with five or more rooms. Of these apartments, a total of 2,984 apartments (91.8% of the total) were permanently occupied, while 212 apartments (6.5%) were seasonally occupied and 53 apartments (1.6%) were empty.[12] As of 2009, the construction rate of new housing units was 8.9 new units per 1000 residents.[9] The vacancy rate for the municipality, in 2010, was 0.11%.[9]
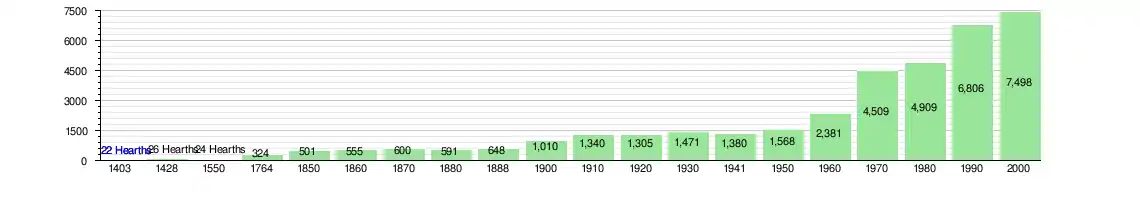
The historical population is given in the following chart:[3][13]
Politics
In the 2007 federal election, the most popular party was the SP, which received 26.06% of the vote. The next three most popular parties were the SVP (20.52%), the Green Party (15.26%) and the FDP (14.33%). In the federal election, a total of 1,763 votes were cast, and the voter turnout was 42.5%.[14]
Economy
As of 2010, Bussigny had an unemployment rate of 4.6%. As of 2008, there were 15 people employed in the primary economic sector and about 5 businesses involved in this sector. 1,978 people were employed in the secondary sector and there were 89 businesses in this sector. 3,882 people were employed in the tertiary sector, with 303 businesses in this sector.[9] There were 4,067 residents of the municipality who were employed in some capacity, of which females made up 42.4% of the workforce.
In 2008 the total number of full-time equivalent jobs was 5,036. The number of jobs in the primary sector was 13, all of which were in agriculture. The number of jobs in the secondary sector was 1,905 of which 1,195 or (62.7%) were in manufacturing and 663 (34.8%) were in construction. The number of jobs in the tertiary sector was 3,118. In the tertiary sector; 1,136 or 36.4% were in wholesale or retail sales or the repair of motor vehicles, 376 or 12.1% were in the movement and storage of goods, 129 or 4.1% were in a hotel or restaurant, 241 or 7.7% were in the information industry, 51 or 1.6% were the insurance or financial industry, 615 or 19.7% were technical professionals or scientists, 101 or 3.2% were in education and 82 or 2.6% were in health care.[15]
In 2000, there were 4,285 workers who commuted into the municipality and 3,054 workers who commuted away. The municipality is a net importer of workers, with about 1.4 workers entering the municipality for every one leaving. About 2.6% of the workforce coming into Bussigny are coming from outside Switzerland.[16] Of the working population, 16.5% used public transportation to get to work, and 65.8% used a private car.[9]
Religion
From the 2000 census, 2,878 or 38.4% were Roman Catholic, while 2,713 or 36.2% belonged to the Swiss Reformed Church. Of the rest of the population, there were 74 members of an Orthodox church (or about 0.99% of the population), there were five individuals (or about 0.07% of the population) who belonged to the Christian Catholic Church, and there were 406 individuals (or about 5.41% of the population) who belonged to another Christian church. There were 10 individuals (or about 0.13% of the population) who were Jewish, and 294 (or about 3.92% of the population) who were Islamic. There were 13 individuals who were Buddhist, eight individuals who were Hindu and 9 individuals who belonged to another church. About 12.07% of the population (905) belonged to no church, are agnostic or atheist, and 377 individuals (or about 5.03% of the population) did not answer the question.[10]
Education
In Bussigny, about 2,830 or (37.7%) of the population have completed non-mandatory upper secondary education, and 845 or (11.3%) have completed additional higher education (either university or a Fachhochschule). Of the 845 who completed tertiary schooling, 54.9% were Swiss men, 24.6% were Swiss women, 14.2% were non-Swiss men and 6.3% were non-Swiss women.[10]
In the 2009/2010 school year, there were a total of 1,001 students in the Bussigny school district. In the Vaud cantonal school system, two years of non-obligatory pre-school are provided by the political districts.[17] During the school year, the political district provided pre-school care for a total of 803 children of which 502 children (62.5%) received subsidized pre-school care. The canton's primary school program requires students to attend for four years. There were 507 students in the municipal primary school program. The obligatory lower secondary school program lasts for six years and there were 465 students in those schools. There were also 29 students who were home schooled or attended another non-traditional school.[18]
As of 2000, there were 93 students in Bussigny who came from another municipality, while 469 residents attended schools outside the municipality.[16]
Transportation
The municipality has a railway station, Bussigny, on the Jura Foot and Simplon lines. It has regular service to Vallorbe, Lausanne, Aigle, and Grandson.
References
- ↑ "Arealstatistik Standard - Gemeinden nach 4 Hauptbereichen". Federal Statistical Office. Retrieved 13 January 2019.
- ↑ Error: Unable to display the reference properly. See the documentation for details.
- 1 2 Bussigny-près-Lausanne in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- 1 2 Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data (in German) accessed 25 March 2010.
- 1 2 Nomenklaturen – Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz Archived 2015-11-13 at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 15 September 2015.
- ↑ Flags of the World.com accessed 22 June 2011.
- ↑ "Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit". bfs.admin.ch (in German). Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB. 31 December 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- 1 2 Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Superweb database - Gemeinde Statistics 1981-2008 Archived June 28, 2010, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 19 June 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Swiss Federal Statistical Office Archived January 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine accessed 22 June 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 STAT-TAB Datenwürfel für Thema 40.3 - 2000 Archived August 9, 2013, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 2 February 2011.
- ↑ Canton of Vaud Statistical Office Archived 2015-03-16 at the Wayback Machine (in French) accessed 29 April 2011.
- 1 2 Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB - Datenwürfel für Thema 09.2 - Gebäude und Wohnungen Archived September 7, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 28 January 2011.
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB Bevölkerungsentwicklung nach Region, 1850-2000 Archived September 30, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 29 January 2011.
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office, Nationalratswahlen 2007: Stärke der Parteien und Wahlbeteiligung, nach Gemeinden/Bezirk/Canton Archived May 14, 2015, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 28 May 2010.
- ↑ Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB Betriebszählung: Arbeitsstätten nach Gemeinde und NOGA 2008 (Abschnitte), Sektoren 1-3 Archived December 25, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 28 January 2011.
- 1 2 Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Statweb (in German) accessed 24 June 2010.
- ↑ Organigramme de l'école vaudoise, année scolaire 2009-2010 Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine (in French) accessed 2 May 2011.
- ↑ Canton of Vaud Statistical Office - Scol. obligatoire/filières de transition Archived 2016-04-25 at the Wayback Machine (in French) accessed 2 May 2011.
External links
- Official site (in French)
- Introduction to the village