| Carpal tunnel syndrome | |
|---|---|
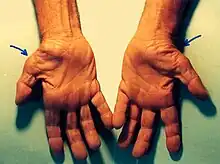 | |
| Untreated carpal tunnel syndrome, showing shrinkage (atrophy) of the muscles at the base of the thumb. | |
| Specialty | Orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery, neurology |
| Symptoms | Numbness, tingling in the thumb, index, middle finger, and half of ring finger.[1][2] |
| Causes | Compression of the median nerve at the carpal tunnel[1] |
| Risk factors | Genetics, work tasks |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, physical examinations, electrodiagnostic tests[2] |
| Differential diagnosis | Peripheral neuropathy, Radiculopathy, Plexopathy |
| Prevention | None |
| Treatment | Wrist splint, corticosteroid injections, surgery[3] |
| Frequency | 5–10%[4][5] |
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the collection of symptoms and signs associated with nerve compression of the median nerve at the carpal tunnel.[6] Most CTS is related to idiopathic compression of the median nerve as it travels through the wrist at the carpal tunnel (IMNCT).[1] Idiopathic means that there is no other disease process contributing to pressure on the nerve. As with most structural issues, it occurs in both hands, and the strongest risk factor is genetics.[1]
Other conditions can cause CTS such as wrist fracture or rheumatoid arthritis. After fracture, swelling, bleeding, and deformity compress the median nerve. With rheumatoid arthritis, the enlarged synovial lining of the tendons causes compression.
The main symptoms are numbness and tingling in the thumb, index finger, middle finger and the thumb side of the ring finger.[1] People often report pain, but pain without tingling is not characteristic of IMNCT. Rather, the numbness can be so intense that it is described as painful.
Symptoms are typically most troublesome at night.[2] Many people sleep with their wrists bent, and the ensuing symptoms may lead to awakening.[7] Untreated, and over years to decades, IMNCT causes loss of sensibility and weakness and shrinkage (atrophy) of the muscles at the base of the thumb.
Work-related factors such as vibration, wrist extension or flexion, hand force, and repetition increase the risk of developing CTS. The only certain risk factor for IMNCT is genetics. All other risk factors are open to debate. It is important to consider IMNCT separately from CTS in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.[8][5][3]
Diagnosis of IMNCT can be made with a high probability based on characteristic symptoms and signs. IMNCT can be measured with electrodiagnostic tests.[9]
People wake less often at night if they wear a wrist splint. Injection of corticosteroids may or may not alleviate better than simulated (placebo) injections.[10][11] There is no evidence that corticosteroid injection alters the natural history of the disease, which seems to be a gradual progression of neuropathy.
Surgery to cut the transverse carpal ligament is the only known disease modifying treatment.[3]
Anatomy

The carpal tunnel is an anatomical compartment located at the base of the palm. Nine flexor tendons and the median nerve pass through the carpal tunnel that is surrounded on three sides by the carpal bones that form an arch. The median nerve provides feeling or sensation to the thumb, index finger, long finger, and half of the ring finger. At the level of the wrist, the median nerve supplies the muscles at the base of the thumb that allow it to abduct, move away from the other four fingers, as well as move out of the plane of the palm. The carpal tunnel is located at the middle third of the base of the palm, bounded by the bony prominence of the scaphoid tubercle and trapezium at the base of the thumb, and the hamate hook that can be palpated along the axis of the ring finger. From the anatomical position, the carpal tunnel is bordered on the anterior surface by the transverse carpal ligament, also known as the flexor retinaculum. The flexor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band that attaches to the pisiform and the hamulus of the hamate. The proximal boundary is the distal wrist skin crease, and the distal boundary is approximated by a line known as Kaplan's cardinal line.[12] This line uses surface landmarks, and is drawn between the apex of the skin fold between the thumb and index finger to the palpated hamate hook.[13]
Pathophysiology

The carpal tunnel is a narrow canal surrounded by bone and fibrous tissue. The median nerve passes through this space along with the flexor tendons and their sheaths. Increased compartmental pressure for any reason can squeeze the median nerve.[14] Specifically, increased pressure can interfere with normal intraneural blood flow, eventually causing a cascade of physiological changes in the nerve itself.[15] There is a dose-respondent curve such that greater and longer periods of pressure are associated with greater nerve dysfunction.[15] Most cases of carpal tunnel syndrome are idiopathic (cause unknown), but common known causes are hypertrophy of the synovial tissue surrounding the flexor tendons of the forearm, and repetitive wrist movements.[14][16]
Prolonged pressure can lead to a cascade of physiological changes in neural tissue. First, the blood-nerve barrier breaks down (increased permeability of perineureum and endothelial cells of endoneural blood vessels).[15] Then edema forms.[17] If the pressure continues, the nerves will start the process of demyelination under the area of compression.[15] This will result in abnormal nerve conduction even when the pressure is relieved leading to persistent sensory symptoms until remyelination can occur. If the compression continues and is severe enough, axons may be injured and Wallerian degeneration will occur.[17] At this point there may be weakness and muscle atrophy, depending on the extent of axon damage.[18]
The critical pressure above which the microcirculatory environment of a nerve becomes compromised depends on diastolic/systolic blood pressure. Higher blood pressure will require higher external pressure on the nerve to disrupt its microvascular environment.[19] The critical pressure necessary to disrupt the blood supply of a nerve is approximately 30mm Hg below diastolic blood pressure or 45mm Hg below mean arterial pressure.[19] For normohypertensive (normal blood pressure) adults, the average values for systolic blood pressure is 116mm Hg diastolic blood pressure is 69mm Hg.[20] Using this data, the average person would become symptomatic with approximately 39mm Hg of pressure in the wrist (69 - 30 = 39 and 69 + (116 - 69)/3 - 45 ~ 40). Carpal tunnel syndrome patients tend to have elevated carpal tunnel pressures (12-31mm Hg) compared to controls (2.5 - 13mm Hg).[21][22][23] Applying pressure to the carpal tunnel of normal subjects in a lab can produce mild neurophysiological changes at 30mm Hg with a rapid, complete sensory block at 60mm Hg.[24] Carpal tunnel pressure is affected by wrist movement/position, with flexion and extension capable of raising the tunnel pressure as high as 111mm Hg.[22] Many of the activities associated with carpal tunnel such as driving, holding a phone, etc. involve flexing the wrist and it is likely due to an increase in carpal tunnel pressure during these activities.[14]
Nerve compression can result in various stages of nerve injury. The majority of carpal tunnel syndrome patients have a degree I nerve injury (Sunderland classification), also called neuropraxia.[15] This is characterized by a conduction block, segmental demyelination, and intact axons. With no further compression, the nerves will remyelinate and fully recover. Severe carpal tunnel syndrome patients may have degree II/III injuries (Sunderland classification), or axonotmesis, where the axon is injured partially or fully.[15] With axon injury there would be muscle weakness or atrophy, and with no further compression the nerves may only partially recover.
While there is evidence that chronic compression is a major cause of carpal tunnel syndrome, it may not be the only cause. Several alternative, potentially speculative, theories exist which describe alternative forms of nerve entrapment.[16] One is the theory of nerve scarring (specifically adherence between the mesoneurium and epineureum) preventing the nerve from gliding during wrist/finger movements, causing repetitive traction injuries.[25] Another is the double crush syndrome, where compression may interfere with axonal transport, and two separate points of compression (e.g. neck and wrist), neither enough to cause local demyelination, may together impair normal nerve function.[26]
Epidemiology
IMNCT is estimated to affect one out of ten people during their lifetime and is the most common nerve compression syndrome.[5] There is notable variation in such estimates based on how one defines the problem, in particular whether one studies people presenting with symptoms vs. measurable median neuropathy (IMNCT) whether or not people are seeking care. IMNCT accounts for about 90% of all nerve compression syndromes.[27] The best data regarding IMNCT and CTS comes from population-based studies, which demonstrate no relationship to gender, and increasing prevalence (accumulation) with age.
Symptoms
The characteristic symptom of CTS is numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the thumb, index, middle, and radial half of the ring finger. These areas process sensation through the median nerve.[28] Numbness or tingling is usually worse with sleep. People tend to sleep with their wrists flexed, which increases pressure on the nerve. Ache and discomfort may be reported in the forearm or even the upper arm, but its relationship to IMNCT is uncertain.[29] Symptoms that are not characteristic of CTS include pain in the wrists or hands, loss of grip strength,[30] minor loss of sleep,[31] and loss of manual dexterity.[32]
As the median neuropathy gets worse, there is loss of sensibility in the thumb, index, middle, and thumb side of the ring finger. As the neuropathy progresses, there may be first weakness, then to atrophy of the muscles of thenar eminence (the flexor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis, and abductor pollicis brevis). The sensibility of the palm remains normal because the superficial sensory branch of the median nerve branches proximal to the TCL and travels superficial to it.[33]
Median nerve symptoms may arise from compression at the level of the thoracic outlet or the area where the median nerve passes between the two heads of the pronator teres in the forearm,[34] although this is debated.
Signs
Severe IMNCT is associated with measurable loss of sensibility. Diminished threshold sensibility (the ability to distinguish different amounts of pressure) can be measured using Semmes-Weinstein monofilament testing.[35] Diminished discriminant sensibility can be measured by testing two-point discrimination: the number of millimeters two points of contact need to be separated before you can distinguish them.[36]
A person with idiopathic median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel will not have any sensory loss over the thenar eminence (bulge of muscles in the palm of hand and at the base of the thumb). This is because the palmar branch of the median nerve, which innervates that area of the palm, separates from the median nerve and passes over the carpal tunnel.[37]
Severe IMNCT is also associated with weakness and atrophy of the muscles at the base of the thumb. People may lose the ability to palmarly abduct the thumb. IMNCT can be detected on examination using one of several maneuvers to provoke paresthesia (a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the median nerve distribution). These so-called provocative signs include:
- Phalen's maneuver. Performed by fully flexing the wrist, then holding this position and awaiting symptoms.[38] A positive test is one that results in paresthesia in the median nerve distribution within sixty seconds.
- Tinel's sign is performed by lightly tapping the median nerve just proximal to flexor retinaculum to elicit paresthesia.[5]
- Durkan test, carpal compression test, or applying firm pressure to the palm over the nerve for up to 30 seconds to elicit paresthesia.[39][40]
- Hand elevation test The hand elevation test is performed by lifting both hands above the head. Paresthesia in the median nerve distribution within 2 minutes is considered positive.
Diagnostic performance characteristics such as sensitivity and specificity are reported, but difficult to interpret because of the lack of a consensus reference standard for CTS or IMNCT.
Causes
Idiopathic median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel
Most people with CTS have idiopathic median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel (IMNCT).
The association of other factors with CTS and IMNCT is a source of notable debate. It is important to distinguish factors that provoke symptoms, and factors that are associated with seeking care, from factors that make the neuropathy worse.
Genetic factors are believed to be the most important determinants of who develops carpal tunnel syndrome due to IMNCT. In other words, one's wrist structure seems programmed at birth to develop IMNCT later in life. A genome-wide association study (GWAS) of carpal tunnel syndrome identified 50 genomic loci significantly associated with the disease, including several loci previously known to be associated with human height.[41]
Factors that may contribute to symptoms, but have not been experimentally associated with neuropathy include obesity, and Diabetes mellitus.[3][42][43] One case-control study noted that individuals classified as obese (BMI >29) are 2.5 times more likely than slender individuals (BMI <20) to be diagnosed with CTS.[44] It is not clear whether this association is due to an alteration of pathophysiology, a variation in symptoms, or a variation in care-seeking.[45]
Discrete pathophysiology and carpal tunnel syndrome
Hereditary neuropathy with susceptibility to pressure palsies is a genetic condition that appears to increase the probability of developing MNCT. Heterozygous mutations in the gene SH3TC2, associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth, may confer susceptibility to neuropathy, including CTS.[46]
Association between common benign tumors such as lipomas, ganglion, and vascular malformation should be handled with care. Such tumors are very common and overlap with IMNCT is more likely than pressure on the median nerve.[47] Similarly, the degree to which transthyretin amyloidosis-associated polyneuropathy and carpal tunnel syndrome is under investigation. Prior carpal tunnel release is often noted in individuals who later present with transthyretin amyloid-associated cardiomyopathy.[48] There is consideration that bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome could be a reason to consider amyloidosis, timely diagnosis of which could improve heart health.[49] Amyloidosis is rare, even among people with carpal tunnel syndrome (0.55% incidence within 10 years of carpal tunnel release).[50] In the absence of other factors associated with a notable probability of amyloidosis, it is not clear that biopsy at the time of carpal tunnel release has a suitable balance between potential harms and potential benefits.[50]
Other specific pathophysiologies that can cause median neuropathy via pressure include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases that cause inflammation of the flexor tendons.
- With severe untreated hypothyroidism, generalized myxedema causes deposition of mucopolysaccharides within both the perineurium of the median nerve, as well as the tendons passing through the carpal tunnel. Association of CTS and IMNCT with lesser degrees of hypothyroidism is questioned.
- Pregnancy may bring out symptoms in genetically predisposed individuals, which may be caused by the temporary changes in hormones and fluid increase pressure in the carpal tunnel.[45] High progesterone levels and water retention may increase the size of the synovium.
- Bleeding and swelling from a fracture or dislocation. This is referred to as acute carpal tunnel syndrome.[51]
- Acromegaly causes excessive secretion of growth hormones. This causes the soft tissues and bones around the carpal tunnel to grow and compress the median nerve.[52]
Other considerations
- Double-crush syndrome is a debated hypothesis that compression or irritation of nerve branches contributing to the median nerve in the neck, or anywhere above the wrist, increases sensitivity of the nerve to compression in the wrist. There is little evidence to support this theory and some concern that it may be used to justify more surgery.[26][53]
Median neuropathy and activity
Work-related factors that increase risk of CTS include vibration (5.4 odds ratio), hand force (4.2), and repetition (2.3). Exposure to wrist extension or flexion at work increases the risk of CTS by two times. The balance of evidence suggests that keyboard and computer use does not cause CTS.[54]
The international debate regarding the relationship between CTS and repetitive hand use (at work in particular) is ongoing. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has adopted rules and regulations regarding so-called "cumulative trauma disorders" based concerns regarding potential harm from exposure to repetitive tasks, force, posture, and vibration.[55][56]
A review of available scientific data by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) indicated that job tasks that involve highly repetitive manual acts or specific wrist postures were associated with symptoms of CTS, but there was not a clear distinction of paresthesia (appropriate) from pain (inappropriate) and causation was not established. The distinction from work-related arm pains that are not carpal tunnel syndrome was unclear. It is proposed that repetitive use of the arm can affect the biomechanics of the upper limb or cause damage to tissues. It is proposed that postural and spinal assessment along with ergonomic assessments should be considered, based on observation that addressing these factors has been found to improve comfort in some studies although experimental data are lacking and the perceived benefits may not be specific to those interventions.[57][58] A 2010 survey by NIOSH showed that two-thirds of the 5 million carpal tunnel diagnosed in the US that year were related to work.[59] Women are more likely to be diagnosed with work-related carpal tunnel syndrome than men.[60] Many if not most patients described in published series of carpal tunnel release are older and often not working.[61]
Normal pressure of the carpal tunnel has been defined as a range of 2–10 mm (0.079–0.394 in).[62] Wrist flexion increases the pressure eight-fold and extension increases it ten-fold.[63] There is speculation that repetitive flexion and extension in the wrist can cause thickening of the synovial tissue that lines the tendons within the carpal tunnel.[64]
Associated conditions
A variety of patient factors can lead to CTS, including heredity, size of the carpal tunnel, associated local and systematic diseases, and certain habits.[65] Non-traumatic causes generally happen over a period of time, and are not triggered by one certain event. Many of these factors are manifestations of physiologic aging.[66]
Diagnosis
There is no consensus reference standard for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. A combination of characteristic symptoms (how it feels) and signs (what the clinician finds on exam) are associated with a high probability of IMNCT without electrophysiological testing.
Electrodiagnostic testing (electromyography and nerve conduction velocity) can objectively measure and verify median neuropathy.[67]
Ultrasound can image and measure the cross sectional diameter of the median nerve, which has some correlation with idiopathic median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel (IMNCT). The role of ultrasound in diagnosis—just as for electrodiagnostic testing—is a matter of debate. EDX cannot fully exclude the diagnosis of CTS due to the lack of sensitivity.
The role of confirmatory electrodiagnostic testing is debated.[5] The goal of electrodiagnostic testing is to compare the speed of conduction in the median nerve with conduction in other nerves supplying the hand. When the median nerve is compressed, as in IMNCT, it will conduct more slowly than normal and more slowly than other nerves. Compression results in damage to the myelin sheath and manifests as delayed latencies and slowed conduction velocities.[65] Electrodiagnosis rests upon demonstrating impaired median nerve conduction across the carpal tunnel in context of normal conduction elsewhere.
It is often stated that normal electrodiagnostic studies do not preclude the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. The rationale for this is that a threshold of neuropathy must be reached before study results become abnormal and also that threshold values for abnormality vary.[68] Others contend that idiopathic median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel with normal electrodiagnostic tests would represent very, very mild neuropathy that would be best managed as a normal median nerve. Even more important, notable symptoms with mild disease is strongly associated with unhelpful thoughts and symptoms of worry and despair. Notable CTS with unmeasurable IMNCT should remind clinicians to always consider the whole person, including their mindset and circumstances, in strategies to help people get and stay healthy.[69]
A joint report published by the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM), the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (AAPM&R), and the American Academy of Neurology defines practice parameters, standards, and guidelines for EDX studies of CTS based on an extensive critical literature review. This joint review concluded median and sensory nerve conduction studies are valid and reproducible in a clinical laboratory setting and a clinical diagnosis of CTS can be made with a sensitivity greater than 85% and specificity greater than 95%. Given the key role of electrodiagnostic testing in the diagnosis of CTS, The AANEM has issued evidence-based practice guidelines, both for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Imaging
The role of MRI or ultrasound imaging in the diagnosis of IMNCT is unclear.[70][71][72] Their routine use is not recommended.[3] Morphological MRI has high sensitivity but low specificity for IMNCT. High signal intensity may suggest accumulation of axonal transportation, myelin sheath degeneration or oedema.[62] However, more recent quantitative MRI techniques which derive repeatable, reliable and objective biomarkers from nerves and skeletal muscle may have utility, including diffusion-weighted (typically diffusion tensor) MRI which has demonstrable normal values and aberrations in carpal tunnel syndrome.[73]
Differential diagnosis
Cervical radiculopathy can also cause paresthesia abnormal sensibility in the hands and wrist.[5] The distribution usually follows the nerve root, and the paresthesia may be provoked by neck movement.[5] Electromyography and imaging of the cervical spine can help to differentiate cervical radiculopathy from carpal tunnel syndrome if the diagnosis is unclear.[5] Carpal tunnel syndrome is sometimes applied as a label to anyone with pain, numbness, swelling, or burning in the radial side of the hands or wrists. When pain is the primary symptom, carpal tunnel syndrome is unlikely to be the source of the symptoms.[9]
When the symptoms and signs point to atrophy and muscle weakness more than numbness, consider neurodegenerative disorders such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis or Charcot-Marie Tooth.[74][75][76]
Prevention
There is little or no data to support the concept that activity adjustment prevents carpal tunnel syndrome.[43] The evidence for wrist rest is debated.[77] There is also little research supporting that ergonomics is related to carpal tunnel syndrome.[78]
Given that biological factors such as genetic predisposition and anthropometric features are more strongly associated with idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome than occupational/environmental factors such as hand use, IMNCT might not be prevented by activity modifications.[43]
Some claim that worksite modifications such as switching from a QWERTY computer keyboard layout to Dvorak is helpful, but meta-analyses of the available studies note limited supported evidence.[79][80]
Treatment
There are more than 50 types of treatments for CTS with varied levels of evidence and recommendation across healthcare guidelines, with evidence most strongly supporting surgery, steroids, splinting for wrist positioning, and physical or occupational therapy interventions.[81] When selecting treatment, it is important to consider the severity and chronicity of the CTS pathophysiology and to distinguish treatments that can alter the natural history of the pathophysiology (disease-modifying treatments) and treatments that only alleviate symptoms (palliative treatments). The strongest evidence for disease-modifying treatment in chronic or severe CTS cases is surgery to change the shape of the carpal tunnel.[82][83]
The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons recommends proceeding conservatively with a course of nonsurgical therapies tried before release surgery is considered.[84] A different treatment should be tried if the current treatment fails to resolve the symptoms within 2 to 7 weeks. Early surgery with carpal tunnel release is indicated where there is evidence of median nerve denervation or a person elects to proceed directly to surgical treatment.[84] Recommendations may differ when carpal tunnel syndrome is found in association with the following conditions: diabetes mellitus, coexistent cervical radiculopathy, hypothyroidism, polyneuropathy, pregnancy, rheumatoid arthritis, and carpal tunnel syndrome in the workplace.[84] CTS related to another pathophysiology is addressed by treating that pathology. For instance, disease-modifying medications for rheumatoid arthritis or surgery for traumatic acute carpal tunnel syndrome.[85][86][87]
There is insufficient evidence to recommend gabapentin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs), yoga, acupuncture, low level laser therapy, magnet therapy, vitamin B6 or other supplements.[88][81]
Splint immobilization


Wrist braces (splints) alleviate symptoms by keeping the wrist straight, which avoids the increased pressure in the carpal tunnel associated with wrist flexion or extension. They are used primarily to help people sleep.[89]
Many health professionals suggest that, for the best results, one should wear braces at night. When possible, braces can be worn during the activity primarily causing stress on the wrists.[90][91] The brace should not generally be used during the day as wrist activity is needed to keep the wrist from becoming stiff and to prevent muscles from weakening.[92]
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroid injections may provide temporary alleviation of symptoms although they are not clearly better than placebo.[93] This form of treatment is thought to reduce discomfort in those with CTS due to its ability to decrease median nerve swelling.[5] The use of ultrasound while performing the injection is more expensive but leads to faster resolution of CTS symptoms.[5] The injections are done under local anesthesia.[94][95] This treatment is not appropriate for extended periods, however. In general, local steroid injections are only used until more definitive treatment options can be used. Corticosteroid injections do not appear to slow disease progression.[5]
Surgery

Release of the transverse carpal ligament is known as "carpal tunnel release" surgery. The purpose of cutting the transverse carpal ligament to relieve pressure on the median nerve, and this type of surgery is called a nerve decompression. It is recommended when there is static (constant, not just intermittent) numbness, muscle weakness, or atrophy, and when night-splinting or other palliative interventions no longer alleviate intermittent symptoms.[96] The surgery may be done with local[97][98][99] or regional anesthesia[100] with[101] or without[98] sedation, or under general anesthesia.[99][100] In general, milder cases can be controlled for months to years, but severe cases are unrelenting symptomatically and are likely to result in surgical treatment.[102]
Physical and occupational therapy
There are many different techniques used in manual therapy for patients with CTS. Some examples are manual and instrumental soft tissue mobilizations, massage therapy, bone mobilizations or manipulations, and neurodynamic techniques, focused on skeletal system or soft tissue.[103]
A randomized control trial published in 2017 sought to examine the efficacy of manual therapy techniques for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. The study included a total of 140 individuals diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome and the patients were divided into two groups. One group received treatment that consisted of manual therapy. Manual therapy included the incorporation of specified neurodynamic techniques, functional massage, and carpal bone mobilizations. Another group only received treatment through electrophysical modalities. The duration of the study was over the course of 20 physical therapy sessions for both groups. Results of this study showed that the group being treated through manual techniques and mobilizations yielded a 290% reduction in overall pain when compared to reports of pain prior to conducting the study. Total function improved by 47%. Conversely, the group being treated with electrophysical modalities reported a 47% reduction in overall pain with a 9% increase in function.[104]
Self-myofascial ligament stretching has been suggested as an effective technique, although a meta-analysis claimed this kind of therapy does not show significant improvement in symptoms or function.[105] Tendon and nerve gliding exercises appear to be useful in carpal tunnel syndrome.[106]
Alternative medicine
A 2018 Cochrane review on acupuncture and related interventions for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome concluded that, "Acupuncture and laser acupuncture may have little or no effect in the short term on symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) in comparison with placebo or sham acupuncture." It was also noted that all studies had an unclear or high overall risk of bias and that all evidence was of low or very low quality.[107]
Prognosis

The natural history of untreated IMNCT seems to be gradual worsening of the neuropathy. It is difficult to prove that this is always the case, but the supportive evidence is compelling.
Atrophy of the muscles of the thenar muscles, weakness of palmar abduction, and loss of sensibility (constant numbness as opposed to intermittent paresthesia) are signs of advanced neuropathy. Advanced neuropathy is often permanent. The nerve will try to recover after surgery for more than 2 years, but the recovery may be incomplete.[108]
Paresthesia may increase after release of advanced carpal tunnel syndrome, and people may feel worse than they did prior to surgery for many months.
Troublesome recovery seems related to symptoms of anxiety or depression, and unhelpful thoughts about symptoms (such as worst-case or catastrophic thinking) as well as advanced neuropathy with potentially permanent neuropathy.[109]
Recurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome after successful surgery is rare.[110][111] Caution is warranted in considering additional surgery for people dissatisfied with the result of carpal tunnel release as perceived recurrence may more often be due to renewed awareness of persistent symptoms rather than worsening pathology.[112]
History
IMNCT was first described long ago, but infrequently diagnosed until relatively recently. People were often diagnosed with acroparesthesia.[113] Clinicians would often ascribe it to "poor circulation" and not pursue it further.[114]
Sir James Paget described median nerve compression at the carpal tunnel in two patients after trauma in 1854.[115][116] The first was due to an injury where a cord had been wrapped around a man's wrist. The second was related to a distal radial fracture. For the first case Paget performed an amputation of the hand. For the second case Paget recommended a wrist splint.
The first to notice the association between the carpal ligament pathology and median nerve compression appear to have been Pierre Marie and Charles Foix in 1913.[117] They described the results of a postmortem of an 80-year-old man with bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome. They suggested that division of the carpal ligament would be curative in such cases. Putman had previously described a series of 37 patients and suggested a vasomotor origin.[118] The association between the thenar muscle atrophy and compression was noted in 1914.[119] The name "carpal tunnel syndrome" appears to have been coined by Moersch in 1938.[120]
Physician George S. Phalen of the Cleveland Clinic drew attention to the pathology of IMNCT as the reason for most CTS after working with a group of patients in the 1950s and 1960s.[121][122]
Treatment
In 1933 Sir James Learmonth outlined a method of decompression of the nerve at the wrist.[123] This procedure appears to have been pioneered by the Canadian surgeons Herbert Galloway and Andrew MacKinnon in 1924 in Winnipeg but was not published.[124] Endoscopic release was described in 1988.[125]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Burton C, Chesterton LS, Davenport G (May 2014). "Diagnosing and managing carpal tunnel syndrome in primary care". The British Journal of General Practice. 64 (622): 262–263. doi:10.3399/bjgp14x679903. PMC 4001168. PMID 24771836.
- 1 2 3 "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Fact Sheet". National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. January 28, 2016. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (February 29, 2016). "Management of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline". Archived from the original on March 30, 2020. Retrieved March 5, 2016.
- ↑ Bickel KD (January 2010). "Carpal tunnel syndrome". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 35 (1): 147–152. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2009.11.003. PMID 20117319.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Padua L, Coraci D, Erra C, Pazzaglia C, Paolasso I, Loreti C, et al. (November 2016). "Carpal tunnel syndrome: clinical features, diagnosis, and management". The Lancet. Neurology (Review). 15 (12): 1273–1284. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30231-9. PMID 27751557. S2CID 9991471.
- ↑ Genova A, Dix O, Saefan A, Thakur M, Hassan A (March 2020). "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Review of Literature". Cureus. 12 (3): e7333. doi:10.7759/cureus.7333. PMC 7164699. PMID 32313774.
- ↑ "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome - Symptoms and Treatment - OrthoInfo - AAOS". www.orthoinfo.org. Retrieved 2023-08-18.
- ↑ Shiri R (December 2014). "Hypothyroidism and carpal tunnel syndrome: a meta-analysis". Muscle & Nerve. 50 (6): 879–883. doi:10.1002/mus.24453. PMID 25204641. S2CID 37496158.
- 1 2 Graham B (December 2008). "The value added by electrodiagnostic testing in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 90 (12): 2587–2593. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.01362. PMID 19047703.
- ↑ Boyer MI (October 2008). "Corticosteroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 33 (8): 1414–1416. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2008.06.023. PMID 18929212.
- ↑ Huisstede BM, Randsdorp MS, van den Brink J, Franke TP, Koes BW, Hoogvliet P (August 2018). "Effectiveness of Oral Pain Medication and Corticosteroid Injections for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review". Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 99 (8): 1609–1622.e10. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2018.03.003. PMID 29626428. S2CID 4683880.
- ↑ Brooks JJ, Schiller JR, Allen SD, Akelman E (October 2003). "Biomechanical and anatomical consequences of carpal tunnel release". Clinical Biomechanics. 18 (8): 685–693. doi:10.1016/S0268-0033(03)00052-4. PMID 12957554.
- ↑ Vella JC, Hartigan BJ, Stern PJ (Jul–Aug 2006). "Kaplan's cardinal line". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 31 (6): 912–918. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2006.03.009. PMID 16843150.
- 1 2 3 Joshi A, Patel K, Mohamed A, Oak S, Zhang MH, Hsiung H, Zhang A, Patel UK (July 2022). "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Pathophysiology and Comprehensive Guidelines for Clinical Evaluation and Treatment". Cureus. 14 (7): e27053. doi:10.7759/cureus.27053. PMC 9389835. PMID 36000134.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Mackinnon SE (May 2002). "Pathophysiology of nerve compression". Hand Clin. 18 (2): 231–41. doi:10.1016/s0749-0712(01)00012-9. PMID 12371026.
- 1 2 Aboonq MS (January 2015). "Pathophysiology of carpal tunnel syndrome". Neurosciences (Riyadh). 20 (1): 4–9. PMC 4727604. PMID 25630774.
- 1 2 Lundborg G, Dahlin LB (May 1996). "Anatomy, function, and pathophysiology of peripheral nerves and nerve compression". Hand Clin. 12 (2): 185–93. doi:10.1016/S0749-0712(21)00303-6. PMID 8724572.
- ↑ Menorca RM, Fussell TS, Elfar JC (August 2013). "Nerve physiology: mechanisms of injury and recovery". Hand Clin. 29 (3): 317–30. doi:10.1016/j.hcl.2013.04.002. PMC 4408553. PMID 23895713.
- 1 2 Szabo RM, Gelberman RH, Williamson RV, Hargens AR (1983). "Effects of increased systemic blood pressure on the tissue fluid pressure threshold of peripheral nerve". J Orthop Res. 1 (2): 172–8. doi:10.1002/jor.1100010208. PMID 6679859. S2CID 367271.
- ↑ Wright JD, Hughes JP, Ostchega Y, Yoon SS, Nwankwo T (March 2011). "Mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure in adults aged 18 and over in the United States, 2001-2008". Natl Health Stat Report (35): 1–22, 24. PMID 21485611.
- ↑ Gelberman RH, Hergenroeder PT, Hargens AR, Lundborg GN, Akeson WH (March 1981). "The carpal tunnel syndrome. A study of carpal canal pressures". J Bone Joint Surg Am. 63 (3): 380–3. doi:10.2106/00004623-198163030-00009. PMID 7204435.
- 1 2 Rojviroj S, Sirichativapee W, Kowsuwon W, Wongwiwattananon J, Tamnanthong N, Jeeravipoolvarn P (May 1990). "Pressures in the carpal tunnel. A comparison between patients with carpal tunnel syndrome and normal subjects". J Bone Joint Surg Br. 72 (3): 516–8. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.72B3.2187880. PMID 2187880.
- ↑ Luchetti R, Schoenhuber R, De Cicco G, Alfarano M, Deluca S, Landi A (August 1989). "Carpal-tunnel pressure". Acta Orthop Scand. 60 (4): 397–9. doi:10.3109/17453678909149305. PMID 2816314.
- ↑ Lundborg G, Gelberman RH, Minteer-Convery M, Lee YF, Hargens AR (May 1982). "Median nerve compression in the carpal tunnel--functional response to experimentally induced controlled pressure". J Hand Surg Am. 7 (3): 252–9. doi:10.1016/s0363-5023(82)80175-5. PMID 7086092.
- ↑ Armstrong TJ, Chaffin DB (July 1979). "Carpal tunnel syndrome and selected personal attributes". J Occup Med. 21 (7): 481–6. PMID 469613.
- 1 2 Molinari WJ, Elfar JC (April 2013). "The double crush syndrome". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 38 (4): 799–801, quiz 801. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2012.12.038. PMC 5823245. PMID 23466128.
- ↑ Ibrahim I, Khan WS, Goddard N, Smitham P (2012). "Carpal tunnel syndrome: a review of the recent literature". The Open Orthopaedics Journal. 6: 69–76. doi:10.2174/1874325001206010069. PMC 3314870. PMID 22470412.
- ↑ Aroori S, Spence RA (January 2008). "Carpal tunnel syndrome". The Ulster Medical Journal. 77 (1): 6–17. PMC 2397020. PMID 18269111.
- ↑ "Carpal tunnel syndrome – Symptoms". NHS Choices. Archived from the original on 2016-05-24. Retrieved 2016-05-21. Page last reviewed: 18/09/2014
- ↑ Atroshi I, Gummesson C, Johnsson R, Ornstein E, Ranstam J, Rosén I (July 1999). "Prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome in a general population". JAMA. 282 (2): 153–158. doi:10.1001/jama.282.2.153. PMID 10411196.
- ↑ Boyko T (January 24, 2022). "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome". TXOSA. Archived from the original on 2022-01-24.
- ↑ "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information Page". National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. December 28, 2010. Archived from the original on December 22, 2010.
- ↑ Norvell JG, Steele M (September 10, 2009). "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome". eMedicine. Archived from the original on August 3, 2010.
- ↑ Netter F (2011). Atlas of Human Anatomy (5th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier. pp. 412, 417, 435. ISBN 978-0-8089-2423-4.
- ↑ Szabo RM, Gelberman RH, Dimick MP (January 1984). "Sensibility testing in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 66 (1): 60–64. doi:10.2106/00004623-198466010-00009. PMID 6690444.
- ↑ Elfar JC, Yaseen Z, Stern PJ, Kiefhaber TR (November 2010). "Individual finger sensibility in carpal tunnel syndrome". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 35 (11): 1807–1812. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2010.08.013. PMC 4410266. PMID 21050964.
- ↑ Netter F (2011). Atlas of Human Anatomy (5th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier. p. 447. ISBN 978-0-8089-2423-4.
- ↑ Cush JJ, Lipsky PE (2004). "Approach to articular and musculoskeletal disorders". Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine (16th ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 2035. ISBN 978-0-07-140235-4.
- ↑ González del Pino J, Delgado-Martínez AD, González González I, Lovic A (February 1997). "Value of the carpal compression test in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome". Journal of Hand Surgery. 22 (1): 38–41. doi:10.1016/S0266-7681(97)80012-5. PMID 9061521. S2CID 25924364.
- ↑ Durkan JA (April 1991). "A new diagnostic test for carpal tunnel syndrome". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 73 (4): 535–538. doi:10.2106/00004623-199173040-00009. PMID 1796937. S2CID 11545887.
- ↑ Skuladottir AT, Bjornsdottir G, Ferkingstad E, Einarsson G, Stefansdottir L, Nawaz MS, et al. (March 2022). "A genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 50 genetic loci associated with carpal tunnel syndrome". Nature Communications. 13 (1): 1598. Bibcode:2022NatCo..13.1598S. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29133-7. PMC 8948232. PMID 35332129.
- ↑ Osterman M, Ilyas AM, Matzon JL (October 2012). "Carpal tunnel syndrome in pregnancy". The Orthopedic Clinics of North America. 43 (4): 515–520. doi:10.1016/j.ocl.2012.07.020. PMID 23026467.
- 1 2 3 Lozano-Calderón S, Anthony S, Ring D (April 2008). "The quality and strength of evidence for etiology: example of carpal tunnel syndrome". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 33 (4): 525–538. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2008.01.004. PMID 18406957.
- ↑ Werner RA, Albers JW, Franzblau A, Armstrong TJ (June 1994). "The relationship between body mass index and the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome". Muscle & Nerve. 17 (6): 632–636. doi:10.1002/mus.880170610. hdl:2027.42/50161. PMID 8196706. S2CID 16722546.
- 1 2 Padua L, Coraci D, Erra C, Pazzaglia C, Paolasso I, Loreti C, et al. (November 2016). "Carpal tunnel syndrome: clinical features, diagnosis, and management". The Lancet. Neurology. 15 (12): 1273–1284. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30231-9. PMID 27751557. S2CID 9991471.
- ↑ Lupski JR, Reid JG, Gonzaga-Jauregui C, Rio Deiros D, Chen DC, Nazareth L, et al. (April 2010). "Whole-genome sequencing in a patient with Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy". The New England Journal of Medicine. 362 (13): 1181–1191. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0908094. PMC 4036802. PMID 20220177.
- ↑ Kellett J, McKeown P, Deane B (2005). "Differences between self-referred and physician-referred hospital admissions". Irish Journal of Medical Science. 174 (3): 70–78. doi:10.1007/BF03170208. PMID 16285343. S2CID 71606479.
- ↑ Conceição I, González-Duarte A, Obici L, Schmidt HH, Simoneau D, Ong ML, Amass L (March 2016). ""Red-flag" symptom clusters in transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy". Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System. 21 (1): 5–9. doi:10.1111/jns.12153. PMC 4788142. PMID 26663427.
- ↑ Donnelly JP, Hanna M, Sperry BW, Seitz WH (October 2019). "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Potential Early, Red-Flag Sign of Amyloidosis". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 44 (10): 868–876. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2019.06.016. PMID 31400950. S2CID 199540407.
- 1 2 Sood RF, Kamenko S, McCreary E, Sather BK, Schmitt M, Peterson SL, Lipira AB (July 2021). "Diagnosing Systemic Amyloidosis Presenting as Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Risk Nomogram to Guide Biopsy at Time of Carpal Tunnel Release". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 103 (14): 1284–1294. doi:10.2106/JBJS.20.02093. PMID 34097669. S2CID 235370526.
- ↑ Dyer G, Lozano-Calderon S, Gannon C, Baratz M, Ring D (October 2008). "Predictors of acute carpal tunnel syndrome associated with fracture of the distal radius". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 33 (8): 1309–1313. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2008.04.012. PMID 18929193.
- ↑ "Carpel Tunnel Syndrome in Acromegaly". Treatmentandsymptoms.com. Archived from the original on 2016-01-26. Retrieved 2011-10-05.
- ↑ Kane PM, Daniels AH, Akelman E (September 2015). "Double Crush Syndrome". The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 23 (9): 558–562. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00176. PMID 26306807. S2CID 207531472.
- ↑ Newington L, Harris EC, Walker-Bone K (June 2015). "Carpal tunnel syndrome and work". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Rheumatology. 29 (3): 440–453. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2015.04.026. PMC 4759938. PMID 26612240.
- ↑ Derebery J (2006). "Work-related carpal tunnel syndrome: the facts and the myths". Clinics in Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 5 (2): 353–67, viii. doi:10.1016/j.coem.2005.11.014 (inactive 1 August 2023). PMID 16647653.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of August 2023 (link) - ↑ Office of Communications and Public Liaison (December 18, 2009). "National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke". Archived from the original on March 3, 2016.
- ↑ Cole DC, Hogg-Johnson S, Manno M, Ibrahim S, Wells RP, Ferrier SE, et al. (Worksite Upper Extremity Research Group) (November 2006). "Reducing musculoskeletal burden through ergonomic program implementation in a large newspaper". International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health. 80 (2): 98–108. Bibcode:2006IAOEH..80...98C. doi:10.1007/s00420-006-0107-6. PMID 16736193. S2CID 21845851.
- ↑ O'Connor D, Page MJ, Marshall SC, Massy-Westropp N (January 2012). "Ergonomic positioning or equipment for treating carpal tunnel syndrome". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD009600. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009600. PMC 6486220. PMID 22259003.
- ↑ Luckhaupt SE, Burris DL (24 June 2013). "How Does Work Affect the Health of the U.S. Population? Free Data from the 2010 NHIS-OHS Provides the Answers". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Archived from the original on 18 January 2015. Retrieved 18 January 2015.
- ↑ Swanson N, Tisdale-Pardi J, MacDonald L, Tiesman HM (13 May 2013). "Women's Health at Work". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Archived from the original on 18 January 2015. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ↑ Gelfman R, Melton LJ, Yawn BP, Wollan PC, Amadio PC, Stevens JC (January 2009). "Long-term trends in carpal tunnel syndrome". Neurology. 72 (1): 33–41. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000338533.88960.b9. PMC 2633642. PMID 19122028.
- 1 2 Zamborsky R, Kokavec M, Simko L, Bohac M (January 2017). "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment Options. Literature Reviev". Ortopedia, Traumatologia, Rehabilitacja. 19 (1): 1–8. doi:10.5604/15093492.1232629. PMID 28436376.
- ↑ Ibrahim I, Khan WS, Goddard N, Smitham P (2012-02-23). "Carpal tunnel syndrome: a review of the recent literature". The Open Orthopaedics Journal. 6 (1): 69–76. doi:10.2174/1874325001206010069. PMC 3314870. PMID 22470412.
- ↑ Lluch AL (April 1992). "Thickening of the synovium of the digital flexor tendons: cause or consequence of the carpal tunnel syndrome?". Journal of Hand Surgery. 17 (2): 209–212. doi:10.1016/0266-7681(92)90091-F. PMID 1588206. S2CID 39895571.
- 1 2 Scott KR, Kothari MJ (October 5, 2009). "Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome". UpToDate.
- ↑ Stevens JC, Beard CM, O'Fallon WM, Kurland LT (June 1992). "Conditions associated with carpal tunnel syndrome". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 67 (6): 541–548. doi:10.1016/S0025-6196(12)60461-3. PMID 1434881.
- ↑ Rosario NB, De Jesus O (2022), "Electrodiagnostic Evaluation Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 32965906, retrieved 2022-07-28
- ↑ Graham B, Regehr G, Naglie G, Wright JG (2006). "Development and validation of diagnostic criteria for carpal tunnel syndrome". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 31 (6): 919–924. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2006.03.005. PMID 16886290.
- ↑ Crum, Alia; Zuckerman, Barry (2017). "Changing Mindsets to Enhance Treatment Effectiveness". JAMA. 317 (20): 2063–2064. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.4545. PMC 7608684. PMID 28418538.
- ↑ Wilder-Smith EP, Seet RC, Lim EC (July 2006). "Diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome--clinical criteria and ancillary tests". Nature Clinical Practice. Neurology. 2 (7): 366–374. doi:10.1038/ncpneuro0216. PMID 16932587. S2CID 22566215.
- ↑ Bland JD (October 2005). "Carpal tunnel syndrome". Current Opinion in Neurology. 18 (5): 581–585. doi:10.1097/01.wco.0000173142.58068.5a. PMID 16155444. S2CID 945614.
- ↑ Jarvik JG, Yuen E, Kliot M (February 2004). "Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: electrodiagnostic and MR imaging evaluation". Neuroimaging Clinics of North America. 14 (1): 93–102, viii. doi:10.1016/j.nic.2004.02.002. PMID 15177259.
- ↑ Rojoa D, Raheman F, Rassam J, Wade RG (October 2021). "Meta-analysis of the normal diffusion tensor imaging values of the median nerve and how they change in carpal tunnel syndrome". Scientific Reports. 11 (1): 20935. Bibcode:2021NatSR..1120935R. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-00353-z. PMC 8536657. PMID 34686721.
- ↑ Genova A, Dix O, Saefan A, Thakur M, Hassan A (March 2020). "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Review of Literature". Cureus. 12 (3): e7333. doi:10.7759/cureus.7333. PMC 7164699. PMID 32313774.
- ↑ Masrori P, Van Damme P (October 2020). "Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a clinical review". European Journal of Neurology. 27 (10): 1918–1929. doi:10.1111/ene.14393. PMC 7540334. PMID 32526057.
- ↑ Nagappa M, Sharma S, Taly AB (2022). "Charcot Marie Tooth". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 32965834. Retrieved 2022-09-06.
- ↑ "Wrist Rests : OSH Answers". Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. Archived from the original on 2017-04-15. Retrieved 2017-04-14.
- ↑ Goodman G (2014-12-08). Ergonomic interventions for computer users with cumulative trauma disorders. International handbook of occupational therapy interventions. 2nd ed. pp. 205–17. ISBN 978-3-319-08140-3.
- ↑ Lincoln AE, Vernick JS, Ogaitis S, Smith GS, Mitchell CS, Agnew J (May 2000). "Interventions for the primary prevention of work-related carpal tunnel syndrome". American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 18 (4 Suppl): 37–50. doi:10.1016/S0749-3797(00)00140-9. PMID 10793280.
- ↑ Verhagen AP, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, Burdorf A, Stynes SM, de Vet HC, Koes BW (December 2013). "Conservative interventions for treating work-related complaints of the arm, neck or shoulder in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2013 (12): CD008742. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008742.pub2. PMC 6485977. PMID 24338903.
- 1 2 Baker NA, Dole J, Roll SC (November 2021). "Meta-synthesis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment Options: Developing Consolidated Clinical Treatment Recommendations to Improve Practice". Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 102 (11): 2261–2268.e2. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2021.03.034. PMID 33932358. S2CID 233477339.
- ↑ Hageman MG, Kinaci A, Ju K, Guitton TG, Mudgal CS, Ring D (September 2014). "Carpal tunnel syndrome: assessment of surgeon and patient preferences and priorities for decision-making". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 39 (9): 1799–1804.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.05.035. PMID 25087865.
- ↑ Wood MR (February 1980). "Hydrocortisone injections for carpal tunnel syndrome". The Hand. 12 (1): 62–64. doi:10.1016/S0072-968X(80)80031-3. PMID 6154006. S2CID 43399056.
- 1 2 3 Clinical Practice Guideline on the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (PDF). American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. September 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-12-11. Retrieved 2010-06-27.
- ↑ Werthel JD, Zhao C, An KN, Amadio PC (November 2014). "Carpal tunnel syndrome pathophysiology: role of subsynovial connective tissue". Journal of Wrist Surgery. 3 (4): 220–226. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1394133. PMC 4208960. PMID 25364632.
- ↑ Mahmoud W, El-Naby MM, Awad AA (2022-11-09). "Carpal tunnel syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis patients: the role of combined ultrasonographic and electrophysiological assessment". Egyptian Rheumatology and Rehabilitation. 49 (1): 62. doi:10.1186/s43166-022-00147-9. ISSN 2090-3235. S2CID 253400371.
- ↑ Gillig JD, White SD, Rachel JN (July 2016). "Acute Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Review of Current Literature". The Orthopedic Clinics of North America. Orthopedic Urgencies and Emergencies. 47 (3): 599–607. doi:10.1016/j.ocl.2016.03.005. PMID 27241382.
- ↑ Piazzini DB, Aprile I, Ferrara PE, Bertolini C, Tonali P, Maggi L, et al. (April 2007). "A systematic review of conservative treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome". Clinical Rehabilitation. 21 (4): 299–314. doi:10.1177/0269215507077294. PMID 17613571. S2CID 39628211.
- ↑ Povlsen B, Bashir M, Wong F (June 2014). "Long-term result and patient reported outcome of wrist splint treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome". Journal of Plastic Surgery and Hand Surgery. 48 (3): 175–178. doi:10.3109/2000656X.2013.837392. PMID 24032598. S2CID 25257778.
- ↑ Premoselli S, Sioli P, Grossi A, Cerri C (June 2006). "Neutral wrist splinting in carpal tunnel syndrome: a 3- and 6-months clinical and neurophysiologic follow-up evaluation of night-only splint therapy". Europa Medicophysica. 42 (2): 121–126. PMID 16767058.
- ↑ Michlovitz SL (October 2004). "Conservative interventions for carpal tunnel syndrome". The Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy. 34 (10): 589–600. doi:10.2519/jospt.2004.34.10.589. PMID 15552705.
- ↑ Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (November 16, 2017). Carpal tunnel syndrome: Wrist splints and hand exercises. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG).
- ↑ Marshall S, Tardif G, Ashworth N (April 2007). Marshall SC (ed.). "Local corticosteroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD001554. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001554.pub2. PMID 17443508.
- ↑ "Carpal Tunnel Steroid Injection". Medscape. Archived from the original on July 29, 2015. Retrieved July 9, 2015.
- ↑ "Carpal Tunnel Injection Information". EBSCO. Archived from the original on 2015-07-10 – via The Mount Sinai Hospital.
- ↑ Hui AC, Wong SM, Tang A, Mok V, Hung LK, Wong KS (April 2004). "Long-term outcome of carpal tunnel syndrome after conservative treatment". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 58 (4): 337–339. doi:10.1111/j.1368-5031.2004.00028.x. PMID 15161116. S2CID 12545439.
- ↑ "Open Carpal Tunnel Surgery for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome". WebMD. Archived from the original on July 7, 2015. Retrieved July 9, 2015.
- 1 2 Al Youha S, Lalonde DH (May 2014). "Update/Review: changing of use of local anesthesia in the hand". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. Global Open. 2 (5): e150. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000000095. PMC 4174079. PMID 25289343.
- 1 2 Nabhan A, Ishak B, Al-Khayat J, Steudel WI (April 2008). "Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release using a modified application technique of local anesthesia: safety and effectiveness". Journal of Brachial Plexus and Peripheral Nerve Injury. 3 (11): e35–e38. doi:10.1186/1749-7221-3-11. PMC 2383895. PMID 18439257.
- 1 2 "AAOS Informed Patient Tutorial – Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery". The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Archived from the original on July 19, 2015. Retrieved July 9, 2015.
- ↑ Lee JJ, Hwang SM, Jang JS, Lim SY, Heo DH, Cho YJ (November 2010). "Remifentanil-propofol sedation as an ambulatory anesthesia for carpal tunnel release". Journal of Korean Neurosurgical Society. 48 (5): 429–433. doi:10.3340/jkns.2010.48.5.429. PMC 3030083. PMID 21286480.
- ↑ Kouyoumdjian JA, Morita MP, Molina AF, Zanetta DM, Sato AK, Rocha CE, Fasanella CC (June 2003). "Long-term outcomes of symptomatic electrodiagnosed carpal tunnel syndrome". Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria. 61 (2A): 194–198. doi:10.1590/S0004-282X2003000200007. PMID 12806496.
- ↑ Bialosky JE, Bishop MD, Price DD, Robinson ME, George SZ (October 2009). "The mechanisms of manual therapy in the treatment of musculoskeletal pain: a comprehensive model". Manual Therapy. 14 (5): 531–538. doi:10.1016/j.math.2008.09.001. PMC 2775050. PMID 19027342.
- ↑ Wolny T, Saulicz E, Linek P, Shacklock M, Myśliwiec A (May 2017). "Efficacy of Manual Therapy Including Neurodynamic Techniques for the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 40 (4): 263–272. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2017.02.004. PMID 28395984. S2CID 4132062.
- ↑ Jiménez-Del-Barrio S, Cadellans-Arróniz A, Ceballos-Laita L, Estébanez-de-Miguel E, López-de-Celis C, Bueno-Gracia E, Pérez-Bellmunt A (February 2022). "The effectiveness of manual therapy on pain, physical function, and nerve conduction studies in carpal tunnel syndrome patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis". International Orthopaedics. 46 (2): 301–312. doi:10.1007/s00264-021-05272-2. PMC 8782801. PMID 34862562.
- ↑ Kim SD (August 2015). "Efficacy of tendon and nerve gliding exercises for carpal tunnel syndrome: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials". Journal of Physical Therapy Science. 27 (8): 2645–2648. doi:10.1589/jpts.27.2645. PMC 4563334. PMID 26357452.
- ↑ Choi GH, Wieland LS, Lee H, Sim H, Lee MS, Shin BC (December 2018). "Acupuncture and related interventions for the treatment of symptoms associated with carpal tunnel syndrome". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12 (12): CD011215. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011215.pub2. PMC 6361189. PMID 30521680.
- ↑ Mondelli M, Reale F, Padua R, Aprile I, Padua L (July 2001). "Clinical and neurophysiological outcome of surgery in extreme carpal tunnel syndrome". Clinical Neurophysiology. 112 (7): 1237–1242. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(01)00555-7. PMID 11516735. S2CID 43083160.
- ↑ Lozano Calderón SA, Paiva A, Ring D (March 2008). "Patient satisfaction after open carpal tunnel release correlates with depression". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 33 (3): 303–307. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2007.11.025. PMID 18343281.
- ↑ Ruch DS, Seal CN, Bliss MS, Smith BP (2002). "Carpal tunnel release: efficacy and recurrence rate after a limited incision release". Journal of the Southern Orthopaedic Association. 11 (3): 144–147. PMID 12539938.
- ↑ Karthik K, Nanda R, Stothard J (June 2012). "Recurrent carpal tunnel syndrome--analysis of the impact of patient personality in altering functional outcome following a vascularised hypothenar fat pad flap surgery". Journal of Hand and Microsurgery. 4 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1007/s12593-011-0051-x. PMC 3371121. PMID 23730080.
- ↑ Amadio PC (September 2009). "Interventions for recurrent/persistent carpal tunnel syndrome after carpal tunnel release". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 34 (7): 1320–1322. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2009.04.031. PMID 19576701.
- ↑ Boskovski MT, Thomson JG (September 2014). "Acroparesthesia and carpal tunnel syndrome: a historical perspective". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 39 (9): 1813–1821.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.05.024. PMID 25063390.
- ↑ Boskovski MT, Thomson JG (September 2014). "Carpal tunnel syndrome, syndrome of partial thenar atrophy, and W. Russell Brain: a historical perspective". The Journal of Hand Surgery. 39 (9): 1822–1829.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.05.025. PMID 25063392.
- ↑ Paget J (1854) Lectures on surgical pathology. Lindsay & Blakinston, Philadelphia
- ↑ Fuller DA (September 22, 2010). "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome". eMedicine. Archived from the original on July 27, 2010.
- ↑ Marie P, Foix C (1913). "Atrophie isolée de l'éminence thenar d'origine névritique: role du ligament annulaire antérieur du carpe dans la pathogénie de la lésion". Rev Neurol. 26: 647–649.
- ↑ Putnam JJ (1880). "A series of cases of paresthesia, mainly of the hand, or periodic recurrence, and possibly of vaso-motor origin". Archives of Medicine. 4: 147–162.
- ↑ Hunt JR (1914). "The neural atrophy of the muscle of the hand, without sensory disturbances". Rev Neurol Psych. 12: 137–148.
- ↑ Moersch FP (1938). "Median thenar neuritis". Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 13: 220.
- ↑ Phalen GS, Gardner WJ, La Londe AA (January 1950). "Neuropathy of the median nerve due to compression beneath the transverse carpal ligament". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume. 32A (1): 109–112. doi:10.2106/00004623-195032010-00011. PMID 15401727.
- ↑ Gilliatt RW, Wilson TG (September 1953). "A pneumatic-tourniquet test in the carpal-tunnel syndrome". Lancet. 265 (6786): 595–597. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(53)90327-4. PMID 13098011.
- ↑ Learmonth JR (1933). "The principle of decompression in the treatment of certain diseases of peripheral nerves". Surg Clin North Am. 13: 905–913.
- ↑ Amadio PC (February 1995). "The first carpal tunnel release?". Journal of Hand Surgery. 20 (1): 40–41. doi:10.1016/s0266-7681(05)80013-0. PMID 7759932. S2CID 534160.
- ↑ Chow JC (1989). "Endoscopic release of the carpal ligament for carpal tunnel syndrome: 22-month clinical result". Arthroscopy. 6 (4): 288–296. doi:10.1016/0749-8063(90)90058-l. PMID 2264896.
External links
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Fact Sheet (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke) Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine
- NHS website carpal-tunnel.net provides a free to use, validated, online self diagnosis questionnaire for CTS
- "Carpal Tunnel Syndrome". MedlinePlus. U.S. National Library of Medicine.