The Chan rearrangement is a chemical reaction that involves rearranging an acyloxy acetate (1) in the presence of a strong base to a 2-hydroxy-3-keto-ester (2).
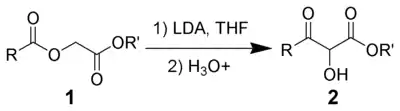
The Chan rearrangement
This procedure was employed in the Holton Taxol total synthesis.
Reaction mechanism
The methylene bridge in the reactant with adjacent carbonyl and acetyl substituents is acidic and can be deprotonated by strong non-nucleophilic bases such as lithium tetramethylpiperidide or lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) as in an aldol reaction. The thus formed enolate then gives a nucleophilic acyl substitution with the adjacent carbonyl of the acetyl group through a short lived intermediate oxirane. Acidic workup liberates the free hydroxyl group.

The mechanism of the Chan rearrangement
References
- ^ Rearrangement of α-acyloxyacetates into 2-hydroxy-3-ketoesters S. D. Lee, T. H. Chan, and K. S. Kwon Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 3399-3402. (doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)91030-5)
- ^ First total synthesis of taxol 1. Functionalization of the B ring Robert A. Holton, Carmen Somoza, Hyeong Baik Kim, Feng Liang, Ronald J. Biediger, P. Douglas Boatman, Mitsuru Shindo, Chase C. Smith, Soekchan Kim, et al.; J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116(4), 1597-1598. (doi:10.1021/ja00083a066)
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.