 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
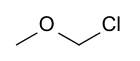
| Preferred IUPAC name
Chloro(methoxy)methane | |
| Other names
MOM-Cl, CMME, MCD, Chlorodimethyl ether, Chloromethoxymethane, Dimethylchloroether, Methylchloromethyl ether | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.165 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1239 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H5ClO | |
| Molar mass | 80.51 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Irritating and acrid |
| Density | 1.06 g/mL |
| Melting point | −103.5 °C (−154.3 °F; 169.7 K) |
| Boiling point | 55–57 °C (131–135 °F; 328–330 K) |
| reacts | |
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohol and diethylether |
| Vapor pressure | 192 mmHg (21°C)[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Carcinogen & Irritant |
| GHS labelling: | |
   | |
| Danger | |
| H225, H302, H312, H319, H332, H350 | |
| P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P301+P312, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P312, P322, P330, P337+P313, P363, P370+P378, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 0 °C (32 °F; 273 K) (open cup)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
OSHA-Regulated Carcinogen, no PEL[2] |
REL (Recommended) |
Carcinogenic[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[2] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Safety Data Sheet Archived |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Chloromethyl methyl ether (CMME) is a compound with formula CH3OCH2Cl. A colorless liquid, it is a chloroalkyl ether. It is used as an alkylating agent. In organic synthesis, it is used for introducing the methoxymethyl ether (MOM) protecting group,[3] and is thus often called MOM-Cl or MOM chloride. It also finds application as a chloromethylating agent in some variants of the Blanc chloromethylation.[4]
Preparation
A convenient synthesis of chloromethyl methyl ether in situ involves the reaction of dimethoxymethane and acetyl chloride in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst[5] This route affords a methyl acetate solution of chloromethyl methyl ether of high purity. A similar method, using a high-boiling acyl chloride, can be used to prepare pure, dimethoxymethane being the only contaminant.[6] In contrast, the classical procedure reported in Organic Syntheses employing formaldehyde, methanol, and hydrogen chloride yields material significantly contaminated with the dangerous bis(chloromethyl) ether and requires fractional distillation.[7]
Safety
The amount of time required to destroy residual chloromethyl methyl ether using various standard aqueous quench solutions (ammonium chloride solution, water, and sodium carbonate solution) has been measured. In all cases, a solution of chloromethyl methyl ether in toluene/methyl acetate was destroyed (to within detection limit) after vigorous stirring with the quench solution for 15 minutes.[5]
CMME is a known human carcinogen.[8] Chronic exposure can increase the incidence of respiratory cancers, including small cell carcinoma.[9] It is one of 13 chemicals regulated by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration despite not having an established permissible exposure limit.[10][11]
It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.[12] It listed in Schedule 1 Part 1 of Canada's Prohibition of Certain Toxic Substances Regulations.[13]
References
- ↑ Sigma-Aldrich
- 1 2 3 4 5 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0129". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, T. W. Greene and P. G. M. Green, 3rd Edition, pages 27-33. ISBN 0-471-16019-9
- ↑ Wuts, Peter G. M. (2001). "Chloromethyl Methyl Ether". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rc118. ISBN 0471936235.
- 1 2 Berliner, Martin A.; Belecki, Katherine (2007). "Synthesis of alpha-Halo Ethers from Symmetric Acetals and in situ Methoxymethylation of an Alcohol". Organic Syntheses. 84: 102. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.084.0102.
- ↑ R.J. Linderman, M. Jaber, B.D. Griedel, J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 6499-6500.
- ↑ C. S. Marvel and P. K. Porter (1929). "Monochloromethyl Ether". Organic Syntheses. 9: 58. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.009.0058.
- ↑ bis(Chloromethyl) Ether and Technical-Grade Chloromethyl Methyl Ether CAS Nos. 542-88-1 and 107-30-2 Report on carcinogens, eleventh edition
- ↑ "Chloromethyl methyl ether". U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Risk Information System. 7 March 2011. Accessed 3 May 2011.
- ↑ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- ↑ "40 C.F.R.: Appendix A to Part 355—The List of Extremely Hazardous Substances and Their Threshold Planning Quantities" (PDF) (July 1, 2008 ed.). Government Printing Office. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 25, 2012. Retrieved October 29, 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ http://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/PDF/SOR-2012-285.pdf
