 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
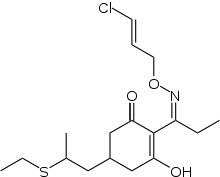
| IUPAC name
2-[(E)-N-[(E)-3-chloroprop-2-enoxy]-C-ethylcarbonimidoyl]-5-(2-ethylsulfanylpropyl)-3-hydroxycyclohex-2-en-1-one | |
| Other names
Centurion, Centurion Plus, Chevron RE 45601 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.128.422 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H26ClNO3S | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H317, H412 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P272, P273, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P321, P330, P333+P313, P363, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Clethodim is an organic compound. A member of the cyclohexanedione family of herbicides, it is used to control grasses, especially Lolium rigidum.[1][2] Although impure samples appear yellowish, the compound is colorless.
References
- ↑ Watson, Keith G. (2011). "Cyclohexane-1,3-dione Oxime Ether Grass-Specific Herbicides and the Discovery of Butroxydim". Australian Journal of Chemistry. 64 (4): 367. doi:10.1071/CH10366.
- ↑ Yu, Qin; Collavo, Alberto; Zheng, Ming-Qi; Owen, Mechelle; Sattin, Maurizio; Powles, Stephen B. (2007). "Diversity of Acetyl-Coenzyme a Carboxylase Mutations in Resistant Lolium Populations: Evaluation Using Clethodim". Plant Physiology. 145 (2): 547–558. doi:10.1104/pp.107.105262. PMC 2048730. PMID 17720757.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.