
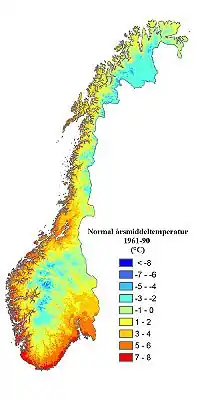
The climate of Norway is more temperate than could be expected for such high latitudes. This is mainly due to the North Atlantic Current with its extension, the Norwegian Current, raising the air temperature;[1] the prevailing southwesterlies bringing mild air onshore; and the general southwest–northeast orientation of the coast, which allows the westerlies to penetrate into the Arctic. The January average in Brønnøysund[2] is 15.8C (28.6F) higher than the January average in Nome, Alaska,[3] even though both towns are situated on the west coast of the continents at 65°N. In July the difference is reduced to 3.2C (5.8F). The January average of Yakutsk, in Siberia but slightly further south, is 42.3C (76.1F) lower than in Brønnøysund.[4]
Precipitation
Norway is among Europe's wettest countries, but with large variation in precipitation amount due to the terrain with mountain chains resulting in orographic precipitation but also creating rain shadows. In some regions, locations with vastly different precipitation amounts can be fairly close. Stryn (1661 mm) get 6 times as much precipitation as Skjåk 90 minutes drive away, Bergen has five times as much precipitation as Lærdal in the same region, and in the north Glomfjord (2141 mm) get 10 times as much precipitation as upper Saltdal (81 m) which is 68 km away as the crow flies. Some areas of Vestlandet and southern Nordland are among Europe's wettest, due to orographic lift, particularly where the westerlies are first intercepted by high mountains. This occurs slightly inland from the outer skerry guard. In the updated 1991-2020 normals, Gullfjellet in Bergen (345 m) has the highest annual precipitation with 4,067 mm (160.1 in). Annual precipitation can exceed 5,000 mm (196.9 in) in mountain areas near the coast. Lurøy at the Arctic Circle gets 3,066 mm (120.7 in) annually, a remarkable amount for a polar location. Precipitation is heaviest in late autumn and winter along the coast, while April to June is the driest. The innermost parts of the long fjords are somewhat drier: annual precipitation in Lærdal is 514 mm (20.2 in), and in the north only 338 mm (13.3 in) in Skibotn at the head of Lyngenfjord. The regions east of the mountain chain (including Oslo) have a more continental climate with generally less precipitation, and precipitation peaks in summer and early autumn, while winter and spring tend to be driest. A large area in the interior of Finnmark receive less than 450 mm (17.7 in) of precipitation annually. Some valleys surrounded by mountains get very scarce precipitation, and often need irrigation in summer. Upper Saltdal (81 m, Storjord) has the lowest annual average with only 211 mm (8.3 in), while in the south of Norway, Skjåk is driest with 295 mm (11.6 in). In Norway's High Arctic archipelagoes, Svalbard Airport has the lowest average annual precipitation with 217 mm (8.5 in), while Jan Mayen get more than double with 648 mm (25.5 in).
Monthly averages vary from 6 mm (0.24 in) in April in upper Saltdal and Skjåk to 509 mm (20.0 in) in December at Gullfjellet. Coastal areas from Lindesnes north to Vardø have more than 200 days per year with precipitation; however, this is with a very low threshold value (0.1 mm precipitation). The average annual number of days with at least 3 mm (0.12 in) precipitation is 77 in Blindern/Oslo, 96 in Kjevik/Kristiansand, 158 in Florida/Bergen, 93 in Værnes/Trondheim, and 109 in Tromsø.[5]
Temperature

The coast experiences milder winters than other areas at the same latitudes. The average temperature difference between the coldest month and the warmest is only 10–15 °C (18–27 °F) in coastal areas; some lighthouses have a yearly amplitude of just 10 °C (18 °F), such as Svinøy in Herøy with a coldest month of 3.7 °C (38.7 °F). The differences of inland areas are larger, with a maximum difference of 28 °C (50 °F) in Karasjok. Finnmarksvidda has the coldest winters in mainland Norway, but inland areas much further south can also experience severe cold. Røros has recorded −50 °C (−58 °F).
Bø i Vesterålen is the most northerly location in the world where all winter months have mean temperatures above 0 °C (32 °F). Spring is the season when the temperature differences between the southern and northern part of the country is largest; this is also the time of year when daytime and nighttime temperatures differ the most. Inland valleys and the innermost fjord areas have less wind and see the warmest summer days. The lowland near Oslo is warmest in summer with 24 July-hr average of 18 °C (64.4 °F) and average daily high up to 23 °C (73.4 °F). Inland areas reach their peak warmth around mid-July and coastal areas by the first half of August. Humidity is usually low in summer.
The North Atlantic Current splits in two over the northern part of the Norwegian Sea, one branch going east into the Barents Sea and the other going north along the west coast of Spitsbergen. This modifies the Arctic polar climate somewhat and results in open water throughout the year at higher latitudes than any other place in the Arctic. On the eastern coast of the Svalbard archipelago, the sea used to be frozen during most of the year, but the last years' warming (graph) have seen open waters noticeably longer.
The warmest temperature ever recorded in Norway is 35.6 °C (96.1 °F) in Nesbyen. The coldest temperature ever is −51.4 °C (−60.5 °F) in Karasjok. The warmest month on record was July 1901 in Oslo, with a mean 24-hour temperature of 22.7 °C (72.9 °F)), and the coldest month was February 1966 in Karasjok, with a mean of −27.1 °C (−16.8 °F). The warmest night recorded in Norway was July 29, 2019 at Sømna-Kvaløyfjellet (302 m) in Sømna near Brønnøysund with overnight low 26.1 °C (79.0 °F).[6] Atlantic lows bringing mild winds in winter further warmed by foehn can give warm temperatures in narrow fjords in winter: Sunndalsøra has recorded 19 °C (66 °F) in January and 18.9 °C (66.0 °F) in February.
Compared to coastal areas, inland valleys and the innermost fjord areas have larger diurnal temperature variations, especially in spring and summer.
Sunlight, time zones, and tides
Areas in Norway located north of the Arctic Circle have extreme darkness in winter, which increases with latitude. At Longyearbyen on the Svalbard islands in the extreme north, the upper part of the sun's disc is above the horizon from 9 April to 23 August, and winter darkness lasts from 27 October to 14 February. The winter darkness is not as dark on the northern mainland, as there is twilight for a few hours around noon.
The southern part of the country also experiences large seasonal variations in daylight; in Oslo, the sun rises at 03:54 and sets 22:54 at the summer solstice, but is only above the horizon from 09:18 to 15:12 at the winter solstice. The northern part of the country is located in the aurora borealis zone; the aurora is occasionally seen in the southern part of the country as well.
| Municipality | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kristiansand | 09:04–16:12 | 08:00–17:25 | 06:45–18:30 | 06:18–20:40 | 05:03–21:45 | 04:23–22:34 | 04:47–22:20 | 05:49–21:15 | 06:56–19:50 | 08:02–18:24 | 08:14–16:10 | 09:08–15:37 |
| Trondheim | 09:38–15:18 | 08:12–16:55 | 06:38–18:18 | 05:51–20:48 | 04:13–22:19 | 03:04–23:34 | 03:41–23:05 | 05:12–21:31 | 06:41–19:45 | 08:05–18:02 | 08:39–15:26 | 09:55–14:32 |
| Tromsø | 11:37–12:10 | 08:17–15:42 | 06:08–17:40 | 04:45–20:47 | 01:46–23:45 | Midnight sun | Midnight sun | 03:42–21:51 | 05:55–19:22 | 07:53–17:05 | 09:23–13:33 | Polar night |
Norway is on Central European Time, corresponding to the 15°E longitude. As the country is very elongated, this is at odds with the local daylight hours in the eastern and western parts. In Vardø, local daylight hours are 64 minutes earlier, and in Bergen, they are 39 minutes later. Thus, Finnmark gains early morning daylight but loses evening daylight, and Vestlandet loses early morning light but gains more evening daylight in this time zone. Daylight saving time (GMT + 2) is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October.
The difference between low tide and high tide is small on the southern coast and large in the north; ranging from on average 0.17 m in Mandal to about 0.30 m in Oslo and Stavanger, 0.90 m in Bergen, 1.80 m in Trondheim, Bodø and Hammerfest and as much as 2.17 m in Vadsø.
Examples
Table
| Location | Elevation | Mean temperature (°C) | Precip | Köppen climate zone | Snow >25 cm (days) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | Apr | Jul | Sep | Nov | Year | |||||
| Blindern/Oslo | 94 m | -2.3 | 6.2 | 17.7 | 12.2 | 2.2 | 7 | 836 mm | Cfb/Dfb | 30 |
| Oslo Airport, Gardermoen | 202 m | -4.4 | 4.6 | 16.5 | 10.6 | 0.5 | 5.4 | 866 mm | Dfb | 76 |
| Lillehammer | 240 m | -6.1 | 4 | 16.1 | 10.1 | -1.2 | 4.4 | 715 mm | Dfb | 108 |
| Tynset | 482 m | -9.1 | 1.5 | 13.7 | 7.5 | -3.7 | 1.4 | 439 mm | Dfc | - |
| Geilo | 772 m | -6.2 | 0.5 | 12.4 | 7.4 | -2.8 | 2.0 | 699 mm | Dfc | 67 |
| Sognefjellhytta in Lom (Sognefjell) | 1413 m | -8.6 | -4.3 | 7.4 | 2.9 | -5.5 | -2 | 948 mm | ET | 244 |
| Sarpsborg | 57 m | -1.4 | 5.8 | 17.4 | 12.2 | 3.1 | 7.2 | 887 mm | Cfb/Dfb | - |
| Notodden | 20 m | -4.5 | 5.6 | 17.1 | 11.2 | 0.6 | 5.7 | 741 mm | Dfb | - |
| Kjevik/Kristiansand | 12 m | 0.2 | 6 | 16.6 | 12.4 | 4 | 7.6 | 1381 mm | Cfb | 21 |
| Sola/Stavanger | 7 m | 2.6 | 6.9 | 15.3 | 13.2 | 5.7 | 8.4 | 1256 mm | Cfb | 0 |
| Bergen | 12 m | 2.6 | 7.2 | 15.6 | 12.6 | 5.3 | 8.4 | 2495 mm | Cfb | 3 |
| Lærdal | 24 m | -0.7 | 6.4 | 15.9 | 10.9 | 2.2 | 6.7 | 508 mm | Cfb/Dfb | 0 |
| Årø/Molde | 3 m | 1.1 | 5.7 | 15.4 | 11.4 | 3.9 | 7.1 | 1640 mm | Cfb | 54 |
| Røros Airport/Røros | 625 m | -8.5 | 0.2 | 12.4 | 6.9 | -4.1 | 1.1 | 525 mm | Dfc | 136 |
| Værnes/Trondheim | 12 m | -1.1 | 5.1 | 15.2 | 11 | 1.7 | 6.1 | 823 mm | Cfb/Dfb | 14 |
| Brønnøysund Airport/Brønnøysund | 5 m | 1.1 | 4.7 | 14.3 | 11.1 | 4 | 6.6 | 1510 mm | Cfb | 9 |
| Bodø Airport/Bodø | 11 m | -0.5 | 3.4 | 13.6 | 10.1 | 2.6 | 5.5 | 1117 mm | Cfb/Dfb | 23 |
| Bardufoss | 76 m | -9.7 | 0.6 | 13.7 | 7.4 | -4.7 | 1.3 | 703 mm | Dfc | 126 |
| Holt/Tromsø | 20 m | -2.1 | 1.7 | 12.4 | 8.3 | 1 | 3.9 | 958 mm | Cfc/Dfc | 160 |
| Kautokeino (Finnmarksvidda) | 307 m | -14.1 | -3 | 13.4 | 6 | -8.4 | -1.4 | 424 mm | Dfc | 135 |
| Alta Airport/Alta | 3 m | -6.8 | 0.4 | 13.7 | 8.2 | -2.8 | 2.3 | 438 mm | Dfc | - |
| Vardø | 10 m | -3.5 | 0.3 | 10 | 7.8 | -0.2 | 2.5 | 623 mm | Dfc | - |
| Jan Mayen | 10 m | -2.9 | -2.1 | 5.7 | 4.5 | -1 | 0.5 | 643 mm | ET (oceanic tundra) | - |
| Longyearbyen/Svalbard | 28 m | -10.9 | -8.8 | 7 | 2 | -6.4 | -3.9 | 217 mm | ET | 34 |
| If coldest winter month is between −3 °C (27 °F) and 0 °C (32 °F) the climate zone is named as Cfb/Dfb (or Cfc/Dfc) as Europe and US use different winter thresholds between C/D climates. Cfb=temperate oceanic/marine west coast; Dfb=humid continental; Cfc=subpolar oceanic (cold oceanic); Dfc=boreal/subarctic; ET=polar tundra or alpine tundra. Sep and Nov used to illustrates different climate zones better. Sognefjellhytta: Mountain lodge along Sognefjellsvegen west of Jotunheimen.Snow: Number of days/year with at least 25 cm (9.8 in) snow on the ground; 1971–2000 base period. Due to warming most lowland areas have less snow in recent years. Snow data from nearby: Rørvik for Brønnøysund, Karasjok for Kautokeino, Tromsø snow from 100 m ASL; Molde snow 1979 - 87. Some locations have Feb colder than Jan; some coastal stations have Aug warmer than Jul. | ||||||||||
As seen from the table, Norway's climate shows large variations, but all populated areas of the Norwegian mainland have temperate or subarctic climates (Köppen groups C and D). Svalbard and Jan Mayen have a polar climate (Köppen group E).

As a consequence of warming since 1990, summers are warmer and longer and winters are getting shorter and milder. With the new official 1991-2020 climate normal, many areas have seen their climate change to a new climate zone compared to 1961-90 normal. Oslo's climate has moved from Dfb to Cfb/Dfb, Lillehammer's from Dfc to Dfb, Kristiansand from Cfb/Dfb to Cfb, Molde and Brønnøysund from Cfc/Dfc to Cfb, Trondheim from Dfc to Cfb/Dfb, Bodø from Cfc/Dfc to Cfb/Dfb, Tromsø (Holt) from Dfc to Cfc/Dfc and Vardø from ET to Dfc. Snow cover has decreased in most populated areas due to winter warming; days/year with 25 cm snow cover in 1991-2020 is 26 days in Oslo (94 m), 2 days in Bergen, 8 days in Trondheim/Værnes and 144 days in Tromsø. The strongest warming has been observed on Svalbard. In addition to warming, precipitation has increased in most areas, especially in winter, increasing erosion and the risk of landslides.
Weatherboxes
| Climate data for Oslo - Blindern 1991-2020 (Köppen: Cfb/Dfb) (94 m, extremes since 1900) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 12.5 (54.5) |
13.8 (56.8) |
21.5 (70.7) |
25.4 (77.7) |
31.1 (88.0) |
33.7 (92.7) |
35.0 (95.0) |
33.6 (92.5) |
26.4 (79.5) |
21.0 (69.8) |
14.4 (57.9) |
12.6 (54.7) |
35.0 (95.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 0.1 (32.2) |
1.1 (34.0) |
5.3 (41.5) |
11.0 (51.8) |
16.7 (62.1) |
20.4 (68.7) |
22.7 (72.9) |
21.3 (70.3) |
16.4 (61.5) |
9.6 (49.3) |
4.4 (39.9) |
0.8 (33.4) |
10.8 (51.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −2.3 (27.9) |
−2 (28) |
1.4 (34.5) |
6.2 (43.2) |
11.4 (52.5) |
15.3 (59.5) |
17.7 (63.9) |
16.5 (61.7) |
12.1 (53.8) |
6.5 (43.7) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
7.0 (44.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −4.7 (23.5) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
2.1 (35.8) |
6.8 (44.2) |
10.8 (51.4) |
13.4 (56.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
8.6 (47.5) |
3.8 (38.8) |
-0.0 (32.0) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
3.6 (38.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −26.0 (−14.8) |
−24.9 (−12.8) |
−21.3 (−6.3) |
−14.9 (5.2) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
0.7 (33.3) |
3.7 (38.7) |
3.7 (38.7) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−8.0 (17.6) |
−16.0 (3.2) |
−20.8 (−5.4) |
−26.0 (−14.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 57.9 (2.28) |
45.6 (1.80) |
41.3 (1.63) |
48.4 (1.91) |
60.1 (2.37) |
79.7 (3.14) |
86.7 (3.41) |
102.8 (4.05) |
82.2 (3.24) |
93.4 (3.68) |
84.6 (3.33) |
53.6 (2.11) |
836.3 (32.95) |
| Average precipitation days | 9.8 | 7.3 | 8.5 | 8.1 | 8.5 | 10.1 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 9.4 | 10.9 | 10.7 | 9.2 | 114.3 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 45.1 | 77.6 | 146.5 | 182.0 | 248.0 | 230.3 | 244.1 | 203.8 | 150.1 | 94 | 50.9 | 40.0 | 1,712.4 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Source: Seklima[8] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Lillehammer 1991-2020 (Dfb) (240 m; extremes 1957 - 2018) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 10.4 (50.7) |
12.5 (54.5) |
16.0 (60.8) |
23.4 (74.1) |
28.5 (83.3) |
34.0 (93.2) |
32.4 (90.3) |
33.0 (91.4) |
26.4 (79.5) |
19.5 (67.1) |
16.2 (61.2) |
11.3 (52.3) |
34.0 (93.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −3.3 (26.1) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
3.7 (38.7) |
9.4 (48.9) |
15.4 (59.7) |
19.3 (66.7) |
21.7 (71.1) |
19.9 (67.8) |
14.9 (58.8) |
7.2 (45.0) |
1.2 (34.2) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
8.7 (47.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −6.1 (21.0) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
4 (39) |
9.4 (48.9) |
13.7 (56.7) |
16.1 (61.0) |
14.5 (58.1) |
10.1 (50.2) |
4.1 (39.4) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
4.4 (39.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −8.4 (16.9) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
0 (32) |
4.5 (40.1) |
8.8 (47.8) |
11.4 (52.5) |
10.1 (50.2) |
6.4 (43.5) |
1.4 (34.5) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
0.9 (33.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −31.0 (−23.8) |
−29.5 (−21.1) |
−24.1 (−11.4) |
−14.0 (6.8) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
0.5 (32.9) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−5.8 (21.6) |
−14.5 (5.9) |
−22.5 (−8.5) |
−31.0 (−23.8) |
−31.0 (−23.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 52 (2.0) |
35 (1.4) |
35 (1.4) |
35 (1.4) |
64 (2.5) |
70 (2.8) |
80 (3.1) |
96 (3.8) |
65 (2.6) |
69 (2.7) |
69 (2.7) |
47 (1.9) |
717 (28.3) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 28 | 68 | 126 | 168 | 212 | 242 | 237 | 195 | 136 | 83 | 44 | 18 | 1,557 |
| Source 1: [9] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: [10] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Fagernes in Nord-Aurdal, Valdres (Dfc) 1991-2020 (358 m, extremes 1982-2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 11.6 (52.9) |
12.2 (54.0) |
15.2 (59.4) |
21.5 (70.7) |
27.5 (81.5) |
31.3 (88.3) |
32.3 (90.1) |
32.3 (90.1) |
26.3 (79.3) |
21.7 (71.1) |
14.9 (58.8) |
11.3 (52.3) |
32.3 (90.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −3.9 (25.0) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
3.3 (37.9) |
8.8 (47.8) |
14.3 (57.7) |
18.6 (65.5) |
21.2 (70.2) |
19.4 (66.9) |
14.4 (57.9) |
7 (45) |
0.9 (33.6) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
8.2 (46.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −7.6 (18.3) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
2.8 (37.0) |
8.1 (46.6) |
12.8 (55.0) |
15.4 (59.7) |
13.8 (56.8) |
9.4 (48.9) |
3.4 (38.1) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
3.4 (38.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −11.1 (12.0) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
3 (37) |
7.8 (46.0) |
10.7 (51.3) |
9.7 (49.5) |
6 (43) |
1 (34) |
−4.1 (24.6) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −36.4 (−33.5) |
−34.4 (−29.9) |
−29.5 (−21.1) |
−18.2 (−0.8) |
−4.9 (23.2) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
1.5 (34.7) |
0 (32) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
−13.4 (7.9) |
−23 (−9) |
−27.7 (−17.9) |
−36.4 (−33.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 44.6 (1.76) |
26.9 (1.06) |
25.1 (0.99) |
27.2 (1.07) |
55.7 (2.19) |
67.2 (2.65) |
87.1 (3.43) |
88.6 (3.49) |
54.6 (2.15) |
52.1 (2.05) |
53.8 (2.12) |
39.9 (1.57) |
622.8 (24.53) |
| Source 1: Norwegian Meteorological Institute[11] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA-WMO averages 91-2020 Norway [12] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Kristiansand Airport Kjevik 1991–2020 (Cfb) (12 m, extremes 1946–2021, sunhrs 1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 13.9 (57.0) |
16.3 (61.3) |
21.9 (71.4) |
23.7 (74.7) |
26.1 (79.0) |
30.7 (87.3) |
31.2 (88.2) |
32.6 (90.7) |
27.5 (81.5) |
20.4 (68.7) |
17.1 (62.8) |
13.6 (56.5) |
32.6 (90.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 3.2 (37.8) |
3.7 (38.7) |
6.2 (43.2) |
10.5 (50.9) |
15.4 (59.7) |
18.9 (66.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
20.4 (68.7) |
16.5 (61.7) |
11.5 (52.7) |
6.9 (44.4) |
3.9 (39.0) |
11.5 (52.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.2 (32.4) |
0.2 (32.4) |
2.3 (36.1) |
6 (43) |
10.7 (51.3) |
14.4 (57.9) |
16.6 (61.9) |
15.9 (60.6) |
12.4 (54.3) |
7.9 (46.2) |
4 (39) |
0.9 (33.6) |
7.6 (45.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −2.8 (27.0) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
1.9 (35.4) |
5.8 (42.4) |
9.7 (49.5) |
12 (54) |
11.6 (52.9) |
8.8 (47.8) |
4.5 (40.1) |
1 (34) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
3.8 (39.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −28.2 (−18.8) |
−27.9 (−18.2) |
−21.7 (−7.1) |
−11.7 (10.9) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
0 (32) |
3.7 (38.7) |
1.9 (35.4) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−18.8 (−1.8) |
−22.9 (−9.2) |
−28.2 (−18.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 147.2 (5.80) |
98.2 (3.87) |
87.5 (3.44) |
64.8 (2.55) |
80.3 (3.16) |
85.5 (3.37) |
80.6 (3.17) |
120.7 (4.75) |
134.3 (5.29) |
169.7 (6.68) |
161.3 (6.35) |
151.4 (5.96) |
1,381.5 (54.39) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 15 | 12 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 12 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 142 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 45 | 84 | 121 | 187 | 228 | 274 | 269 | 231 | 150 | 93 | 57 | 39 | 1,778 |
| Source 1: Seklima[8] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA-WMO averages 91-2020 Norway [13] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Bergen 1991-2020 (Cfb) (12 m, Florida/met.office) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 16.9 (62.4) |
13.5 (56.3) |
19.8 (67.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
31.2 (88.2) |
30.3 (86.5) |
33.4 (92.1) |
31.0 (87.8) |
27.1 (80.8) |
23.8 (74.8) |
17.9 (64.2) |
13.9 (57.0) |
33.4 (92.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 4.7 (40.5) |
4.9 (40.8) |
6.9 (44.4) |
11.1 (52.0) |
15 (59) |
17.7 (63.9) |
19.6 (67.3) |
19.4 (66.9) |
16.1 (61.0) |
11.7 (53.1) |
7.6 (45.7) |
5.3 (41.5) |
11.7 (53.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.6 (36.7) |
2.3 (36.1) |
3.8 (38.8) |
7.2 (45.0) |
10.7 (51.3) |
13.6 (56.5) |
15.6 (60.1) |
15.4 (59.7) |
12.6 (54.7) |
8.6 (47.5) |
5.3 (41.5) |
3.1 (37.6) |
8.4 (47.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 0.6 (33.1) |
0.1 (32.2) |
1.3 (34.3) |
3.9 (39.0) |
6.9 (44.4) |
10.1 (50.2) |
12.4 (54.3) |
12.4 (54.3) |
9.9 (49.8) |
6.1 (43.0) |
3.1 (37.6) |
1 (34) |
5.6 (42.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −16.3 (2.7) |
−13.4 (7.9) |
−12.0 (10.4) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
−3.2 (26.2) |
0.8 (33.4) |
2.5 (36.5) |
2.5 (36.5) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
−10.0 (14.0) |
−13.0 (8.6) |
−16.3 (2.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 256.3 (10.09) |
209.3 (8.24) |
201.7 (7.94) |
140.6 (5.54) |
108.5 (4.27) |
132.3 (5.21) |
157.5 (6.20) |
207.9 (8.19) |
248.5 (9.78) |
268.1 (10.56) |
275.1 (10.83) |
289.8 (11.41) |
2,495.6 (98.26) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 19 | 18 | 18 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 19 | 200 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 78 | 76 | 73 | 72 | 72 | 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 79 | 78 | 79 | 76 |
| Source 1: Meteoclimat (temperatures)[14] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA-WMO averages 91-2020 Norway [15] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Sunndalsøra 1991-2020 (6 m, extremes 1983-2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 19 (66) |
18.9 (66.0) |
18.4 (65.1) |
22.2 (72.0) |
28.1 (82.6) |
31.2 (88.2) |
32.1 (89.8) |
31.7 (89.1) |
27.6 (81.7) |
25 (77) |
21.6 (70.9) |
18.3 (64.9) |
32.1 (89.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 5.1 (41.2) |
4.3 (39.7) |
6.9 (44.4) |
10.7 (51.3) |
14.7 (58.5) |
17.6 (63.7) |
19.9 (67.8) |
19.4 (66.9) |
16 (61) |
10.8 (51.4) |
7.5 (45.5) |
5.1 (41.2) |
11.5 (52.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.6 (34.9) |
1.1 (34.0) |
2.9 (37.2) |
6.6 (43.9) |
10.2 (50.4) |
13.1 (55.6) |
15.5 (59.9) |
15.2 (59.4) |
12 (54) |
7.3 (45.1) |
4.3 (39.7) |
1.8 (35.2) |
7.6 (45.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −1.2 (29.8) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
0.1 (32.2) |
3 (37) |
6.3 (43.3) |
9.4 (48.9) |
12 (54) |
11.9 (53.4) |
8.7 (47.7) |
4.4 (39.9) |
1.5 (34.7) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
4.4 (40.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −16.6 (2.1) |
−18.9 (−2.0) |
−16 (3) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
−1 (30) |
0.7 (33.3) |
4 (39) |
0.9 (33.6) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−7.3 (18.9) |
−11.4 (11.5) |
−16.7 (1.9) |
−18.9 (−2.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 92 (3.6) |
85 (3.3) |
79 (3.1) |
59 (2.3) |
58 (2.3) |
80 (3.1) |
73 (2.9) |
100 (3.9) |
95 (3.7) |
93 (3.7) |
89 (3.5) |
101 (4.0) |
1,004 (39.4) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 13 | 13 | 14 | 11 | 12 | 15 | 14 | 15 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 155 |
| Source 1: Norwegian Meteorological Institute[16] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Noaa WMO averages 91-2020 Norway [17] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Røros 1981-2010 (Dfc) (625 m, precipitation days 1961-90, extremes 1900 - 2018) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 10.4 (50.7) |
10.8 (51.4) |
14.5 (58.1) |
19.0 (66.2) |
26.7 (80.1) |
29.5 (85.1) |
30.7 (87.3) |
29.8 (85.6) |
25.7 (78.3) |
21.2 (70.2) |
11.8 (53.2) |
7.6 (45.7) |
30.7 (87.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −4.9 (23.2) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
0.3 (32.5) |
4.8 (40.6) |
11 (52) |
15.2 (59.4) |
18.1 (64.6) |
16.4 (61.5) |
11.4 (52.5) |
5.1 (41.2) |
−1 (30) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
5.7 (42.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −9.6 (14.7) |
−8.8 (16.2) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
0.3 (32.5) |
5.8 (42.4) |
9.9 (49.8) |
12.7 (54.9) |
11.4 (52.5) |
7.1 (44.8) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
1.0 (33.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −14.4 (6.1) |
−13.9 (7.0) |
−9.9 (14.2) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
0.6 (33.1) |
4.5 (40.1) |
7.2 (45.0) |
6.4 (43.5) |
2.6 (36.7) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
−8 (18) |
−14 (7) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −50.3 (−58.5) |
−43.5 (−46.3) |
−41.0 (−41.8) |
−32.3 (−26.1) |
−18.9 (−2.0) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
−4.9 (23.2) |
−11.3 (11.7) |
−28.4 (−19.1) |
−36.4 (−33.5) |
−44.0 (−47.2) |
−50.3 (−58.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 39.3 (1.55) |
32 (1.3) |
25.9 (1.02) |
24.7 (0.97) |
33.6 (1.32) |
58.6 (2.31) |
75.8 (2.98) |
74.3 (2.93) |
50.8 (2.00) |
37.8 (1.49) |
36.4 (1.43) |
35 (1.4) |
524.2 (20.7) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 9 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 113 |
| Source 1: Meteo climat stats | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: met.no/eklima | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Trondheim Airport Værnes 1991–2020 (Cfb/Dfb) (12 m, extremes 1946–2020, sunhrs 2016–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 13.7 (56.7) |
13.8 (56.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
23.3 (73.9) |
27.9 (82.2) |
34.3 (93.7) |
33.5 (92.3) |
31.3 (88.3) |
27.9 (82.2) |
22.1 (71.8) |
16.1 (61.0) |
13.1 (55.6) |
34.3 (93.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 1.9 (35.4) |
2.0 (35.6) |
4.6 (40.3) |
9.3 (48.7) |
13.8 (56.8) |
17.1 (62.8) |
19.8 (67.6) |
19.1 (66.4) |
15.0 (59.0) |
9.3 (48.7) |
4.7 (40.5) |
2.3 (36.1) |
9.9 (49.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1 (30) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
1 (34) |
5.1 (41.2) |
9.2 (48.6) |
12.6 (54.7) |
15.2 (59.4) |
14.6 (58.3) |
11 (52) |
5.8 (42.4) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
6.1 (43.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −4.1 (24.6) |
−4.1 (24.6) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
1.4 (34.5) |
5.3 (41.5) |
8.9 (48.0) |
11.4 (52.5) |
11.0 (51.8) |
7.8 (46.0) |
2.9 (37.2) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
2.8 (37.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −25.6 (−14.1) |
−25.5 (−13.9) |
−23.0 (−9.4) |
−13.9 (7.0) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
2.3 (36.1) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
−4.9 (23.2) |
−10.8 (12.6) |
−19.0 (−2.2) |
−23.5 (−10.3) |
−25.6 (−14.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 64.6 (2.54) |
63.9 (2.52) |
61.3 (2.41) |
42.1 (1.66) |
52.7 (2.07) |
76.1 (3.00) |
74.4 (2.93) |
82.8 (3.26) |
88.9 (3.50) |
77 (3.0) |
64.4 (2.54) |
75 (3.0) |
823.2 (32.43) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 13 | 13 | 13 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 11 | 14 | 149 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 34 | 71 | 124 | 205 | 236 | 234 | 229 | 167 | 130 | 116 | 46 | 16 | 1,608 |
| Source 1: Seklima [8] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOOA-WMO averages 91-2020 Norway [18] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Brønnøysund Airport 1991-2020 (Cfb) (9 m, precipitation 1961-90, extremes 1873-2020 includes earlier stations) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
10.9 (51.6) |
14.7 (58.5) |
21.1 (70.0) |
27.2 (81.0) |
30.3 (86.5) |
32.1 (89.8) |
30.1 (86.2) |
24.6 (76.3) |
20.3 (68.5) |
17.6 (63.7) |
12.2 (54.0) |
32.1 (89.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 2 (36) |
2 (36) |
4 (39) |
8 (46) |
12 (54) |
15 (59) |
18 (64) |
17 (63) |
14 (57) |
9 (48) |
6 (43) |
4 (39) |
9 (49) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.1 (34.0) |
0.4 (32.7) |
1.4 (34.5) |
4.7 (40.5) |
8.1 (46.6) |
11.2 (52.2) |
14.3 (57.7) |
14 (57) |
11.1 (52.0) |
6.8 (44.2) |
4 (39) |
1.9 (35.4) |
6.6 (43.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 0 (32) |
−1 (30) |
−1 (30) |
2 (36) |
5 (41) |
9 (48) |
12 (54) |
12 (54) |
9 (48) |
5 (41) |
2 (36) |
1 (34) |
5 (40) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −17.1 (1.2) |
−18.4 (−1.1) |
−15.5 (4.1) |
−10.1 (13.8) |
−5 (23) |
0 (32) |
1 (34) |
1.1 (34.0) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
−5.2 (22.6) |
−11.3 (11.7) |
−18.2 (−0.8) |
−18.4 (−1.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 138 (5.4) |
102 (4.0) |
114 (4.5) |
97 (3.8) |
66 (2.6) |
83 (3.3) |
123 (4.8) |
113 (4.4) |
180 (7.1) |
192 (7.6) |
145 (5.7) |
157 (6.2) |
1,510 (59.4) |
| Source 1: yr.no - Meteorologisk Institutt[19] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weatheronline.co.uk[20] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Røst 1991-2020 (Csc) (4 m, extremes 1957-2021) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 10.0 (50.0) |
10.4 (50.7) |
10.7 (51.3) |
14.7 (58.5) |
18.9 (66.0) |
22.5 (72.5) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.2 (72.0) |
17.9 (64.2) |
15.2 (59.4) |
13.5 (56.3) |
11.7 (53.1) |
23.1 (73.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 3.6 (38.5) |
3.1 (37.6) |
3.6 (38.5) |
5.6 (42.1) |
8.5 (47.3) |
11.1 (52.0) |
13.8 (56.8) |
13.9 (57.0) |
11.9 (53.4) |
8.6 (47.5) |
6.2 (43.2) |
4.8 (40.6) |
7.9 (46.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.0 (35.6) |
1.3 (34.3) |
1.8 (35.2) |
3.5 (38.3) |
6.4 (43.5) |
9.1 (48.4) |
11.6 (52.9) |
11.8 (53.2) |
9.9 (49.8) |
6.8 (44.2) |
4.5 (40.1) |
2.7 (36.9) |
6.0 (42.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −0.3 (31.5) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
1.7 (35.1) |
4.5 (40.1) |
7.4 (45.3) |
9.9 (49.8) |
10.2 (50.4) |
8.3 (46.9) |
5.1 (41.2) |
2.6 (36.7) |
1.0 (33.8) |
4.2 (39.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −12.4 (9.7) |
−12.1 (10.2) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
5.6 (42.1) |
3.9 (39.0) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
−6.1 (21.0) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−12.4 (9.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 126.0 (4.96) |
84.6 (3.33) |
68.0 (2.68) |
44.5 (1.75) |
42.8 (1.69) |
36.8 (1.45) |
48.8 (1.92) |
61.8 (2.43) |
75.9 (2.99) |
88.7 (3.49) |
98.3 (3.87) |
97.7 (3.85) |
873.9 (34.41) |
| Source: Norwegian Centre for Climate Services[21] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Tromsø 1991-2020 (Dfc, Cfc at Tromsø-Holt) (100 m, extremes 1920-2022) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 8.4 (47.1) |
8.2 (46.8) |
9.7 (49.5) |
17 (63) |
26.6 (79.9) |
29.9 (85.8) |
30.2 (86.4) |
28.4 (83.1) |
22.4 (72.3) |
18.6 (65.5) |
11.9 (53.4) |
9.7 (49.5) |
30.2 (86.4) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −1 (30) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
0.6 (33.1) |
4.1 (39.4) |
8.8 (47.8) |
13 (55) |
16.3 (61.3) |
15 (59) |
10.9 (51.6) |
5.2 (41.4) |
2.1 (35.8) |
0.3 (32.5) |
6.2 (43.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3 (27) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
1.2 (34.2) |
5.5 (41.9) |
9.4 (48.9) |
12.3 (54.1) |
11.3 (52.3) |
7.8 (46.0) |
3.1 (37.6) |
0.2 (32.4) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
3.4 (38.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −5.3 (22.5) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
2.4 (36.3) |
6.2 (43.2) |
9 (48) |
8.3 (46.9) |
5.3 (41.5) |
0.9 (33.6) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
0.8 (33.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −18.3 (−0.9) |
−18.4 (−1.1) |
−17.0 (1.4) |
−14.3 (6.3) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
0.7 (33.3) |
1.1 (34.0) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
−14.2 (6.4) |
−16.8 (1.8) |
−18.4 (−1.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 108.3 (4.26) |
96.7 (3.81) |
96.7 (3.81) |
71.1 (2.80) |
56.5 (2.22) |
58 (2.3) |
72.5 (2.85) |
88 (3.5) |
111.3 (4.38) |
127.4 (5.02) |
94.4 (3.72) |
109.7 (4.32) |
1,090.6 (42.99) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 15.4 | 12.9 | 11.4 | 11.6 | 11.1 | 10.3 | 12.8 | 12.6 | 14.9 | 17.7 | 13.5 | 15.6 | 160.1 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 3 | 36 | 111 | 171 | 215 | 239 | 226 | 164 | 96 | 55 | 8 | 0 | 1,324 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Source 1: Met Norway,[22][23] The Weather Network,[24] Meteostat.net[25] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather Atlas[26] (UV index) | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Lakselv Airport, Banak in Porsanger 1991-2020 (Dfc) (5 m, extremes 1979-2022) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 9.4 (48.9) |
9.4 (48.9) |
13 (55) |
15.9 (60.6) |
25.7 (78.3) |
32.5 (90.5) |
34.3 (93.7) |
32.8 (91.0) |
25 (77) |
15.1 (59.2) |
11.9 (53.4) |
10.1 (50.2) |
34.3 (93.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −4.2 (24.4) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
3.6 (38.5) |
9 (48) |
13.7 (56.7) |
17.4 (63.3) |
15.8 (60.4) |
11.4 (52.5) |
4.5 (40.1) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
5.3 (41.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −7.9 (17.8) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
0.1 (32.2) |
5.3 (41.5) |
9.6 (49.3) |
12.9 (55.2) |
11.6 (52.9) |
7.8 (46.0) |
1.9 (35.4) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
1.7 (35.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −11.8 (10.8) |
−11.8 (10.8) |
−8.5 (16.7) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
1.6 (34.9) |
6.1 (43.0) |
9.2 (48.6) |
7.8 (46.0) |
4.5 (40.1) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
−1.9 (28.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −33.6 (−28.5) |
−33 (−27) |
−29.9 (−21.8) |
−24.7 (−12.5) |
−11.4 (11.5) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
−21.2 (−6.2) |
−26.4 (−15.5) |
−30 (−22) |
−33.6 (−28.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 24.7 (0.97) |
18.5 (0.73) |
19.9 (0.78) |
17.1 (0.67) |
25.5 (1.00) |
42.5 (1.67) |
57.2 (2.25) |
54.3 (2.14) |
37.7 (1.48) |
33.4 (1.31) |
23.6 (0.93) |
27.5 (1.08) |
381.9 (15.01) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 12 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 12 | 14 | 166 |
| Source 1: yr.no/Norwegian Meteorological Institute[27] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA WMO averages 91-2020 Norway [28] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Svalbard Airport Longyearbyen 1991-2020 (Et) (28 m, extremes 1975-2022) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 7.7 (45.9) |
7 (45) |
6.3 (43.3) |
7.5 (45.5) |
12.9 (55.2) |
15.7 (60.3) |
21.7 (71.1) |
18.1 (64.6) |
15.2 (59.4) |
10.1 (50.2) |
9.2 (48.6) |
8.7 (47.7) |
21.7 (71.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −7.7 (18.1) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
−8.8 (16.2) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
5.6 (42.1) |
9.4 (48.9) |
8.2 (46.8) |
4 (39) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
−6.1 (21.0) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −10.9 (12.4) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
−12 (10) |
−8.8 (16.2) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
3.6 (38.5) |
7 (45) |
6 (43) |
2 (36) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
−3.9 (25.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −14.2 (6.4) |
−15 (5) |
−15.5 (4.1) |
−12.1 (10.2) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
2.2 (36.0) |
5.4 (41.7) |
4.4 (39.9) |
0.3 (32.5) |
−6.1 (21.0) |
−9.3 (15.3) |
−12.2 (10.0) |
−6.3 (20.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −38.8 (−37.8) |
−43.7 (−46.7) |
−46.3 (−51.3) |
−39.1 (−38.4) |
−21.7 (−7.1) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
−12.6 (9.3) |
−20.8 (−5.4) |
−33.2 (−27.8) |
−35.6 (−32.1) |
−46.3 (−51.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 21 (0.8) |
17 (0.7) |
16 (0.6) |
9 (0.4) |
8 (0.3) |
8 (0.3) |
20 (0.8) |
23 (0.9) |
26 (1.0) |
18 (0.7) |
22 (0.9) |
24 (0.9) |
212 (8.3) |
| Source 1: Norwegian Meteorological Institute[29] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Meteostat[30] | |||||||||||||
Climate change

All regions and seasons of Norway are expected to become warmer and wetter due to climate change.
On a per-capita basis, Norway is the world's largest producer, and exporter, of oil and natural gas outside the Middle East.[31] In 2016, 56 new licenses for oil exploration near the Lofoten Islands were issued. However, 98% of Norway's electricity demand is supplied by renewable sources, mostly from hydroelectric power, generated using Norway's extensive freshwater reserves.[32] Emissions are also generated through transportation, although Norway is a world leader in electric vehicles.
Warmer temperatures in Norway are causing permafrost and glaciers to retreat, and leading to shifts in precipitation patterns. Climate change is particularly impacting Norway's Arctic region. Biodiversity and forested areas are experiencing shifts due to the phenomenon, with significant implications for the agriculture and economy of the country. Indigenous Sámi people's practices are being impacted by climate change.
Norway's government have introduced several social and economic policies towards climate change mitigation, including through carbon capture and storage. Norway wants to achieve carbon neutrality by 2030, partly by investing in projects with emissions reduction abroad. It wants to achieve zero emission in the country by 2050.[33] In 2020, Norway pledged to achieve a 50% - 55% reduction in domestic emissions from the level of 1990 by 2030.[34]See also
Notes
- ↑ Measurements from fifteenth of month. Daylight saving in effect from last Sunday in March to last Sunday in October. In Tromsø, the sun is below the horizon until 15 January, but is blocked by mountains until 21 January.
References
- ↑ "News - NORKLIMA". www.forskningsradet.no. Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 16 April 2012.
- ↑ "Bronnoysund Norway, Weather History and Climate Data". www.worldclimate.com.
- ↑ "Nome, Alaska (U.S.A.) Weather History and Climate Data". www.worldclimate.com.
- ↑ "JAKUTSK USSR, Weather History and Climate Data". www.worldclimate.com.
- ↑ Lippestad, Heidi, ed. (29 December 2004). "Nedbør" [Precipitation]. Norwegian Meteorological Institute (in Norwegian). Archived from the original on 28 September 2006. Retrieved 31 December 2019.
- ↑ "Sømna målte varmeste tropenatt noen gang i Norge". 28 July 2019.
- ↑ Almanakk for Norge; University of Oslo, 2011.
- 1 2 3 seklima.met.no
- ↑ "yr.no statistics (mean, precipitation)". Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- ↑ "Meteo climat stats (avg high and low)". Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- ↑ "Eklima/met.no". Archived from the original on 2021-01-28. Retrieved 2022-07-02.
- ↑ "NOAA-WMO normals Norway 1991-2020".
- ↑ "NOAA WMO normals Norway 1991-2020".
- ↑ Solenn Nadal des Moutiers en Retz (7 November 2009). "Météo climat stats | Moyennes 1981/2010 / Données Météorologiques Gratuites". Meteo-climat-bzh.dyndns.org. Retrieved 26 February 2022.
- ↑ "NOAA WMO normals Norway 1991-2020".
- ↑ "Meteorologisk institutt". Norwegian Meteorological Institute (in English and Norwegian). Archived from the original on Jul 5, 2023. Retrieved 25 July 2023.
- ↑ "NOAA WMO normals Norway 1991-2020".
- ↑ "NOAA WMO normals Norway 1991-2020".
- ↑ "Brønnøysund Airport statistics". yr.no. Retrieved 28 March 2021.
- ↑ "Weatheronline climate robot (average high and low)".
- ↑ "Observations and weather statistics". Norwegian Meteorological Institute. Retrieved 2021-07-05.
- ↑ Norwegian Meteorological Institute's eklima site
- ↑ "Tromsø (Troms)". June 2013. Archived from the original on 2018-12-14. Retrieved 2022-07-02.
- ↑ "Climate Statistics for Tromsø, Norway (1991-2020)". November 2011.
- ↑ "Tromso - Weather History & Climate". Meteostat. Retrieved 6 February 2022.
- ↑ "Tromsø, Norway - Monthly weather forecast and Climate data". Weather Atlas. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ "Last 13 months". www.yr.no. Norwegian Meteorological Institute.
- ↑ "NOAA WMO normals Norway 1991-2020".
- ↑ "EKlima". Archived from the original on 28 January 2021. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ↑ "Meteostat.net". Retrieved 2022-02-06.
- ↑ "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". www.CIA.gov. Archived from the original on 16 June 2013. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ↑ "Vannkraftpotensialet". nve.no. Archived from the original on 18 January 2017. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ↑ "Norway: Carbon-neutral as soon as 2030". Nordic Energy Research. Retrieved 11 May 2020.
- ↑ "Norway steps up 2030 climate goal to at least 50 % towards 55 %". Government.no. 7 February 2020. Retrieved 11 May 2020.
