Innlandet County
Innlandet fylke | |
|---|---|
 | |
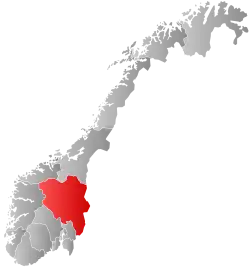 Innlandet within Norway | |
 Innlandet County  Innlandet County | |
| Coordinates: 61°30′00″N 10°40′00″E / 61.5°N 10.666667°E | |
| Country | Norway |
| County | Innlandet |
| District | Eastern Norway |
| Established | 1 Jan 2020 |
| • Preceded by | Oppland and Hedmark |
| Administrative centre | Hamar |
| Government | |
| • Body | Innlandet County Municipality |
| • Governor (2019) | Knut Storberget (Ap) |
| • County mayor (2023) | Thomas Breen (Ap) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 52,072 km2 (20,105 sq mi) |
| • Land | 49,391 km2 (19,070 sq mi) |
| • Water | 2,681 km2 (1,035 sq mi) 5.1% |
| • Rank | #1 in Norway |
| Highest elevation | 2,469 m (8,100 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 120 m (390 ft) |
| Population (2021) | |
| • Total | 370,603 |
| • Rank | #7 in Norway |
| • Density | 7.5/km2 (19/sq mi) |
| • Change (10 years) | |
| Demonym | Innlending[1] |
| Official language | |
| • Norwegian form | Neutral |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | NO-34[3] |
| Website | Official website |
Innlandet is a county in Norway.[4] It was created on 1 January 2020[5] with the merger of the old counties of Oppland and Hedmark (the municipalities of Jevnaker and Lunner were transferred to the neighboring county of Viken on the same date). The new county has an area of 52,113 square kilometres (20,121 sq mi), making it the largest county in Norway.[6]
The region was known as Opplandene or Opplanda since the middle ages. Historically part of Akershus, Oplandene County existed from 1757 to 1781, when it was divided into Christian County and Hedemarken County, also known as Western and Eastern Oplandene. In 1919 the two counties were renamed Oppland and Hedmark, and in 2020 they were again merged under the name Innlandet. The latter name is a newly constructed name with no historical basis that translates to "The Inland". The county covers approximately 17% of the total area of the mainland area of Norway. It stretches from the Viken county and the Oslo region in the south to Trøndelag county in the north. In the northwest, the county borders Møre og Romsdal and the Vestland county in the west. To the east the county borders the Swedish counties of Värmland and Dalarna.
The northern and western areas of the county are dominated by the mountainous areas Rondane, Dovrefjell and Jotunheimen. The Galdhøpiggen mountain is located within the Innlandet part of Jotunheimen and at 2,469 m (8,100 ft) it is the tallest mountain in Norway. The eastern and southern areas of the county are mainly made up of forests and agricultural land. Mjøsa, Norway's largest lake, is located in the southern end of Innlandet, and Glomma the longest river in Norway also flows through the county.
Agriculture and forestry are two important industries in the county with approximately 20% of Norway's agricultural production[7] and about 40% of timber.[8]
The 1994 Winter Olympics were held at Lillehammer, the second-largest city in Innlandet county.
Municipalities
Innlandet County has a total of 46 municipalities:[9][10]
| No. | Municipality No. | Name | Created | Former Municipality No. | Former County |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3428 | Alvdal | Jan 1, 2020 | 0438 Alvdal | Hedmark |
| 2 | 3431 | Dovre | Jan 1, 2020 | 0511 Dovre | Oppland |
| 3 | 3416 | Eidskog | Jan 1, 2020 | 0420 Eidskog | Hedmark |
| 4 | 3420 | Elverum | Jan 1, 2020 | 0427 Elverum | Hedmark |
| 5 | 3425 | Engerdal | Jan 1, 2020 | 0434 Engerdal | Hedmark |
| 6 | 3450 | Etnedal | Jan 1, 2020 | 0541 Etnedal | Oppland |
| 7 | 3429 | Folldal | Jan 1, 2020 | 0439 Folldal | Hedmark |
| 8 | 3441 | Gausdal | Jan 1, 2020 | 0522 Gausdal | Oppland |
| 9 | 3407 | Gjøvik | Jan 1, 2020 | 0502 Gjøvik | Oppland |
| 10 | 3446 | Gran | Jan 1, 2020 | 0534 Gran | Oppland |
| 11 | 3417 | Grue | Jan 1, 2020 | 0423 Grue | Hedmark |
| 12 | 3403 | Hamar | Jan 1, 2020 | 0403 Hamar | Hedmark |
| 13 | 3401 | Kongsvinger | Jan 1, 2020 | 0402 Kongsvinger | Hedmark |
| 14 | 3432 | Lesja | Jan 1, 2020 | 0512 Lesja | Oppland |
| 15 | 3405 | Lillehammer | Jan 1, 2020 | 0501 Lillehammer | Oppland |
| 16 | 3434 | Lom | Jan 1, 2020 | 0514 Lom | Oppland |
| 17 | 3412 | Løten | Jan 1, 2020 | 0415 Løten | Hedmark |
| 18 | 3451 | Nord-Aurdal | Jan 1, 2020 | 0542 Nord-Aurdal | Oppland |
| 19 | 3436 | Nord-Fron | Jan 1, 2020 | 0516 Nord-Fron | Oppland |
| 20 | 3414 | Nord-Odal | Jan 1, 2020 | 0418 Nord-Odal | Hedmark |
| 21 | 3448 | Nordre Land | Jan 1, 2020 | 0538 Nordre Land | Oppland |
| 22 | 3430 | Os | Jan 1, 2020 | 0441 Os | Hedmark |
| 23 | 3424 | Rendalen | Jan 1, 2020 | 0432 Rendalen | Hedmark |
| 24 | 3439 | Ringebu | Jan 1, 2020 | 0520 Ringebu | Oppland |
| 25 | 3411 | Ringsaker | Jan 1, 2020 | 0412 Ringsaker | Hedmark |
| 26 | 3437 | Sel | Jan 1, 2020 | 0517 Sel | Oppland |
| 27 | 3433 | Skjåk | Jan 1, 2020 | 0513 Skjåk | Oppland |
| 28 | 3413 | Stange | Jan 1, 2020 | 0417 Stange | Hedmark |
| 29 | 3423 | Stor-Elvdal | Jan 1, 2020 | 0430 Stor-Elvdal | Hedmark |
| 30 | 3447 | Søndre Land | Jan 1, 2020 | 0536 Søndre Land | Oppland |
| 31 | 3449 | Sør-Aurdal | Jan 1, 2020 | 0540 Sør-Aurdal | Oppland |
| 32 | 3438 | Sør-Fron | Jan 1, 2020 | 0519 Sør-Fron | Oppland |
| 33 | 3415 | Sør-Odal | Jan 1, 2020 | 0419 Sør-Odal | Hedmark |
| 34 | 3426 | Tolga | Jan 1, 2020 | 0436 Tolga | Hedmark |
| 35 | 3421 | Trysil | Jan 1, 2020 | 0428 Trysil | Hedmark |
| 36 | 3427 | Tynset | Jan 1, 2020 | 0437 Tynset | Hedmark |
| 37 | 3454 | Vang | Jan 1, 2020 | 0545 Vang | Oppland |
| 38 | 3452 | Vestre Slidre | Jan 1, 2020 | 0543 Vestre Slidre | Oppland |
| 39 | 3443 | Vestre Toten | Jan 1, 2020 | 0529 Vestre Toten | Oppland |
| 40 | 3435 | Vågå | Jan 1, 2020 | 0515 Vågå | Oppland |
| 41 | 3419 | Våler | Jan 1, 2020 | 0426 Våler | Hedmark |
| 42 | 3442 | Østre Toten | Jan 1, 2020 | 0528 Østre Toten | Oppland |
| 43 | 3440 | Øyer | Jan 1, 2020 | 0521 Øyer | Oppland |
| 44 | 3453 | Øystre Slidre | Jan 1, 2020 | 0544 Øystre Slidre | Oppland |
| 45 | 3422 | Åmot | Jan 1, 2020 | 0429 Åmot | Hedmark |
| 46 | 3418 | Åsnes | Jan 1, 2020 | 0425 Åsnes | Hedmark |
Settlements



Most of the settlements in Innlandet are fairly small. As of 1 January 2020 Hamar is the largest with a population of 28,434.[11] Lillehammer, Gjøvik, Elverum, Kongsvinger and Brumunddal are the only other cities with populations above 10,000. However, Raufoss, Moelv, Vinstra, Fagernes and Otta also have city status.
Churches and parishes
The whole county belongs to the Diocese of Hamar (plus two municipalities in neighboring Viken County.
Geography
Mountains
- Galdhøpiggen 2,469 m (8,100 ft)
- Blåkampen 1,662 m (5,453 ft)
- Høgvagltindene 1,576 m (5,171 ft)
- Mjellknapp 1,678 m (5,505 ft)
- Røykeskardhøi 1,808 m (5,932 ft)
- Søndre Svarthåmåren 1,854 m (6,083 ft)
- Søndre Kjølhaugen 1,768 m (5,801 ft)
- Sørhellhøi 1,951 m (6,401 ft)
- Sørhellhøin
- Søverhøi
- Steinahøfjellet 1,711 m (5,614 ft)
- Svånåtindene, mountain range
Government
A county (fylke) is the chief local administrative area in Norway. The whole country is divided into 11 counties. A county is also an election area, with popular votes taking place every 4 years. In Innlandet, the government of the county is the Innlandet County Municipality. It includes 57 members who are elected to form a county council (Fylkesting). Heading the Fylkesting is the county mayor (fylkesordfører). Since 2020, the Innlandet County Municipality has been led by Even Aleksander Hagen, the county mayor. The county also has a County Governor (Statsforvalteren) who is the representative of the King and Government of Norway. Knut Storberget is the current County Governor of Innlandet. The offices for the county governor are located in Lillehammer.[12][6]
See also
- Districts in Innlandet
- Former municipalities in Innlandet
- Lakes in Innlandet
- Rivers in Innlandet
- Towns and Cities in Innlandet
- Valleys in Innlandet
- Villages in Innlandet
References
- ↑ "Navn på steder og personer: Innbyggjarnamn" (in Norwegian). Språkrådet.
- ↑ "Forskrift om målvedtak i kommunar og fylkeskommunar" (in Norwegian). Lovdata.no.
- ↑ Bolstad, Erik; Thorsnæs, Geir, eds. (2023-01-26). "Kommunenummer". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget.
- ↑ "Arealstatistikk for Norge". Kartverket (in Norwegian Bokmål). 2013-03-08. Retrieved 2020-01-02.
- ↑ moderniseringsdepartementet, Kommunal- og (7 July 2017). "Regionreform". Regjeringen.no. Archived from the original on 23 March 2018. Retrieved 28 April 2018.
- 1 2 Mæhlum, Lars, ed. (2019-04-09). "Innlandet". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget. Retrieved 2019-05-20.
- ↑ Bondelaget. "Landbruket i Innlandet skaper verdier" (PDF). Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- ↑ Hobbelstad, Kåre. "Ressurssituasjonen i Hedmark of Oppland" (PDF). Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- ↑ List of Norwegian municipality numbers (Norwegian)
- ↑ List of municipality numbers of Norway (English)
- ↑ "Population and land area in urban settlements". Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- ↑ Berg, Ole T., ed. (2021-03-05). "fylke". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget. Retrieved 2022-02-05.

