Vestland County
Vestland fylke | |
|---|---|
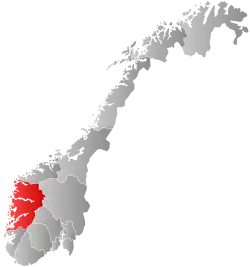 Vestland within Norway | |
| Coordinates: 60°55′30″N 6°26′42″E / 60.92500°N 6.44500°E | |
| Country | Norway |
| County | Vestland |
| District | Western Norway |
| Established | 1 Jan 2020 |
| • Preceded by | Hordaland and Sogn og Fjordane counties |
| Administrative centre | Bergen |
| Government | |
| • Body | Vestland County Municipality |
| • Governor (2023) | Liv Signe Navarsete (Sp) |
| • County mayor | Jon Askeland (Sp) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 33,871 km2 (13,078 sq mi) |
| • Land | 31,969 km2 (12,343 sq mi) |
| • Water | 1,902 km2 (734 sq mi) 5.6% |
| • Rank | #5 in Norway |
| Population (2021) | |
| • Total | 638,821 |
| • Rank | #3 in Norway |
| • Density | 20/km2 (50/sq mi) |
| • Change (10 years) | |
| Demonym | Vestlending[1] |
| Official language | |
| • Norwegian form | Nynorsk |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | NO-46[3] |
| Website | Official website |
Vestland is a county in Norway established on 1 January 2020.[4][5] The county is located in Western Norway and it is centred around the city of Bergen, Norway's second largest city. The administrative centre of the county is the city of Bergen, where the executive and political leadership is based, but the County Governor is based in Hermansverk. The county is one of two counties in Norway that have Nynorsk as their official written language form (the others are neutral as to which form people use).[6]
Vestland was created in 2020 when the former counties of Hordaland and Sogn og Fjordane (with the exception of Hornindal municipality, which became part of Volda municipality in Møre og Romsdal county) were merged.[7]
History
Vestland county is a newly created county, but it has been inhabited for millennia. The area was made up of many petty kingdoms under the Gulating during the Middle Ages. The northern part was the known as Firdafylke (now the Fjordane region; Nordfjord-Sunnfjord), the central are was known as Sygnafylke (now the Sogn region), and the southern part was known as Hordafylke.
In the early 16th century, Norway was divided into four len. The Bergenhus len was headquartered in Bergen and encompassed much of western and northern Norway including Firdafylke, Sygnafylke, Hordafylke, and Sunnmørafylke (in the present day Møre og Romsdal county). The new Bergenhus len was administered from the Bergenhus Fortress in the city of Bergen.
In 1662, the lens were replaced by amts. On 19 February 1662, a royal decree changed the name to Bergenhus amt. The new Bergenhus amt originally consisted of the present-day areas of Vestland and the Sunnmøre region of Møre og Romsdal, plus the far northern Nordlandene amt was subordinate to Bergenhus amt. The Sunnmøre region was transferred to Romsdalen amt in 1689 and the Nordlandene amt was separated around that time as well.
In 1763, the amt was divided into northern and southern parts: Nordre Bergenhus amt and Søndre Bergenhus amt. When the amt was split, the present day municipality of Gulen was split with the southern part ending up in Søndre Bergenhus amt. In 1773, the border was re-drawn so that all of Gulen was located in the northern part.
On 1 January 1919, Nordre Bergenhus amt was renamed Sogn og Fjordane fylke and Søndre Bergenhus amt was renamed Hordaland fylke during a period of time when many location names in Norway were changed.[8]
The city of Bergen was removed from the Bergenhus amt in 1831 and it was classified as a city-county (byamt) from 1831 to 1972. During that time in 1915, the municipality of Årstad was annexed into Bergen. In 1972, the neighbouring municipalities of Arna, Fana, Laksevåg and Åsane were annexed into the city of Bergen. Also at that same time, the city of Bergen lost its county status, and became a part of Hordaland county once again.
On 1 January 2020, Hordaland and Sogn og Fjordane counties were merged back together once again, forming Vestland county.
Geography
Vestland is located on the western coast of Norway. It is split up by several long, deep fjords including the Nordfjorden, Sognefjorden, and Hardangerfjorden, some of Norway's most notable fjords and great tourist attractions. About half of the Hardangervidda National Park is in the county. It also includes the Jostedal, Folgefonna, and Hardangerjøkulen glaciers. The county also includes many well-known waterfalls, such as Vøringsfossen, Brudesløret[9][10] and Stykkjedalsfossen. Ramnefjellsfossen (previously called Utigardfossen) is the tallest in Norway and third tallest in the world and Vettisfossen is one of Norway's highest waterfalls with a vertical drop of 275 m (902 ft). Both are located in the Jotunheim mountains.
Outside of the Bergen metropolitan area, the county is mostly a rural area with a scattered population. Cruise ships visit Vestland all summer because of the unique vistas of high mountains and deep blue fjords. The famous Nærøyfjord is located in the south of the county. This is a UNESCO listed fjord area. There are several archipelagos, including Øygarden, Austevoll, Bulandet, Bremangerlandet, and Kinn. The westernmost point in Norway proper is Holmebåen in Solund municipality. The island of Unst, part of Shetland Islands is around 300 km (190 mi) west of Holmebåen.
The terrain changes quite rapidly with mostly smaller mountains on the coastline, gradually increasing to mountains reaching more than 2,000 m (6,600 ft). Because of the steep rise in elevation and fjords cutting through the terrain, the amount of precipitation is very high. Low pressure systems come in from the west and meet the mountains (a phenomenon known as orographic lifting) and cause rain and snowfall.
Government
A county (fylke) is the chief local administrative area in Norway. The whole country is divided into 11 counties. A county is also an election area, with popular votes taking place every 4 years. In Vestland, the government of the county is the Vestland County Municipality. It includes 65 members who are elected to form a county council (Fylkesting). Heading the Fylkesting is the county mayor (fylkesordførar). Since 2020, the Vestland County Municipality has been led by Jon Askeland, the county mayor.[11][12][13]
The county also has a County Governor (fylkesmann) who is the representative of the King and Government of Norway. Lars Sponheim is the current County Governor of Vestland and this office is based in Hermansverk.[13]
The municipalities in Vestland are divided among several district courts (tingrett): Nordhordland District Court, Sunnhordland District Court, Bergen District Court, Hardanger District Court, and Sogn og Fjordane District Court. All of these courts are subordinate to the Gulating Court of Appeal district based in Bergen.[13]
Media gallery
 Myklebustdalen valley east of Byrkjelo
Myklebustdalen valley east of Byrkjelo The village of Hoddevik on the Stad peninsula in Selje
The village of Hoddevik on the Stad peninsula in Selje Some old houses in Lærdalsøyri, Lærdal
Some old houses in Lærdalsøyri, Lærdal View from Aurland
View from Aurland Finse is the highest point of the Norwegian Railway System, located at 1,222 m (4,009 ft) above sea level
Finse is the highest point of the Norwegian Railway System, located at 1,222 m (4,009 ft) above sea level
Municipalities
Vestland County has a total of 43 municipalities:[14]
| Municipal Number | Name | Adm. Centre | Location in the county | Established | Old Municipal No. (before 2020) | Former County (before 2020) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4601 | Bergen |  | 1 Jan 1972 | 1201 Bergen | Hordaland | |
| 4602 | Florø |  | 1 Jan 2020 | 1401 Flora 1439 Vågsøy (part) | Sogn og Fjordane | |
| 4611 | Etnesjøen |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1211 Etne | Hordaland | |
| 4612 | Sveio |  | 1 Jan 1865 | 1216 Sveio | ||
| 4613 | Svortland |  | 1 Jan 1916 | 1219 Bømlo | ||
| 4614 | Leirvik | 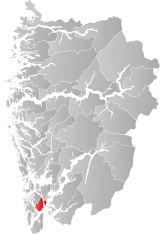 | 1 Jan 1838 | 1221 Stord | ||
| 4615 | Fitjar |  | 1 Jan 1863 | 1222 Fitjar | ||
| 4616 | Uggdal |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1223 Tysnes | ||
| 4617 | Rosendal | 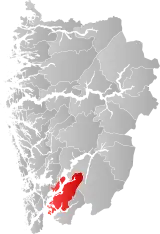 | 1 Jan 1838 | 1224 Kvinnherad | ||
| 4618 | Odda | 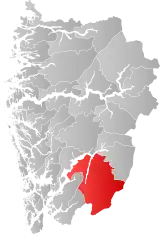 | 1 Jan 1838 | 1227 Jondal 1228 Odda 1230 Ullensvang | ||
| 4619 | Eidfjord | 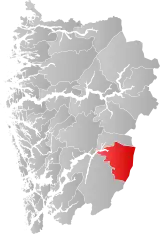 | 1 Jan 1977 | 1232 Eidfjord | ||
| 4620 | Ulvik |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1233 Ulvik | ||
| 4621 | Vossevangen |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1234 Granvin 1235 Voss | ||
| 4622 | Norheimsund |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1238 Kvam | ||
| 4623 | Tysse |  | 1 Jan 1907 | 1242 Samnanger | ||
| 4624 | Osøyro |  | 1 Jan 2020 | 1241 Fusa 1243 Os | ||
| 4625 | Storebø |  | 1 Jan 1886 | 1244 Austevoll | ||
| 4626 | Straume |  | 1 Jan 1964 | 1245 Sund 1246 Fjell 1259 Øygarden | ||
| 4627 | Kleppestø |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1247 Askøy | ||
| 4628 | Dale |  | 1 Jan 1964 | 1251 Vaksdal | ||
| 4629 | Mo | 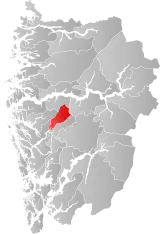 | 1 Jan 1910 | 1252 Modalen | ||
| 4630 | Lonevåg | 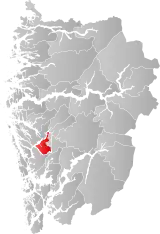 | 1 Jan 1964 | 1253 Osterøy | ||
| 4631 | Knarvik |  | 1 Jan 2020 | 1256 Meland 1260 Radøy 1263 Lindås | ||
| 4632 | Årås |  | 1 Jan 1910 | 1264 Austrheim | ||
| 4633 | Fedje | 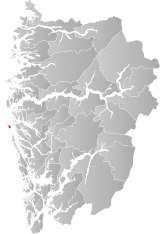 | 1 Jan 1947 | 1265 Fedje | ||
| 4634 | Masfjordnes |  | 1 Mar 1879 | 1266 Masfjorden | ||
| 4635 | Eivindvik | 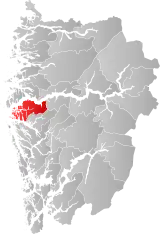 | 1 Jan 1838 | 1411 Gulen | Sogn og Fjordane | |
| 4636 | Hardbakke | 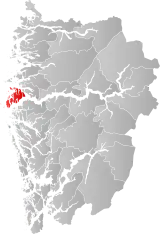 | 1 Jan 1858 | 1412 Solund | ||
| 4637 | Hyllestad | 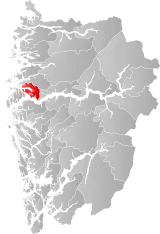 | 1 Jan 1862 | 1413 Hyllestad | ||
| 4638 | Høyanger | 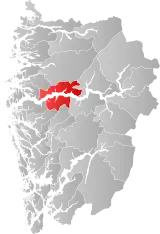 | 1 Jan 1964 | 1416 Høyanger | ||
| 4639 | Vikøyri |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1417 Vik | ||
| 4640 | Hermansverk |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1418 Balestrand 1419 Leikanger 1420 Sogndal | ||
| 4641 | Aurlandsvangen |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1421 Aurland | ||
| 4642 | Lærdalsøyri |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1422 Lærdal | ||
| 4643 | Årdalstangen |  | 1 Jan 1863 | 1424 Årdal | ||
| 4644 | Gaupne |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1426 Luster | ||
| 4645 | Askvoll |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1428 Askvoll | ||
| 4646 | Dale | 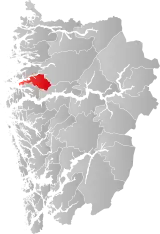 | 1 Jan 1838 | 1429 Fjaler | ||
| 4647 | Førde |  | 1 Jan 2020 | 1430 Gaular 1431 Jølster 1432 Førde 1433 Naustdal | ||
| 4648 | Svelgen |  | 1 Jan 1866 | 1438 Bremanger | ||
| 4649 | Nordfjordeid |  | 1 Jan 2020 | 1439 Vågsøy (part) 1441 Selje 1443 Eid | ||
| 4650 | Sandane |  | 1 Jan 1838 | 1445 Gloppen | ||
| 4651 | Stryn |  | 1 Jan 1843 | 1449 Stryn |
See also
References
- ↑ "Navn på steder og personer: Innbyggjarnamn" (in Norwegian). Språkrådet.
- ↑ "Forskrift om målvedtak i kommunar og fylkeskommunar" (in Norwegian). Lovdata.no.
- ↑ Bolstad, Erik; Thorsnæs, Geir, eds. (26 January 2023). "Kommunenummer". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget.
- ↑ "Arealstatistikk for Norge". Kartverket (in Norwegian Bokmål). 8 March 2013. Archived from the original on 11 May 2020. Retrieved 2 January 2020.
- ↑ "19 fylker blir til 11 – dette skal de hete (19 counties becoming 11 – this will be their names)" (in Norwegian). 6 April 2018. Archived from the original on 30 April 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "Forskrift om målvedtak i kommunar og fylkeskommunar (målvedtaksforskrifta)" (in Norwegian). Lovdata.no. Archived from the original on 26 January 2020. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ↑ "Navn på nye kommuner (Name of new municipalities)" (in Norwegian). Archived from the original on 1 September 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ Natvik, Oddvar (29 August 2005). "Sogn og Fjordane". Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 23 August 2008.
- ↑ "Vil behalde Brudesløret" (in Norwegian). nrk.no. 27 November 2007. Retrieved 9 September 2013.
- ↑ "Brudesløret". World Waterfall Database.
- ↑ Berg, Ole T., ed. (5 March 2021). "fylke". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget. Archived from the original on 19 October 2020. Retrieved 5 February 2022.
- ↑ Berg, Ole T., ed. (19 February 2020). "fylkeskommune". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget. Archived from the original on 16 August 2022. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- 1 2 3 Thorsnæs, Geir, ed. (12 October 2020). "Vestland". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget. Archived from the original on 24 June 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2022.
- ↑ List of Norwegian municipality numbers



