| Copernican | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronology | ||||||
| ||||||
| Usage information | ||||||
| Celestial body | Earth's Moon | |||||
| Time scale(s) used | Lunar Geologic Timescale | |||||
| Definition | ||||||
| Chronological unit | Period | |||||
The Copernican Period in the lunar geologic timescale runs from approximately 1.1 billion years ago to the present day. The base of the Copernican period is defined by impact craters that possess bright optically immature ray systems. The crater Copernicus is a prominent example of rayed crater, but it does not mark the base of the Copernican period.

Copernican age deposits are mostly represented by crater ejecta, but a small area of mare basalt has covered part of (and is thus younger than) some of the rays of the Copernican crater Lichtenberg, and therefore the basalt is mapped as Copernican age.[1]
Definition
The base of the Copernican period is defined based on the recognition that freshly excavated materials on the lunar surface are generally "bright" and that they become darker over time as a result of space weathering processes. Operationally, this period was originally defined as the time at which impact craters "lost" their bright ray systems. This definition, however, has recently been subjected to some criticism as some crater rays are bright for compositional reasons that are unrelated to the amount of space weathering they have incurred. In particular, if the ejecta from a crater formed in the highlands (which is composed of bright anorthositic materials) is deposited on the low albedo mare, it will remain bright even after being space weathered.

Examples
Other than Copernicus itself, there are many examples of Copernican craters. Large examples on the near side include Tycho, Aristillus, Autolycus, Stevinus, Kepler, Theophilus, Taruntius, Eudoxus, Bürg, Römer, Harpalus, Carpenter, Philolaus, Anaxagoras, Glushko, Hayn, Zucchius, and Rutherfurd. Examples on the far side include Ohm, Jackson, King, Necho, Giordano Bruno, O'Day, Crookes, Robertson, Vavilov, and Sharonov.[2]
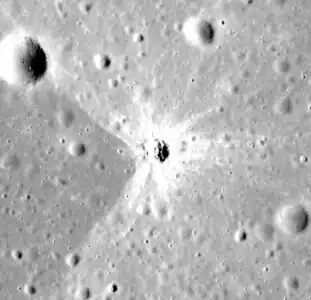 500 m diameter crater with rays in Mare Serenitatis
500 m diameter crater with rays in Mare Serenitatis_2.png.webp) Copernicus
Copernicus Tycho
Tycho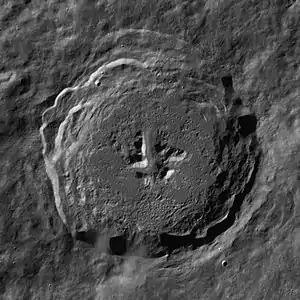 Hayn
Hayn Jackson
Jackson Necho (Apollo 14)
Necho (Apollo 14) Interior of Crookes (Apollo 8)
Interior of Crookes (Apollo 8)
Many craters visited by the Apollo astronauts were of Copernican age. These include North Ray and South Ray on Apollo 16, which were dated by cosmic ray exposure to approximately 50 million and 2 million years age, respectively.
Relationship to Earth's geologic time scale
Its Earth equivalents are the Neoproterozoic era of the Proterozoic eon and the whole of the Phanerozoic eon. So, while animal life bloomed on Earth, the Moon's geologic activity was coming to an end.
References
- ↑ Wilhelms, Don E.; McCauley, John F.; Trask, Newell J. (1987). "The geologic history of the Moon". USGS. Professional paper 1348.
- ↑ Unified Geologic Map of the Moon, C. M. Fortezzo, P. D. Spudis, S. L. Harrel, 2020. United States Geological Survey.
- Martel, Linda M. V. (2004-09-28). "Lunar Crater Rays Point to a New Lunar Time Scale". Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP). Planetary Science Research Discoveries (PSRD).