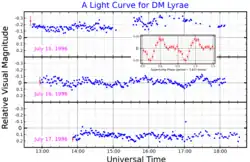
 A visual band light curve for DM Lyrae, adapted from Nogami et al. (2003).[1] The inset plot shows the superhump variations. | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Lyra |
| Right ascension | 18h 58m 44.43s[2] |
| Declination | +30° 15′ 33.0″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +18 (quiet), +13.6 (burst)[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | ? / White dwarf |
| Variable type | SU UMa[1] |
| Orbit[3] | |
| Period (P) | 0.0654092±0.000002 d |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2,451,343.8565±0.0015 HJD |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 37±5 km/s |
| Details | |
| Donor star | |
| Mass | 0.095±0.022[4] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.145±0.011[4] R☉ |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
DM Lyrae (DM Lyr for short) is a dwarf nova in the constellation Lyra. This binary system is composed of a primary star of unknown type, and a white dwarf companion. It erupted in 1928 and 1996 and reached about magnitude 13.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Nogami, D.; et al. (2003). "The SU UMa Nature of the Dwarf Nova, DM Lyrae". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan. 55 (2): 483–488. arXiv:astro-ph/0301036. Bibcode:2003PASJ...55..483N. doi:10.1093/pasj/55.2.483. S2CID 18844865.
- 1 2 3 Downes, Ronald A.; et al. (2001). "A Catalog and Atlas of Cataclysmic Variables: The Living Edition". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 113 (784): 764. arXiv:astro-ph/0102302. Bibcode:2001PASP..113..764D. doi:10.1086/320802. S2CID 16285959.
- ↑ Thorstensen, John R.; Fenton, William H. (January 2003). "Five Dwarf Novae with Orbital Periods below Two Hours". The Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 115 (803): 37–42. arXiv:astro-ph/0209172. Bibcode:2003PASP..115...37T. doi:10.1086/345103. S2CID 119343404.
- 1 2 Knigge, Christian (December 2006). "The donor stars of cataclysmic variables". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 373 (2): 484–502. arXiv:astro-ph/0609671. Bibcode:2006MNRAS.373..484K. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.11096.x. S2CID 2616606.
- ↑ "DM Lyr". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2021-11-15.
External links
- "DM Lyr: A new UGSU Star". Retrieved June 22, 2006.
- "DM Lyr". VSNET. Retrieved June 22, 2006.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.