 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[Dibutyl(dodecanoyloxy)stannyl] dodecanoate | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.946 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3146 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| (CH3(CH2)10CO2)2Sn((CH2)3CH3)2 | |
| Molar mass | 631.570 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless oily liquid or soft waxy crystals |
| Odor | Fatty[2] |
| Density | 1.066 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 22 to 24 °C (72 to 75 °F; 295 to 297 K) [1] |
| Boiling point | 205 °C at 1.3 kPa[1][2] |
| Practically insoluble (less than 1 mg/mL at 68 °F (20 °C))[1] | |
| Solubility | Practically insoluble in methanol Soluble in petroleum ether, benzene, acetone, ether, carbon tetrachloride, organic esters |
| Vapor pressure | <0.01 hPa (0.2 mmHg at 160 °C)[2] |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4683 at 20 °C (for light at wavelength of 589.29 nm)[1] |
| Viscosity | 42 cP[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   | |
| Danger | |
| H341, H360FD, H372[1] | |
| P260, P264, P270, P280, P281, P319, P405, P501[1] | |
| Flash point | 191 °C[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
|
LC50 (median concentration) |
150 mg/m3 (inhalation, mouse, 2 hours)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Dibutyltin dilaurate (abbreviated DBTDL) is an organotin compound with the formula (CH3(CH2)10CO2)2Sn((CH2)3CH3)2. It is a colorless viscous and oily liquid. It is used as a catalyst .
Description
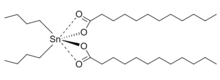
In terms of its structure, the molecule of dibutyltin dilaurate consists of two laurate groups and two butyl groups attached to a tin(IV) atom. The molecular geometry at tin is tetrahedral. Based on the crystal structure of the related bis(bromobenzoate), the oxygen atoms of the carbonyl groups are weakly bonded to tin atom.[3]
Decomposition
Upon heating to decomposition temperature (which is above 250 °C[2]), dibutyltin dilaurate emits acrid smoke and fumes.[1]
Uses
Dibutyltin dilaurate is used as a paint additive.[1] Together with dibutyltin dioctanoate, dibutyltin dilaurate is used as a catalyst for polyurethane production from isocyanates and diols. It is also useful as a catalyst for transesterification and for the room temperature vulcanization of silicones. It is also used as a stabilizer in polyvinyl chloride,[4][1] vinyl ester resins, lacquers, and elastomers.[1] It is also added to animal feed to remove cecal worms, roundworms, and tapeworms in chickens and turkeys and to prevent or provide treatment against hexamitosis and coccidiosis.[5]
Hazards and toxicity
Dibutyltin dilaurate can be absorbed through the skin. It irritates skin and eyes (causes redness of skin and eyes). It is a neurotoxin. It can cause injuries to the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract. The symptoms of poisoning with dibutyltin dilaurate include nausea, headache, muscular weakness and even paralysis. Dibutyltin dilaurate is combustible.[1] Its vapor is denser than air (21.8 times denser than air[1]), so it can spread on the floors, forming explosive mixtures with air. On fire, it emits irritating and toxic fumes and smoke which contain tin, tin oxides and carbon oxides.[2] Dibutyltin dilaurate is very reactive with acids and oxidizers.[1]
Related compounds
- Dibutyltin dioctanoate: CAS#4731-77-5
- Dibutyltin diacetate: CAS #1067-33-0
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 "Dibutyltin dilaurate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Dibutyltin dilaurate 95 77-58-7".
- ↑ Weng Ng, Seik; Das, V. G. Kumar; Yip, Wai-Hing; Wang, Ru-Ji; Mak, Thomas C. W. (1990-08-28). "Di-n-butyltin(IV) di-o-bromobenzoate, a weakly-bridged dimer". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 393 (2): 201–204. doi:10.1016/0022-328X(90)80199-A. ISSN 0022-328X.
- ↑ Davies, Alwyn George (2004). Organotin chemistry (2nd ed.). Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. Applications, Environmental Issues, and Analysis. ISBN 3-527-31023-1.
- ↑ PubChem. "Butynorate". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2019-08-23.