 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
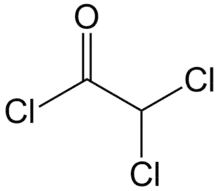
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dichloroacetyl chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1209426 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.091 |
| EC Number |
|
| 430743 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1765 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2HCl3O | |
| Molar mass | 147.38 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless fuming liquid |
| Density | 1.5315 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 107 °C (225 °F; 380 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Dichloroacetyl chloride is the organic compound with the formula CHCl2COCl. It is the acyl chloride of dichloroacetic acid.[1] It is a colourless liquid and is used in acylation reactions.[2][3]
Preparation
Unlike typical acid chlorides, which are often prepared from the associated carboxylic acid, dichloroacetyl chloride is not prepared from dichloroacetic acid. Instead, industrial routes include oxidation of 1,1,2-trichloroethane, hydrolysis of pentachloroethane, and the carboxylation of chloroform:[4]
- CHCl2CH2Cl + O2 → CHCl2COCl + H2O
- CHCl2CCl3 + H2O → CHCl2COCl + 2 HCl
- CHCl3 + CO2 → CHCl2COCl + 1/2 O2
Uses
It is a precursor to various herbicides including dichlormid.[5]
Hydrolysis gives dichloroacetic acid. It is one of the precursors to antibiotics, including chloramphenicol.
References
- ↑ "Pubchem". Pubchem. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ↑ Richard P. Pohanish; Stanley A. Greene (25 August 2009). Wiley Guide to Chemical Incompatibilities. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 327–8. ISBN 978-0-470-52330-8.
- ↑ Science of Synthesis: Houben-Weyl Methods of Molecular Transformations Vol. 26: Ketones. Georg Thieme Verlag. 14 May 2014. pp. 759–60. ISBN 978-3-13-172011-5.
- ↑ Koenig, G.; Lohmar, E.; Rupprich, N. "Chloroacetic Acids". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_537. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ Riechers, Dean E.; Kreuz, Klaus; Zhang, Qin (2010). "Detoxification without Intoxication: Herbicide Safeners Activate Plant Defense Gene Expression". Plant Physiology. 153 (1): 3–13. doi:10.1104/pp.110.153601. PMC 2862420. PMID 20237021.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.