 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Bis(methylsulfanyl)methanethione[1] | |
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dimethyl trithiocarbonate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
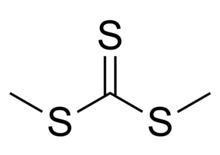
| (CH3S)2CS | |
| Molar mass | 138.26 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow liquid[2] |
| Odor | Stench[3] |
| Density | 1.254 g/cm3[2] |
| Melting point | −3 °C (27 °F; 270 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 101–102 °C (214–216 °F; 374–375 K) at 16 hPa[2] |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.675[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 97 °C (207 °F) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Dimethyl carbonate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Dimethyl trithiocarbonate is an organic compound with the chemical formula S=C(SCH3)2. It is a methyl ester of trithiocarbonic acid. This chemical belongs to a subcategory of esters called thioesters. It is a sulfur analog of dimethyl carbonate O=C(OCH3)2, where all three oxygen atoms are replaced with sulfur atoms. Dimethyl trithiocarbonate is a yellow liquid with a strong and unpleasant odor.[2][3]
Synthesis
In terms of its name, dimethyl trithiocarbonate is formally derived by esterification of trithiocarbonic acid with methanethiol.
One synthesis starts from thiophosgene as described in this simplified equation:[4]
- CSCl2 + 2 CH3SH → CS(SCH3)2 + 2 HCl
Alternatively, it can be prepared by treating carbon disulfide with aqueous base, a phase transfer reagent, and methyl iodide.[5]
Uses
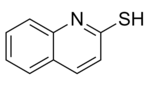
Dimethyl trithiocarbonate is used in preparation of methyl-β,β′-dicarbonyldithiocarboxylate derivatives, in generation of tris(organothiyl)methyl radicals (RS)3C•, and in preparation of β-oxodithiocarboxylates.[2] Dimethyl trithiocarbonate is also a useful reagent in the preparation of 2-mercaptoquinoline and its analogues which are potential antileishmanial agents.[6]
Hazards and toxicity
Dimethyl trithiocarbonate is combustible. Upon catching fire, irritating, suffocating and toxic gases are released, like carbon oxides and sulfur oxides.[3]
References
- 1 2 3 "Dimethyl trithiocarbonate".
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/GB/en/coa/ALDRICH/397180/MKBC1532
- 1 2 3 https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/GB/en/sds/aldrich/397180
- ↑ Godt, H. C.; Wann, R. E. (1961). "The Synthesis of Organic Trithiocarbonates1". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 26 (10): 4047–4051. doi:10.1021/jo01068a097.
- ↑ Lee, Albert W. M.; Chan, W. H.; Wong, H. C. (1988). "One Pot Phase Transfer Synthesis of Trithiocarbonates from Carbon Bisulphide and Alkyl Halides". Synthetic Communications. 18 (13): 1531–1536. doi:10.1080/00397918808081310.
- ↑ "2314-48-9 | Dimethyl Trithiocarbonate | C₃H₆S₃ | TRC".