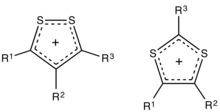
Dithiolium salts are compounds of the formula [(RC)3S2]+X− (R = H, alkyl, aryl, etc.). These salts consist of a planar organic cation with a variety of anions such as halides. The five-membered ring cations are observed in either of two isomers, 1,2- and 1,3-dithiolium cations. These cations differ with respect to the relative positions of the pair of sulfur atoms. Both isomers feature a planar ring, which is aromatic owing to the presence of 6π electrons.[1] For example, the 1,2-ditholium ring can be represented as an allyl cation of the three carbons,[2] with each sulfur atom donating one of its lone pairs of electrons to give a total of three pairs.
Preparation, occurrence, reactions
1,2-Dithiolium cations have been prepared from 1,3-diketones by treatment with H2S and oxidants such as bromine.[2]
- (RCO)2CH2 + 2 H2S + Br2 → [(RC)3S2]+Br− + 2 H2O + HBr
1,3-Dithiolium cations are often prepared by alkylation of the corresponding unsaturated dithio- or trithiocarbonates:
- (RC)2S2CE + R'+ → [(RC)2S2CER']+
The analogous reaction of electrophiles with 1,2-dithiole-2-ones affords 1,2-dithiolium cations.
References
- ↑ Noël Lozac'h; Madeleine Stavaux (1981). The 1,2- and 1,3-Dithiolium Ions. Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry. Vol. 27. pp. 151–239. doi:10.1016/S0065-2725(08)60997-6. ISBN 978-0-12-020627-8.
- 1 2 Hendrickson, A. R.; Martin, R. L. (1973). "Improved Synthesis of Alkyl Substituted 1,2-Dithiolium Salts". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 38 (14): 2548–9. doi:10.1021/jo00954a028.
- ↑ E. Uhlemann; F. Weller (1992). "3,5-Diphenyl-1,2-dithiolium-hydrogensulfat—Bildung und Struktur" [3.5-Diphenyl-l,2-dithiolium Hydrogensulphate—Synthesis and Structure]. Z. Naturforsch. B (in German). 47 (11): 1501–1504. doi:10.1515/znb-1992-1102. S2CID 95736614.