| Duaenhor | |
|---|---|
| Prince of Egypt | |
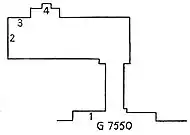 Plan of Duaenhor's tomb in Giza | |
| Burial | mastaba G 7550, Giza |
| Spouse | unknown woman |
| Issue | Nebtyhotep |
| Religion | Ancient Egyptian religion |
Duaenhor was a Prince of Egypt. He was named after god Horus.
Family
Duaenhor is thought by some to be a son of Crown Prince Kawab and Queen Hetepheres II. If so, he would have been a grandson of Pharaoh Khufu and Queen Meritites I.[1] On the other hand, based on his titles, he may be one of the younger sons of Khufu (along with Khaemsekhem (G 7660), and Mindjedef (G 7760)).[2]
Duaenhor's brothers were Kaemsekhem and Mindjedef.[2] A daughter of Duaenhor was named Nebtyhotep.[3]
He held the titles King’s son of his body and Companion of his father.[4]
Tomb
Duaenhor was buried at Giza in mastaba G 7550. In the tomb his father and mother are mentioned. His daughter is also mentioned on the south entrance facade.[3]
The scenes in the tomb show:
- (1) Duaenhor and his family
- (2) Table scene
- (3) Butchers at work
- (4) False door of Duaenhor
References
- ↑ Dodson, Aidan and Hilton, Dyan. The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson. 2004, pp 50-61. ISBN 0-500-05128-3
- 1 2 Flentye, Laurel. "The Development of the Eastern and GIS Cemeteries at Giza during the Fourth Dynasty." In Miroslav Bárta, ed. The Old Kingdom Art and Archaeology. Proceedings of the Conference held in Prague, May 31-June 4, 2004. Prague: Czech Institute of Egyptology, 2006, pp. 141-142, pl. 5 (8).
- 1 2 http://gizapyramids.org page on G 7550
- ↑ Porter and Moss, Topographical Bibliography of Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphic Texts, Reliefs, and Paintings; Part III
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.