| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Musca |
| Right ascension | 12h 17m 34.27716s[2] |
| Declination | −67° 57′ 38.6486″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.0 - 4.3[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | asymptotic giant branch[4] |
| Spectral type | M5 III[5] |
| Variable type | SRb[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 7.1±0.7 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −231.04±0.13[2] mas/yr Dec.: −26.39±0.13[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 10.82 ± 0.17 mas[2] |
| Distance | 301 ± 5 ly (92 ± 1 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.77[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | <1.5-2[7] M☉ |
| Radius | ~130[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1800-2300[7] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3400[7] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
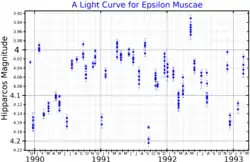
Epsilon Muscae, Latinized as ε Muscae, is a red giant star of spectral type M5III in the constellation Musca.[5] Originally a main-sequence star of around 1.5 to 2 solar masses, it is now on the asymptotic giant branch[4] and has now expanded to 130 times the Sun's diameter and 1800 to 2300 its luminosity.[7] It is a semiregular variable, varying between visual magnitudes 4.0 and 4.3[3] in eight distinct periods ranging from a month to over half a year in length.[5] It is located around 300 light-years distant,[2] the same distance as the Lower Centaurus–Crux subgroup of the Scorpius–Centaurus association, although it is moving much faster at around 100 km/s and does not share a common origin.[7]
References
- ↑ "/ftp/cats/more/HIP/cdroms/cats". Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Strasbourg astronomical Data Center. Retrieved 15 October 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600
- 1 2 3 Samus, N. N.; et al. (2017). "General Catalogue of Variable Stars". Astronomy Reports. 5.1. 61 (1): 80–88. Bibcode:2017ARep...61...80S. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. S2CID 255195566.
- 1 2 Eggen, Olin J. (July 1992), "Asymptotic giant branch stars near the sun", Astronomical Journal, 104 (1): 275–313, Bibcode:1992AJ....104..275E, doi:10.1086/116239.
- 1 2 3 Tabur, V.; Bedding, T. R.; Kiss, L. L.; Moon, T. T.; Szeidl, B.; Kjeldsen, H. (2009). "Long-term photometry and periods for 261 nearby pulsating M giants". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 400 (4): 1945–1961. arXiv:0908.3228. Bibcode:2009MNRAS.400.1945T. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15588.x. S2CID 15358380.
- ↑ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv:1108.4971, Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, S2CID 119257644.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Kaler, Jim. "Epsilon Muscae". Stars. University of Illinois. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.