| |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl benzoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.078 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 150.177 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.050 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −34 °C (−29 °F; 239 K) |
| Boiling point | 211–213 °C (412–415 °F; 484–486 K) |
| 0.72 mg/mL | |
| log P | 2.64 |
| −93.32×10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H411 | |
| P264, P273, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P391, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Ethyl benzoate, C9H10O2, is an ester formed by the condensation of benzoic acid and ethanol. It is a colorless liquid that is almost insoluble in water, but miscible with most organic solvents.
As with many volatile esters, ethyl benzoate has a pleasant odor described as sweet, wintergreen, fruity, medicinal, cherry and grape.[1] It is a component of some fragrances and artificial fruit flavors.
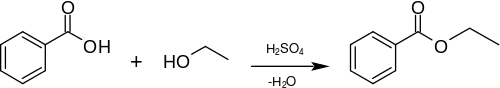
Preparation
A simple and commonly used method for the preparation of ethyl benzoate in the laboratory is the acidic esterification of benzoic acid with ethanol and sulfuric acid as catalyst:[2]
References
- ↑ Ethyl benzoate, thegoodscentscompany.com
- ↑ Arthur Israel Vogel. Rev. by Brian S. Furniss: Vogel’s textbook of practical organic chemistry. 5. Auflage. Longman, Harlow 1989, ISBN 0-582-46236-3, S. 1076
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.