| Eublaberus distanti | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Blattodea |
| Family: | Blaberidae |
| Genus: | Eublaberus |
| Species: | E. distanti |
| Binomial name | |
| Eublaberus distanti (Kirby, WF 1903) | |
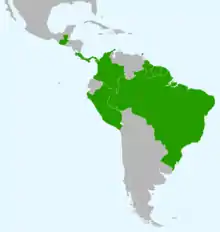 | |
| Range by country | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Eublaberus distanti, known as the six-spotted,[2] four-spotted,[3] four-spot,[4] or Trinidad bat-cave[5][6] roach or cockroach, is a primarily cave-dwelling[7] Central and South American[8] cockroach of the genus Eublaberus (Hebard, 1920) and named after William Lucas Distant.
Nymphs turn a dark brown, and the common name "six spotted cockroach" refers to six yellow spots along the sides of the nymph. Adults of both genders have wings but do not fly. They grow to approximately 6.4 cm (2.5 in) in length. Males are generally smaller than females, with longer wings, and a small rear sternite compared to females.
Range
E. distanti are found in Trinidad and Tobago, Guatemala, Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, French Guiana, Suriname, Guyana, Brazil, and Peru.[8][9]

Habitat
E. distanti in Trinidad were observed to prefer relatively dry guano-rich areas in caves, but are occasionally found in rotting logs, under decaying litter, in epiphytes, and in "the rot holes and hollows of trees, particularly those that house bats."[7] Nymphs burrow in organically rich soil on cave floors until their 6th or 7th instar, then climb onto rocky, often guano-covered walls.[10] Caves with guano support typically contain very large populations of a small number of cockroach species that are able to "exploit the abundant, rich, but rather monotonous food bonanza."[7] A single chamber of a Trinidad cave housed more than 43,000 E. distanti.[7]
Diet
E. distanti is a scavenger, taking advantage of any animal or vegetable matter available, picking out energy-rich parts of food presented to them. In Tamana Cave, Trinidad, E. distanti wait buried beneath guano nightly, with antennae extended above the surface, until local insectivorous bats return from foraging around 3:00 a.m., then emerge to consume the fresh guano droppings.[7] A local frugivorous bat is found in the same cave, but E. distanti only burrow in their droppings, rather than eat them.
Pheromones
A tracheal gland of E. distanti associated with the second abdominal spiracle secretes an alarm pheromone that triggers a disruption and escape behavior, and mandibular glands secrete an aggressive pheromone and an aggregation pheromone.[7][10][11] A defense response against predators of younger nymphs is to burrow in guano, while older nymphs and adults crawl into crevices.[10] Aggregations of E. distanti were observed to be relatively stable within E. distanti, with 90% remaining in the same group over a 30-day period, although it wasn't clear if the loyalty was toward the group or its location.[7]
Parasites
A new genus and species of ectoparasitic mite, Blaberpolipus cavernicola (n. gen, n. sp.), was described in 2003 from samples found on Peruvian specimens of E. distanti and Blaberus parabolicus.[9]
Uses
Feeder insects
E. distanti are kept and raised as feeder insect for captive reptiles, amphibians, tarantulas and other insectivores. While generally suitable nutritionally, a comparison with other popular feeder cockroaches (Blatta lateralis, known as lats, and Gromphadorhina portentosa, known as Madagascar hissing cockroaches), crickets, and beetle larvae found their fat content to be higher, making it a poorer protein source except in certain circumstances.[2]
Blatticomposting
Eublaberus cockroaches are well suited for experiments in blatticomposting, the use of cockroaches to convert human food wastes into compost. They are relatively easy to care for and breed in captivity, and tolerate crowding well.[12]
References
- ↑ "Synonyms of Four-spot Roach (Eublaberus distanti)". Encyclopedia of Life. Retrieved 24 December 2013.
- 1 2 Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; Dierenfeld, E.S. (2012). "An Investigation Into the Chemical Composition of Alternative Invertebrate Prey" (PDF). Zoo Biology. 31 (1): 40–54. doi:10.1002/zoo.20382. ISSN 0733-3188. PMID 21442652. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-04-21. Retrieved 2013-12-26.
- ↑ "Eublaberus distanti (Four-spotted cockroach)". The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt). UniProt Consortium. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ↑ "Common Names for Four-spot Roach (Eublaberus distanti)". Encyclopedia of Life. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ↑ Çınar, Ümüt (2012). "English cockroach names" (PDF). Kmoksy.com. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ "Global Species – Eublaberus distanti (Trinidad bat-cave cockroach)". Global Species. Myers Enterprises II. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Bell, WJ; Roth, LM; Nalepa, CA (2007). Cockroaches: Ecology, Behavior, and Natural History (PDF). JHU Press. pp. 51–53, 74, 87, 133. ISBN 978-0-8018-8616-4. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2019-12-11.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - 1 2 Beccaloni, GW (2007). "Species Eublaberus distanti (Kirby, 1903)". Blattodea Species File Online. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- 1 2 Husband, Robert W.; OConnor, Barry M. (2003). "A new genus and species of mite (Acari: Tarsonemina: Podapolipidae), ectoparasite of the Peruvian cockroaches, Blaberus parabolicus (Walker) and Eublaberus distanti (Kirby) (Blattodea: Blaberidae)". International Journal of Acarology. 29 (4): 331–338. doi:10.1080/01647950308684349. ISSN 0164-7954. S2CID 83655413.
- 1 2 3 Schal, C; Gautier, J-Y; Bell, WJ (1984). "Behavioural ecology of cockroaches*" (PDF). Biological Reviews. 59 (2): 209–254. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.461.6743. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185x.1984.tb00408.x. S2CID 51756192.
- ↑ Brossut, R (1983). "Allomonal secretions in cockroaches". Journal of Chemical Ecology. 9 (1): 143–158. doi:10.1007/BF00987778. PMID 24408627. S2CID 42910359.
- ↑ "Research & Resources – Composting – Blatticomposting". Environmental Interpretive Center. University of Michigan – Dearborn. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
External links
- Rehn, James A. G. (August 1905). "Notes on the orthoptera of Costa Rica, with descriptions of new species". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. 57: 790–843.
- Kirby, W. F. (1903). "Notes on Blattidæ &c., with descriptions of new genera and species in the collection of the British Museum, South Kensington – No. I". The Annals and Magazine of Natural History. 11 (7): 404–415. doi:10.1080/00222930308678790.