| Fam221b | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | 4930412F15Rikfamily with sequence similarity 221member B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | HomoloGene: 52184 GeneCards: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FAM221B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAM221B gene [2] . FAM221B is also known by the alias C9orf128, is expressed at low level, and is defined by 17 GenBank accessions [3] . It is predicted to function in transcription regulation as a transcription factor.
Gene
Locus
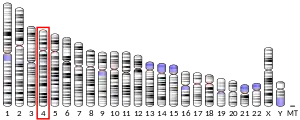
FAM221B can be found around the end of the short arm of human chromosome 9.


Expression patterns
FAM221B is expressed at low levels in human and mouse tissues. Expression is highest in germ cell tissues and cells. This differential expression is most pronounced in testes tissue. Compared to Homo sapiens, Mus musculus shows more differential expression of FAM221B in testes tissue [4] [5] [6] [7] . Mature beta cells express FAM221B at higher rates than do fetal beta cells [8] .
 FAM221B expression for BioGPS dataset in various tissues in Homo sapiens
FAM221B expression for BioGPS dataset in various tissues in Homo sapiens FAM221B expression for GEO dataset GDS 3113 in various tissues in Homo sapiens
FAM221B expression for GEO dataset GDS 3113 in various tissues in Homo sapiens FAM221B expression for BioGPS dataset in various tissues in Mus musculus
FAM221B expression for BioGPS dataset in various tissues in Mus musculus FAM221B expression for GEO dataset GDS 3142 in various tissues in Mus musculus
FAM221B expression for GEO dataset GDS 3142 in various tissues in Mus musculus
mRNA
Alternative splicing and isoforms
FAM221B has a total of 5 transcript variants: the putative sequence, Isoform X1 [9] , Isoform X2 [10] , Isoform X3 [11] , and Isoform X4. Isoform X4 does not exist in humans but is found in various primates.
Exons

There are a total of six exons in the putative sequence of FAM221B. However, a total of seven exons exist for FAM221B, as the seventh exon is an alternative exon.
Protein

General characteristics
The putative sequence for FAM221B is 402 amino acids long and weighs 45.4 kilodaltons. Amino acids expressed at abnormal rates include Histidine, Cysteine, Glutamic acid, and Tyrosine. When compared to typical proteins, FAM221B expresses Histidine at a much higher frequency at 6.0% of protein, Cysteine at a slightly higher frequency at 4.7% of protein, Glutamic acid at a slightly higher frequency at 11.4% of protein, and Tyrosine at a slightly lower frequency at 1.0% of protein [15] . The isoelectric point of FAM221B is 5.264, suggesting FAM221B is an acidic protein at a normal physiological pH (7.4) [15] . There is strong evidence that FAM221B is a protein found within the nucleus [16] .
Compositional features
FAM221B is predicted to have two distinct alpha helices in its secondary structure [17] [18] [19] . Secondary structure predicting programs predict beta sheets but are not as consistent as the two alpha helices.
Post-translational modifications
FAM221B is predicted to have a high number of phosphorylation sites.
Protein interactions
There is evidence that FAM221B interacts with the proteins Autophagy related 13 (KIAA0652), RB1-inducible coiled-coil 1 (RB1CC1), and Ephrin-B3 (EFNB3) [20] . These proteins are predicted to be localized in the nucleus at the same confidence level as FAM221B.
Homology and evolution
FAM221B is conserved in Eutheria. However, both orthologous and paralogous transcripts predating ancestral Boroeutheria can be found.
Paralogs
One paralog exists for FAM221B in humans: FAM221A [21] . FAM221A and FAM221B's ancestral gene is predicted to have diverged in prokarya.
| Gene name | Accession number | Sequence length (aa) | Sequence identity to human protein | Sequence similarity to human protein | Notes |
| FAM221A | NP_954587.2 | 402 | 28% | 46% | Exists in other organisms |
Orthologs
| Genus and species | Common name | Divergence from human liineage (MYA) | Accession number | Sequence length (aa) | Sequence identity to human protein | Sequence similarity to human protein |
| Rhinopithecus roxellana | Golden Snub-nosed Monkey | 29.1 | XP_010374448.1 | 402 | 92% | 95% |
| Saimiri boliviensis | Black-capped Squirrel Monkey | 43.1 | XP_003943837.1 | 402 | 92% | 93% |
| Tsuga chinensis | Chinese Tree Shrew | 85.9 | XP_006143215.1 | 518 | 78% | 88% |
| Cavia porcellus | Guinea Pig | 90.9 | XP_003470749.1 | 415 | 72% | 83% |
| Odobenus rosmarus divergens | Pacific Walrus | 97.5 | XP_004392324.1 | 398 | 72% | 81% |
| Orcinus orca | Killer Whale | 97.5 | XP_004271469.1 | 410 | 70% | 78% |
| Felis catus | Feral Cat | 97.5 | XP_006939339.1 | 429 | 68% | 75% |
| Loxodonta africana | African Bush Elephant | 105 | XP_003407335.1 | 414 | 66% | 78% |
| Ornithorhynchus anatinus | Platypus | 179.2 | XP_007656406.1 | 262 | 65% | 75% |
| Anolis carolinensis | Carolina Anole | 320.5 | XP_008122390.1 | 550 | 63% | 69% |
| Thamnophis sirtalis | Common Garter Snake | 320.5 | XP_013924342.1 | 411 | 62% | 74% |
| Lepisosteus oculatus | Alligator Gar | 429.6 | XP_015222126.1 | 272 | 62% | 74% |
| Callorhinchus milii | Australian Ghostshark | 482.9 | XP_007895354.1 | 326 | 58% | 76% |
| Strongylocentrotus purpuratus | Sea Urchin | 747.8 | XP_781628.1 | 409 | 57% | 73% |
| Crassostrea gigas | Pacific Oyster | 847 | EKC20817.1 | 420 | 56% | 70% |
| Clonorchis sinensis | Chinese Liver Fluke | 847 | GAA48218.1 | 359 | 42% | 55% |
| Nematostella vectensis | Startlet Sea Anemone | 936 | XP_001628705.1 | 244 | 42% | 57% |
Homologous domains
There are three conserved domains within FAM221B: DUF4475 super family [22] , PRCC super family [23] , and Caprin-1_C [24] . DUF4475 is the most conserved domain of the three.
Clinical significance
FAM221B is linked to mutations in the RNA component of RNase MRP, which causes pleiotropic human disease cartilage–hair hypoplasia. Also, as patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia often carry genetic alterations in the short arm of human chromosome 9, FAM221B has two consistent non-synonymous amino acid variations associated with the disease. In acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients, Histidine is substituted for an Arginine at position 345, and a Leucine is substituted for a Phenylalanine at position 277 of the protein.
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "FAM221B Gene - GeneCards".
- ↑ "AceView entry on FAM221B".
- ↑ "GEO GDS 3113 entry on FAM221B in Homo sapiens".
- ↑ "GEO GDS 3142 entry on FAM221B in Mus musculus".
- ↑ "BioGPS entry on FAM221B in Homo sapiens".
- ↑ "BioGPS entry on FAM221B in Mus musculus".
- ↑ "Markers for mature beta-cells and methods of using the same".
- ↑ "FAM221B Homo sapiens Isoform X1".
- ↑ "FAM221B Homo sapiens Isoform X2".
- ↑ "FAM221B Homo sapiens Isoform X3".
- ↑ "PHYRE2 secondary structure prediction for FAM221B".
- ↑ "MyHits motif scan for post-translational modifications".
- ↑ "NetPhos 2.0 phosphorylation site predictor".
- 1 2 "General protein characteristics from SDSC Biology WorkBench SAPS tool".
- ↑ "PSORT II predictions on FAM221B".
- ↑ "LOMETS prediction for FAM221B".
- ↑ "MUSTER prediction for FAM221B".
- ↑ "SWISS-model prediction and constructor for FAM221B". Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 10 May 2016.
- ↑ "BioGrid summary for protein interactions for FAM221B".
- ↑ "FAM221A Gene - GeneCards".
- ↑ "NCBI entry on DUF 4475 super family".
- ↑ "NCBI entry on PRCC super family".
- ↑ "NCBI entry on Caprin-1_C".
Suggested reading
- Ridanpää M, van Eenennaam H, Pelin K, et al. (26 January 2001). "Mutations in the RNA component of RNase MRP cause a pleiotropic human disease, cartilage-hair hypoplasia". Cell. 104 (2): 195–203. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00205-7. PMID 11207361. S2CID 13977736.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, Derge JG, et al. (24 December 2002). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 99 (26): 16899–16903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Sarhadi VK, Lahti L, Scheinin I, et al. (16 January 2013). "Targeted resequencing of 9p in acute lymphoblastic leukemia yields concordant results with array CGH and reveals novel genomic alterations". Genomics. 102 (3): 182–188. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2013.01.001. PMID 23333812.