Francesco Guardi | |
|---|---|
 Francesco Guardi portrayed by Pietro Longhi (1764) | |
| Born | 5 October 1712 Venice, Republic of Venice (now Italy) |
| Died | 1 January 1793 (aged 80) Venice, Republic of Venice |
| Nationality | Venetian |
| Known for | Painting |
| Movement | Venetian School |
Francesco Lazzaro Guardi (Italian pronunciation: [franˈtʃesko ˈgwardi]; 5 October 1712 – 1 January 1793) was an Italian painter, nobleman, and a member of the Venetian School. He is considered to be among the last practitioners, along with his brothers, of the classic Venetian school of painting.
In the early part of his career he collaborated with his older brother Gian Antonio in the production of religious paintings. After Gian Antonio's death in 1760, Francesco concentrated on vedute. The earliest of these show the influence of Canaletto, but he gradually adopted a looser style characterized by spirited brush-strokes and freely imagined architecture.
Biography
Francesco Guardi was born in Venice into a family of nobility from Trentino. His father Domenico (born in 1678) and his brothers Niccolò and Gian Antonio were also painters, later inheriting the family workshop after the father's death in 1716. They probably all contributed as a team to some of the larger commissions later attributed to Francesco. His sister Maria Cecilia married the pre-eminent Veneto-European painter of his epoch, Giovanni Battista Tiepolo.
In 1735, Guardi moved to the workshop of Michele Marieschi, where he remained until 1743. His first certain works are from 1738, for a parish at Vigo d'Anuania, in Trentino. In this period he worked alongside his older brother, Gian Antonio. The first work signed by Francesco is a Saint Adoring the Eucharist (c. 1739).

His works in this period included both landscapes and figure compositions. His early vedute show influence both from Canaletto and Luca Carlevarijs. On 15 February 1757, he married Maria Mattea Pagani, the daughter of painter Matteo Pagani. In 1760 his brother Gian Antonio died and his first son, Vincenzo, was born. His second son, Giacomo, was born in 1764.
In 1763 he worked in Murano, in the church of San Pietro Martire, finishing a Miracle of a Dominican Saint clearly influenced by Alessandro Magnasco in its quasi-expressionistic style.
Francesco Guardi's most important later works include the Doge's Feasts, a series of twelve canvases celebrating the ceremonies held in 1763 for the election of Doge Alvise IV Mocenigo. In his later years, Canaletto's influence on his art diminished, as shown by the Piazzetta in the Ca' d'Oro of Venice. In circa 1778, he painted the severe Holy Trinity Appearing to Sts. Peter and Paul in the parish church of Roncegno.

In 1782 Guardi was commissioned by the Venetian government six canvases to celebrate the visit of the Russian Grand Dukes to the city, of which only two remain, and two others for that of Pope Pius VI. On September 12 of that year he was admitted to the Fine Art Academy of Venice.
A stronger attention to colours is present in late works such as the Concerto of 80 Orphans of 1782, now in Munich, in the Façade of Palace with Staircase in the Accademia Carrara of Bergamo.
Guardi died at Campiello de la Madona in Cannaregio (Venice) in 1793.
Mature style

Among all the paintings attributed to either Francesco and his brother Gian Antonio Guardi, the most praised work is not a landscape, but instead the airy sfumato Story of Tobit painted for the organ loft in the small Chiesa dell'Angelo San Raffaele. To quote from the Web Gallery of Art:
Perspective, organized aerial space, the Palladian solidity of Tiepolo... are exchanged for a personal style of coloured handwriting – now brilliantly calligraphic, and now brilliantly cloudy.[1]
Guardi's painterly style is known as pittura di tocco (of touch) for its small dotting and spirited brush-strokes. This looser style of painting had been used by Giovanni Piazzetta and Sebastiano Ricci, and recalls, in some religious themes, the sweetened sfumato of Barocci's Bolognese style. In this he differs from the more linear and architecturally accurate style of Canaletto's painting. This style, a century later, would make Guardi's works highly prized by the French Impressionists.
Canaletto, as a vedutista, concentrated on glamorous urban architecture erected by the serene republic; on the other hand, in Guardi, the buildings often appear to be melting and sinking into a murky lagoon.[2][3] Canaletto's canvases often have intricate linear and brilliant details, and depict Venice in sunny daylight. Guardi paints clouded skies above a city at dusk. These contrasts, however, simplify the facts, since Canaletto often painted the drab communal life and neighborhoods (creating in them some epic artistic qualities), while Guardi did not avoid sometimes painting the ceremonies of Ducal Venice.[4] Ultimately, Guardi's paintings evoke the onset of the dissipation. The citizenry has shrunken to an impotent lilliputian crowd of "rubber-neckers", unable to rescue the crumbling Republic, as for example in the Fire in the Oil Depot in San Marcuola.[5] It was fitting depiction of the rapidly declining empire, which had declined, in Napoleon's assessment, into a "drawing room of Europe" peopled with casinos, carnivals, and courtesans for hire.
Gallery
 Departure of Tobias and Angel, Chiesa dell'Angelo San Raffaele (Venice)
Departure of Tobias and Angel, Chiesa dell'Angelo San Raffaele (Venice)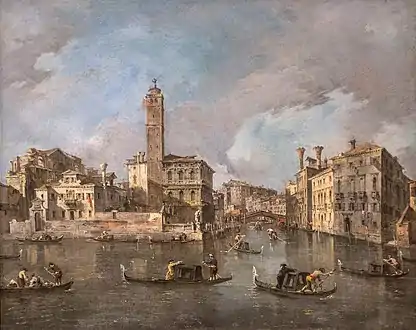 View on the Grand Canal at San Geremia, Venice (1760–1765), Frick Collection
View on the Grand Canal at San Geremia, Venice (1760–1765), Frick Collection The Bucintoro Festival of Venice (1780–1793), National Gallery of Denmark
The Bucintoro Festival of Venice (1780–1793), National Gallery of Denmark Miracle of a Dominican Saint (1763), private collection
Miracle of a Dominican Saint (1763), private collection Regatta in Venice (1770), Frick Collection
Regatta in Venice (1770), Frick Collection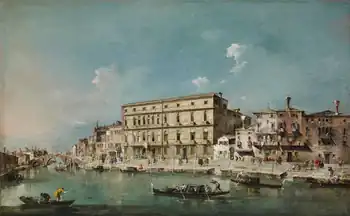 View of the Cannaregio Canal (c. 1770)
View of the Cannaregio Canal (c. 1770) Procession of Gondolas in the Bacino di San Marco (c. 1782), Museum of Fine Arts, Boston
Procession of Gondolas in the Bacino di San Marco (c. 1782), Museum of Fine Arts, Boston_Fire_in_the_oil_warehouses_at_San_Marcuola_by_Francesco_Guardi_-_Gallerie_Accademia.jpg.webp) Fire in the Oil Depot in San Marcuola (1789), Gallerie dell'Accademia
Fire in the Oil Depot in San Marcuola (1789), Gallerie dell'Accademia Venice landscape, Ryazan fine art museum, Ryazan
Venice landscape, Ryazan fine art museum, Ryazan Lagoon Looking Towards Murano from the Fondamenta Nuova (1765-1770), Fitzwilliam Museum[6]
Lagoon Looking Towards Murano from the Fondamenta Nuova (1765-1770), Fitzwilliam Museum[6] A Colonnade, Partly Ruined, with Figures (1780 – 90), Metropolitan Museum of Art
A Colonnade, Partly Ruined, with Figures (1780 – 90), Metropolitan Museum of Art
Footnotes
- ↑ "Web Gallery of Art, image collection, virtual museum, searchable database of European fine arts (1100-1850)". Wga.hu. Retrieved 2012-09-13.
- ↑ "San Cristoforo, San Michele and Murano, Seen from the Fondamenta Nuove by GUARDI, Francesco". Wga.hu. Retrieved 2012-09-13.
- ↑ "The Lagoon with Boats, Gondolas, and Rafts by GUARDI, Francesco". Wga.hu. Retrieved 2012-09-13.
- ↑ "Ducal Palace". Wga.hu. Retrieved 2012-09-13.
- ↑ "Web Gallery of Art, image collection, virtual museum, searchable database of European fine arts (1100-1850)". Wga.hu. Retrieved 2012-09-13.
- ↑ Oil on canvas, 31,7 x 52,7 cm. Fitzwilliam Museum, Cambridge.
References
- Short biography in the Web Gallery of Art
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 12 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 656.
- Aldo Rizzi, I maestri della pittura veneta del '700, Electa - Milano 1973
- The Doge on the Bucintoro near the Riva di Sant'Elena (painting), also known as The Departure Of the Bucentaur For The Ascension Day Ceremony, held at the Louvre in Paris
- Erwin von Busse-Granand (1925). Francesco Guardi und die Kleinmeister des venezianischen Rokoko [Francesco Guardi and the Minor Masters of Venetian Rococo]. Bibliothek der Kunstgeschichte (in German). Vol. 83. Leipzig: E.A. Seemann
External links
![]() Media related to Francesco Guardi at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Francesco Guardi at Wikimedia Commons
- 121 artworks by or after Francesco Guardi at the Art UK site
- Canaletto, a full text exhibition catalog from The Metropolitan Museum of Art, which contains material on Guardi
- Works by Guardi in the Wallace Collection
- Julia L. Valiela, "The Grand Canal with San Simeone Piccolo and Santa Lucia by Francesco Guardi (cat. 303)," in The John G. Johnson Collection: A History and Selected Works, a Philadelphia Museum of Art free digital publication