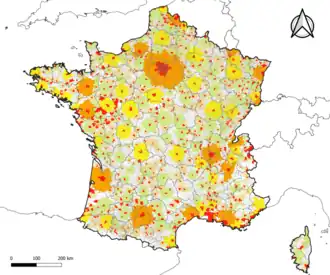
|
Communes in the main population and employment centre of a functional area
Communes in a secondary population and employment centre of a functional area
Communes in the commuting zone of a functional area (functional areas with more than 700,000 inhabitants)
Communes in the commuting zone of a functional area (functional areas between 200,000 and 700,000 inhabitants)
Communes in the commuting zone of a functional area (functional areas between 50,000 and 200,000 inhabitants)
Communes in the commuting zone of a functional area (functional areas with less than 50,000 inhabitants)
Communes outside of functional areas
|
An aire d'attraction d'une ville[note 1] (or AAV, literally meaning "catchment area of a city") is a statistical area used by France's national statistics office INSEE since 2020, officially translated as functional area in English by INSEE,[2] which consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and the surrounding exurbs, towns and intervening rural areas that are socioeconomically tied to the central urban agglomeration, as measured by commuting patterns.[1] INSEE's functional area (AAV) is therefore akin to what is most often called metropolitan area in English.
Definition
INSEE's AAV follows the same definition as the Functional Urban Area (FUA) used by Eurostat and the OECD, and the AAVs are thus strictly comparable to the FUAs.[2] Before 2020, INSEE used another metropolitan statistical area, the aire urbaine (AU), which was defined differently than the AAV, but the AU has now been discontinued and replaced with the AAV in order to facilitate international comparisons with Eurostat's FUAs.[2]
The functional area is a grouping of communes comprising a 'population and employment centre' (pôle de population et d'emploi in French),[2][3] which Eurostat calls "city" or "greater city" (depending on the FUA),[4] defined according to population and employment criteria, and an outlying 'commuting zone' (couronne in French),[2][3] which Eurostats calls "commuting zone" in English,[4] like INSEE, but zone de navettage in French[5] (unlike INSEE which calls it couronne), in which at least 15% of the working population work in the population and employment centre.[2]
List of functional areas (AAV)
The following is a list of the thirty five largest functional areas (AAV) in France, based on their population at the 2020 census. Population at the 2008 and 1990 censuses is indicated for comparison.
| Rank (2020) |
Rank (2008) |
Rank (1990) |
Functional area (AAV) |
Population (2020)[6] |
Population (2008)[7] |
Population (1990)[8] |
Yearly change (2008-2020) |
Yearly change (1990-2008) |
Land area (km²)[9] |
Number of communes[10] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Paris | 13,125,142 | 12,479,272 | 11,392,740 | +0.42% | +0.51% | 18,941 | 1,929 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | Lyon | 2,293,180 | 2,050,795 | 1,790,325 | +0.94% | +0.77% | 4,606 | 398 |
| 3 | 3 | 3 | Marseille - Aix-en-Provence | 1,879,601 | 1,800,122 | 1,594,849 | +0.36% | +0.68% | 3,972 | 115 |
| 4 | 4 | 4 | Lille (French part) | 1,515,061 | 1,448,868 | 1,390,191 | +0.37% | +0.23% | 1,666 | 201 |
| 5 | 5 | 6 | Toulouse | 1,470,899 | 1,252,358 | 935,009 | +1.35% | +1.65% | 6,520 | 527 |
| 6 | 6 | 5 | Bordeaux | 1,376,375 | 1,171,456 | 986,179 | +1.35% | +0.97% | 6,316 | 275 |
| 7 | 7 | 7 | Nantes | 1,022,775 | 873,569 | 722,234 | +1.32% | +1.07% | 3,471 | 116 |
| 8 | 8 | 8 | Strasbourg (French part) | 860,744 | 805,611 | 704,238 | +0.55% | +0.76% | 2,227 | 268 |
| 9 | 10 | 13 | Montpellier | 813,272 | 680,929 | 501,936 | +1.49% | +1.73% | 2,414 | 161 |
| 10 | 12 | 12 | Rennes | 763,749 | 659,941 | 521,255 | +1.22% | +1.33% | 3,804 | 183 |
| 11 | 9 | 10 | Grenoble | 720,081 | 689,042 | 614,455 | +0.37% | +0.65% | 2,876 | 204 |
| 12 | 11 | 9 | Rouen | 708,289 | 680,844 | 646,549 | +0.33% | +0.29% | 2,792 | 317 |
| 13 | 13 | 11 | Nice[note 2] | 618,489 | 606,605 | 558,520 | +0.16% | +0.46% | 2,073 | 100 |
| 14 | 14 | 16 | Toulon | 576,648 | 542,008 | 481,466 | +0.52% | +0.67% | 1,004 | 35 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | Tours | 522,317 | 492,968 | 437,547 | +0.48% | +0.67% | 3,632 | 162 |
| 16 | 15 | 14 | Nancy | 508,947 | 510,668 | 496,486 | -0.03% | +0.16% | 3,121 | 353 |
| 17 | 18 | 18 | Clermont-Ferrand | 507,954 | 471,581 | 432,862 | +0.62% | +0.48% | 2,845 | 209 |
| 18 | 17 | 15 | Saint-Étienne | 500,851 | 483,053 | 491,789 | +0.30% | -0.10% | 1,636 | 105 |
| 19 | 19 | 19 | Caen | 475,144 | 446,464 | 399,635 | +0.52% | +0.62% | 2,597 | 296 |
| 20 | 20 | 20 | Orléans | 454,208 | 424,419 | 374,252 | +0.57% | +0.71% | 3,422 | 136 |
| 21 | 30 | 41 | Geneva - Annemasse (French part)[note 3] | 439,300 | 347,977 | 258,475 | +1.96% | +1.68% | 1,737 | 158 |
| 22 | 22 | 23 | Angers | 437,560 | 403,371 | 355,626 | +0.68% | +0.71% | 2,419 | 81 |
| 23 | 26 | 34 | Perpignan | 418,104 | 375,133 | 301,619 | +0.91% | +1.23% | 1,775 | 118 |
| 24 | 23 | 22 | Dijon | 413,996 | 394,820 | 365,025 | +0.40% | +0.44% | 3,896 | 333 |
| 25 | 21 | 21 | Mulhouse | 410,008 | 404,298 | 370,251 | +0.12% | +0.49% | 1,227 | 132 |
| 26 | 24 | 30 | Cannes - Antibes | 393,232 | 391,654 | 332,735 | +0.03% | +0.92% | 432 | 24 |
| 27 | 27 | 26 | Metz | 373,821 | 363,595 | 338,432 | +0.23% | +0.40% | 1,877 | 245 |
| 28 | 28 | 27 | Brest | 373,808 | 357,835 | 335,795 | +0.36% | +0.36% | 1,265 | 68 |
| 29 | 29 | 33 | Le Mans | 369,976 | 356,861 | 326,702 | +0.30% | +0.50% | 2,340 | 144 |
| 30 | 32 | 32 | Reims | 355,617 | 343,808 | 329,208 | +0.28% | +0.24% | 3,251 | 294 |
| 31 | 31 | 31 | Amiens | 354,217 | 346,294 | 329,927 | +0.19% | +0.27% | 3,076 | 369 |
| 32 | 25 | 25 | Fort-de-France | 347,170 | 380,831 | 340,815 | -0.77% | +0.62% | 974 | 28 |
| 33 | 39 | 40 | Nîmes | 347,033 | 315,480 | 259,675 | +0.80% | +1.10% | 1,468 | 92 |
| 34 | 34 | 28 | Valenciennes (French part) | 337,293 | 334,996 | 335,758 | +0.06% | -0.01% | 725 | 102 |
| 35 | 38 | 38 | Avignon | 337,039 | 317,744 | 272,025 | +0.49% | +0.88% | 964 | 48 |
See also
- List of metropolitan areas in Europe by population
- Larger Urban Zone
- Demographics of France
- Unité urbaine, a different statistical concept developed by INSEE, measuring contiguously built-up areas
Notes
- ↑ Plural: aires d'attraction des villes.[1]
- ↑ Does not include Cannes-Antibes, which is a considered by INSEE a separate AAV, contrary to the old aire urbaine of Nice which included Cannes and Antibes.
- ↑ French part of the Geneva Functional Urban Area (2,292 km2 (885 sq mi))[11] which extends over Swiss and French territory, and had a population of 1,044,766 in Jan. 2020 (Swiss estimates and French census), 605,466 of them on Swiss territory and 439,300 on French territory.[12]
References
- 1 2 "Le nouveau zonage en aires d'attraction des villes". INSEE. Retrieved 2022-04-26.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Functional areas - Definition". INSEE. Retrieved 2022-04-26.
- 1 2 "Aire d'attraction des villes - Définition". INSEE. Retrieved 2022-04-26.
- 1 2 "What is a city? - Spatial units". Eurostat. Retrieved 2022-04-26.
- ↑ "Qu'est-ce qu'une ville? — Unités spatiales". Eurostat. Retrieved 2022-04-26.
- ↑ INSEE. "France par aire d'attraction des villes - Population municipale 2020 >> Tableau". Retrieved 2023-03-09.
- ↑ INSEE. "France par aire d'attraction des villes - Population municipale (historique depuis 1876) 2008 >> Tableau". Retrieved 2022-04-27.
- ↑ INSEE. "France par aire d'attraction des villes - Population municipale 1990 >> Tableau". Retrieved 2022-04-27.
- ↑ INSEE. "Comparateur de territoire". Retrieved 2022-04-27.
- ↑ INSEE. "Base des aires d'attraction des villes 2020 au 1ᵉʳ janvier 2022". Retrieved 2022-04-29.
- ↑ As of 2020, the Eurostat-defined Functional Urban Area of Geneva was made up of 93 Swiss communes and 158 French communes: Federal Statistical Office spreadsheet listing the Swiss and French communes of the Geneva Functional Urban Area.
Land area of the 93 Swiss communes: 555.1 km² (source: ).
Land area of the 158 French communes: 1737.1 km² (source: ). - ↑ As of 2020, the Eurostat-defined Functional Urban Area of Geneva was made up of 93 Swiss communes and 158 French communes: Federal Statistical Office spreadsheet listing the Swiss and French communes of the Geneva Functional Urban Area.
Population of the 93 Swiss communes in January 2019: 605,466 (source: ).
Population of the 158 French communes in January 2019: 439,300 (source: ).