Godavari River Delta

Dowleswaram Barrage near Rajahmundry on River Godavari
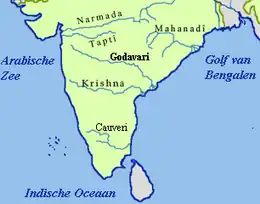
The Godavari River has its catchment area[1] in seven states of India: Maharashtra, Telangana, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Odisha. The number of dams constructed in Godavari basin is the highest among all the river basins in India.[2] Nearly 350 major and medium dams and barrages had been constructed in the river basin by the year 2012.[3][4][5]
- Jalaput
- Chintalapudi lift[6]
- Uttarrandhra Sujala Sravanthi lift[7]
- Balimela Reservoir
- Upper Kolab[8]
- Dummugudem Lift Irrigation Schemes
- Nizam Sagar
- Sriram Sagar or Pochampadu
- Kakatiya Canal
- SRSP Flood Flow Canal
- Manjara Dam
- Manjira Reservoir
- Singur Dam
- Shanigaram Reservoir
- Lower Manair Dam
- Mid Manair Dam
- Upper Manair Dam
- Yellampally
- Taliperu Project
- Babli barrage or Babhali
- Devadula lift irrigation project
- Polavaram Project
- Inchampalli Project
- Sadarmat[9]

Panoramic view of Alisagar lake.
- Alisagar lift irrigation scheme
- Kaddam
- Sri Komaram Bheem Project
- Lower Tirna
- Siddeshwar or Purna
- Yeldari Dam
- Godavari Canal
- Mula Dam
- Bhandardara Dam
- Isapur Dam or Upper Penganga
- Upper Dudhana Dam
- Jayakwadi or Paithan
- Upper Pravara
- Upper Indravati dam[10]
- Upper Wain Ganga (Bheemgarh Dam)[11]
- Upper Wardha Dam
- Lower Wardha Dam
- Majalgaon Dam
- Ghatghar Dam
- Upper Vaitarana Dam
- Vishnupuri Barrage[12][13]
- Sirpur Dam or Bagh reservoir
- Gosi kd Dam or Gosi Kund dam
- Totladoh Dam
- Yeldari Dam
- Kamthikhairy Dam or Pench dam
- Erai Dam
- Tultuli Dam
- Arunawati Dam
- Lower Wunna Dam or Wadgaon
- Manar Dam
- Lower Pus Dam
- Ramtek Dam
- Pench diversion Project, Madhya Pradesh[14]
See also
External links
- For Irrigation Projects in Maharashtra, refer to http://www.mahagovid.org/maha_dams.htm Archived 16 December 2004 at the Wayback Machine
- The Majalgaon dynamic regulation pilot project
- https://web.archive.org/web/20050404205051/http://ceamt.vidcngp.com/pro/index.htm
- https://web.archive.org/web/20050406062502/http://www.godavarimahamandal.com/
- For Irrigation Projects in Madhya Pradesh, refer to: http://www.mp.nic.in/wrd/Comp_Works/SRLD/SRLD_index.asp%5B%5D
- Godavari River Delta
- Godavari river water sharing accord
- Interstate river water disputes act - 1956 and its legal provisions
References
- ↑ "Godavari river basin map" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 October 2013. Retrieved 30 January 2012.
- ↑ "National register of dams in India" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2016. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- ↑ "Dams & barrages location map in India". Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 14 December 2012.
- ↑ "Head works (Dam, Barrage, Weir, Anicut, Lift)". Archived from the original on 28 May 2015. Retrieved 30 March 2016.
- ↑ "Major Medium Irrigation Projects in Godavari Basin". Water Resources Information System of India. Archived from the original on 19 July 2016.
- ↑ "Refer PPT file '11. CHLIS P (NSP)' for Chintalapudi lift". Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- ↑ "Uttarrandhra Sujala Sravanthi lift irrigation project". Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ↑ "Upper Kolab Dam D01660". Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ↑ "Sadarmat anicut in Adilabad stands the test of time". The Hindu. 9 September 2014. Retrieved 2 April 2016.
- ↑ "Indravati Power Station". Orissa Hydro power Corporation Ltd. Archived from the original on 17 November 2006.
- ↑ "अब कैसे मिलेगा पीने का पानी" [How now to get drinking water?]. Patrika Seoni News (in Hindi). 13 April 2016. Archived from the original on 21 July 2016.
- ↑ "Vishnupuri Barrage B00473". Water Resources Information System of India. 3 April 2014. Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ Vishnupuri Barrage location (Map). Archived from the original on 21 July 2016. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ "Pench Diversion Project JI00945". Retrieved 2 April 2016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.