Harstad Municipality
Harstad kommune Hársttáid suohkan | |
|---|---|
 Waterfront of Harstad | |
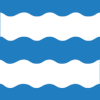 Flag | |
 Troms within Norway | |
 Harstad within Troms | |
| Coordinates: 68°48′00″N 16°32′45″E / 68.80000°N 16.54583°E | |
| Country | Norway |
| County | Troms |
| District | Central Hålogaland |
| Established | 1 January 1904 |
| • Preceded by | Trondenes Municipality |
| Administrative centre | Harstad |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2022) | Kari-Anne Opsal (Ap) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 445.29 km2 (171.93 sq mi) |
| • Land | 428.48 km2 (165.44 sq mi) |
| • Water | 16.79 km2 (6.48 sq mi) 3.8% |
| • Rank | #226 in Norway |
| Population (2023) | |
| • Total | 24,903 |
| • Rank | #49 in Norway |
| • Density | 58.1/km2 (150/sq mi) |
| • Change (10 years) | |
| Demonym | Harstadværing[1] |
| Official language | |
| • Norwegian form | Neutral |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | NO-5503[3] |
| Website | Official website |
ⓘ (Northern Sami: Hárstták[4]) is the second-most populated municipality in Troms county, Norway. It is mostly located on the large island of Hinnøya. The municipal center is the town of Harstad, which is the most populous town in Central Hålogaland and the third-largest in all of Northern Norway.[5][6] The town was incorporated in 1904. Villages in the municipality include Elgsnes, Fauskevåg, Gausvik, Grøtavær, Kasfjord, Lundenes, Nergården and Sørvika.
The 445-square-kilometre (172 sq mi) municipality is the 226th largest by area out of Norway's 356 municipalities and it is the 49th most populous with a population of 24,903. Its population density is 58.1 inhabitants per square kilometre (150/sq mi) and the population has increased by 2.5% over the previous 10-year period.[7][8]
Geography

The municipality is located on many islands in southern Troms og Finnmark county. Most of the municipality is located on the large island of Hinnøya, which is Norway's largest coastal island (three islands in the Svalbard archipelago are larger). The northern part of the municipality is located on the smaller islands of Grytøya, Bjarkøya, Sandsøya, Helløya, Flatøya and Krøttøya and many even smaller islands between the Andfjorden (to the west) and the Vågsfjorden (to the east). The municipality contains several small islands, including Arnøya, Gressholman, Helløya, Kjeøya, Kjøtta, Kjøttakalven, Flatøya, Meløyvær, Måga, Rogla, Lille Rogla and Åkerøya.
Harstad is bordered by the municipality Kvæfjord to the west and Tjeldsund (in Nordland county) to the south. To the southeast, the Tjeldsund Bridge connects Hinnøya with Skånland municipality and the mainland across Tjeldsundet, and to the northeast is the Vågsfjorden, where Harstad shares a water border with Ibestad municipality. The city itself is located on the northeastern part of on Hinnøya; it is the only city on the island, and is popularly known as Vågsfjordens perle (The pearl of Vågsfjorden).
The highest mountain in Harstad is Sætertinden, which is 1,095 m (3,593 ft) above sea level.[9] It is located near the village of Sandtorg in southern Harstad. The 412-metre (1,352 ft) tall mountain, Nupen, is located in the northwestern part of the municipality on the border with Kvæfjord.
Climate and light
Despite being located north of the Arctic Circle, Harstad features either a dry-summer subarctic climate (Köppen climate classification: Dsc), or (barely, by only half a degree C)[10] the rare cold-summer mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: Csc), depending on if the 0 °C (32 °F) or the −3 °C (27 °F) isotherm is used. Harstad features relatively mild, wet winters and cool, dry summers. Harstad does not have the brutal winters most locations north of the Arctic Circle experience, and is sheltered from Atlantic gales by mountains in the west, and has the main part of the Scandinavian Mountains to the east. The city experiences warmer winters than major cities located 25 degrees farther south in latitude such as Beijing, Chicago and Toronto. Summers in Harstad are cool, with average high temperatures seldom breaking the 22 °C (72 °F) mark. Since the weather station opened August 2002, July 2014 was the warmest month with mean 16.9 °C (62 °F), average daily high 21.8 °C (71 °F) and all-time high 31.7 °C (89 °F) on 10 July. The record low of −16.1 °C (3 °F) was recorded in February 2010. The coldest month recorded was January 2003 with mean −6.5 °C (20 °F) and average daily low −9.5 °C (15 °F). The city enjoys the midnight sun during the summer months, from 22 May to 18 July. There is also a period from early May to early August with twilight for a few hours each night as the sun just dips below the horizon, so there is no darkness. The polar night, when the sun is always below the horizon, lasts from 30 November to 12 January. At this time, there are 3–4 hours of dawn and dusk around noon, sometimes with colourful skies towards the south. From late January, the period of daylight rapidly increases, reaching 12 hours by March and 18 hours in April. Harstad is located in the midst of the aurora borealis (a.k.a. the northern lights) zone, and the aurora can often be seen on clear nights, but not in summer due to the continuous daylight.
| Climate data for Harstad (45 m, averages 2004–2018, extremes 2002–2023) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 8.8 (47.8) |
8.5 (47.3) |
10.9 (51.6) |
16.9 (62.4) |
23.9 (75.0) |
29.6 (85.3) |
31.7 (89.1) |
31.5 (88.7) |
21.9 (71.4) |
17.5 (63.5) |
13.8 (56.8) |
9.8 (49.6) |
31.7 (89.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −0.8 (30.6) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
1.8 (35.2) |
6 (43) |
10.5 (50.9) |
13.2 (55.8) |
17.2 (63.0) |
15.9 (60.6) |
12.3 (54.1) |
7 (45) |
3.3 (37.9) |
1.2 (34.2) |
7.3 (45.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −2.2 (28.0) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
3 (37) |
7.3 (45.1) |
10.2 (50.4) |
13.9 (57.0) |
12.9 (55.2) |
9.5 (49.1) |
5 (41) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
4.8 (40.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −4 (25) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
0.1 (32.2) |
4.1 (39.4) |
7.3 (45.1) |
10.5 (50.9) |
9.8 (49.6) |
6.8 (44.2) |
3 (37) |
0 (32) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
2.3 (36.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −15.4 (4.3) |
−16.1 (3.0) |
−13.3 (8.1) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
4.6 (40.3) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
−10.3 (13.5) |
−14.5 (5.9) |
−16.1 (3.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 85 (3.3) |
80 (3.1) |
65 (2.6) |
50 (2.0) |
35 (1.4) |
37 (1.5) |
53 (2.1) |
58 (2.3) |
80 (3.1) |
110 (4.3) |
97 (3.8) |
100 (3.9) |
850 (33.5) |
| Source 1: [11] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: [12] | |||||||||||||
History
The town of Harstad was established as a municipality on 1 January 1904 when it was separated from the municipality of Trondenes because it had just been declared a ladested (small seaport). The initial population of the town of Harstad was 1,246. During the 1960s, there were many municipal mergers across Norway due to the work of the Schei Committee. On 1 January 1964, the town of Harstad (population: 3,808) was merged with neighboring municipalities of Sandtorg (population: 7,512) and Trondenes (population: 6,567) to form a new, larger municipality of Harstad with a population of 17,882. Prior to the merger, the town of Harstad had 3,808 residents.[13] On 1 January 2013, the municipality of Bjarkøy (to the north) was merged with Harstad, forming a new, larger municipality of Harstad. On 1 January 2020, the municipality became part of the new Troms og Finnmark county which replaced the old Troms county. On 1 January 2024, the Troms og Finnmark county was divided and the municipality once again became part of Troms county.[14]
In recent years, a 3000-year-old bronze axe[15] and a 2600-year-old bronze collar[16] have been found at the Trondenes peninsula, just north of the city center. These, together with the burial cairns built close to the sea, are indications of a well-developed Bronze Age culture in the Harstad area.
There is also substantial archeological evidence of a well-developed Iron Age culture in the area, around 200 AD.
Trondenes is mentioned in the Heimskringla as a power centre in the Viking Age and a place to meet and discuss important issues (Trondarting). In 2020 archeologist concluded that Sandtorg, located along the Tjeldsundet strait, south of Harstad town, was the location of the only known Viking age trading place in Northern Norway.[17] The Tjeldsundet strait was very likely an important ship lane back then as it still is today.
Trondenes Church, the world's northernmost medieval church, which dates back to the 13th–15th century, is situated just outside the town.
Adjacent to the church is the Trondenes Historical Center and nearby is the Adolf Gun, an enormous land-based cannon from World War II, and the last of four cannons originally constructed by the Nazis. Harstad is one of the few towns in this part of Norway which were left largely undamaged by World War II.
 Sandtorg, where a trading place from the Viking age was located
Sandtorg, where a trading place from the Viking age was located Harstad Kulturhus (culture house)
Harstad Kulturhus (culture house) Rikard Kaarbø was the founder of Harstad.
Rikard Kaarbø was the founder of Harstad. Trondenes Church at Trondenes.
Trondenes Church at Trondenes. Northern part of Harstad at night, early August. View towards north-west from Gangsåstoppen
Northern part of Harstad at night, early August. View towards north-west from Gangsåstoppen
Origin of the name
The municipality (and town) is named after the old Harstad farm (Old Norse: Harðarstaðir), since the town is built where the farm once was located.[18] The first element is (probably) the genitive case of the male name Hǫrðr. The last element is staðir which means "homestead" or "farm".[18] On 6 February 2017, the municipality of Harstad adopted a co-equal Sami language name for the municipality: Hárstták. The Sami language name spelling changes depending on how it is used. It is called Hárstták when it is spelled alone, but it is Hársttáid suohkan when using the Sami language equivalent to "Harstad municipality".[4][19]
Coat of arms
The coat of arms was granted on 24 April 1953. The official blazon is "Azure, two bars wavy argent" (Norwegian: To bølgende sølv bjelker på blå bunn). This means the arms have a blue field (background) and the charge is two wavy bars. The bars have a tincture of argent which means they are commonly colored white, but if it is made out of metal, then silver is used. The blue color in the field symbolizes the importance of sea and the wavy bars were chosen to represent the waves in the sea. Since the town of Harstad is located in the municipality, a mural crown is typically shown above the shield. The arms were designed by Jardar Lunde in cooperation with Hallvard Træteberg.[20][21][22]
Government
All municipalities in Norway are responsible for primary education (through 10th grade), outpatient health services, senior citizen services, welfare and other social services, zoning, economic development, and municipal roads and utilities. The municipality is governed by a municipal council of directly elected representatives. The mayor is indirectly elected by a vote of the municipal council.[23] The municipality is under the jurisdiction of the Midtre Hålogaland District Court and the Hålogaland Court of Appeal.
Municipal council
The municipal council (Kommunestyre) of Harstad is made up of 35 representatives that are elected to four-year terms. The tables below show the current and historical composition of the council by political party.
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 11 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 6 | |
| Green Party (Miljøpartiet De Grønne) | 1 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 7 | |
| Industry and Business Party (Industri- og Næringspartiet) | 2 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 1 | |
| Red Party (Rødt) | 2 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 2 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 1 | |
| Total number of members: | 35 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 11 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 5 | |
| Green Party (Miljøpartiet De Grønne) | 2 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 6 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 1 | |
| Red Party (Rødt) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 6 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 1 | |
| Total number of members: | 35 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 13 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 8 | |
| Green Party (Miljøpartiet De Grønne) | 1 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 4 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 1 | |
| Red Party (Rødt) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 2 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 4 | |
| Total number of members: | 35 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 10 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 12 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 5 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 1 | |
| Red Party (Rødt) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 3 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 35 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 13 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 10 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 10 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 1 | |
| Red Electoral Alliance (Rød Valgallianse) | 2 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 4 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 1 | |
| Total number of members: | 43 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 14 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 8 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 7 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 2 | |
| Red Electoral Alliance (Rød Valgallianse) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 4 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 6 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 1 | |
| Total number of members: | 43 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 22 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 6 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 14 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 3 | |
| Red Electoral Alliance (Rød Valgallianse) | 2 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 3 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 3 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 55 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 22 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 5 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 16 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 3 | |
| Red Electoral Alliance (Rød Valgallianse) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 4 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 55 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 18 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 3 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 19 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 2 | |
| Red Electoral Alliance (Rød Valgallianse) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 4 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 6 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 55 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 20 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 7 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 18 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 2 | |
| Red Electoral Alliance (Rød Valgallianse) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 1 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 3 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 55 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 20 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 4 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 21 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 3 | |
| Red Electoral Alliance (Rød Valgallianse) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 1 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 3 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 55 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 20 | |
| Progress Party (Fremskrittspartiet) | 1 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 23 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 4 | |
| Red Electoral Alliance (Rød Valgallianse) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 2 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 55 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 19 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 22 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 5 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 4 | |
| Socialist Left Party (Sosialistisk Venstreparti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 55 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 24 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 19 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 2 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 4 | |
| Socialist People's Party (Sosialistisk Folkeparti) | 3 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 55 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 25 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 21 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 1 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 2 | |
| Socialist People's Party (Sosialistisk Folkeparti) | 2 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 4 | |
| Total number of members: | 55 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 27 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 18 | |
| Christian Democratic Party (Kristelig Folkeparti) | 2 | |
| Centre Party (Senterpartiet) | 2 | |
| Socialist People's Party (Sosialistisk Folkeparti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 5 | |
| Total number of members: | 55 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 9 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 17 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 29 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 10 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 15 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 29 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 10 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 10 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 3 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 4 | |
| Local List(s) (Lokale lister) | 1 | |
| Total number of members: | 28 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 9 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 9 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 6 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 4 | |
| Total number of members: | 28 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 7 | |
| Conservative Party (Høyre) | 6 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 9 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Joint List(s) of Non-Socialist Parties (Borgerlige Felleslister) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 28 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 8 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Joint list of the Conservative Party (Høyre) and the Free-minded People's Party (Frisinnede Folkeparti) | 12 | |
| List of workers, fishermen, and small farmholders (Arbeidere, fiskere, småbrukere liste) | 3 | |
| Local List(s) (Lokale lister) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 28 | |
| Note: Due to the German occupation of Norway during World War II, no elections were held for new municipal councils until after the war ended in 1945. | ||
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 10 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 4 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Joint list of the Conservative Party (Høyre) and the Free-minded People's Party (Frisinnede Folkeparti) | 8 | |
| Local List(s) (Lokale lister) | 3 | |
| Total number of members: | 28 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 8 | |
| Temperance Party (Avholdspartiet) | 1 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 6 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 5 | |
| Joint list of the Conservative Party (Høyre) and the Free-minded People's Party (Frisinnede Folkeparti) | 8 | |
| Total number of members: | 28 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 8 | |
| Temperance Party (Avholdspartiet) | 1 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 6 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 5 | |
| Joint list of the Conservative Party (Høyre) and the Free-minded Liberal Party (Frisinnede Venstre) | 6 | |
| Local List(s) (Lokale lister) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 28 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 7 | |
| Temperance Party (Avholdspartiet) | 4 | |
| Communist Party (Kommunistiske Parti) | 5 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Joint list of the Conservative Party (Høyre) and the Free-minded Liberal Party (Frisinnede Venstre) | 7 | |
| Local List(s) (Lokale lister) | 2 | |
| Total number of members: | 28 | |
| Party name (in Norwegian) | Number of representatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour Party (Arbeiderpartiet) | 5 | |
| Temperance Party (Avholdspartiet) | 4 | |
| Social Democratic Labour Party (Socialdemokratiske Arbeiderparti) |
1 | |
| Liberal Party (Venstre) | 3 | |
| Joint list of the Conservative Party (Høyre) and the Free-minded Liberal Party (Frisinnede Venstre) | 9 | |
| Joint List(s) of Non-Socialist Parties (Borgerlige Felleslister) | 6 | |
| Total number of members: | 28 | |
Mayors
The mayors (Norwegian: ordfører) of Harstad:[48][49]
- 1904–1906: Hans Buck (H)
- 1914–1916: Karl Eystein Kvam (V)
- 1929–1932: Israel Wulff (Ap)
- 1932–1935: Nils J. Hunstad (H)
- 1935–1938: Hans Stordahl (Ap)
- 1938–1940: Nils J. Hunstad (H)
- 1941–1945: Hans Methi (NS)
- 1945–1945: Odd Gangnæs (NS)
- 1945–1945: Alf Haaland (V)
- 1945–1945: Nils J. Hunstad (H)
- 1946–1947: Sigurd Simensen (NKP)
- 1948–1952: Sigurd Torgersen (Ap)
- 1952–1964: Leif Bothner (H)
- 1964–1968: Bjarne Berg-Sæther (Ap)
- 1968–1969: Leif Arne Heløe (H)
- 1970–1977: Arnljot Norwich (H)
- 1978–1987: Johan Nordvik (H)
- 1987–1993: Kjell Joachimsen (H)
- 1993–1995: Britt S. Nordlund (H)
- 1995–1998: Helge Aune (Ap)
- 1998–2007: Halvar Hansen (Ap)
- 2007–2011: Helge Eriksen (H)
- 2011–2019: Marianne Bremnes (Ap)
- 2019–present: Kari-Anne Opsal (Ap)
Economy
The oil industry of North Norway is centered in Harstad; including Statoil's main office for a new operational area for Northern Norway,[50] the DNV office for Northern Norway,[51] as well as other regional offices including TotalEnergies,[52] Det Norske Oljeselskap ASA[53] and Aibel.[54][55] Harstad also has shipyards and other industries that are important for the economy. Harstad and the surrounding area have traditionally been among the most productive agricultural regions in Northern Norway,.[56] The old seabed, now dry land due to isostatic rebound (up to 60 to 80 metres or 200 to 260 feet above sea level), creating fertile soil that is well-suited for farming.[57]

Institutions and culture

The city hosts the annual week-long Festival of North Norway in June.[58] It is also the home of the Arctic Moving Image and Film Festival, held in October each year.[59]
Harstad University College, with approximately 1,100 students,[60] has a thriving foreign exchange program with students from all over the world. The hospital in Harstad is part of the University Hospital of North Norway.
The most successful local football team is Harstad Idrettslag (a.k.a. HIL),[61] and the most successful basketball team is the Harstad Vikings.[62]
Harstad is home port for the Anna Rogde, the world's oldest sailing schooner, also known as the sailing queen of Norway.[63]
Harstad Camping is a campsite located in the municipality.
Churches
The Church of Norway has five parishes (sokn) within the municipality of Harstad. It is part of the Trondenes prosti (deanery) in the Diocese of Nord-Hålogaland.
| Parish (sokn) | Church name | Location of the church | Year built |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bjarkøy og Sandsøy | Bjarkøy Church | Nergården | 1766 |
| Sandsøy Church | Sandsøya | 1888 | |
| Grytøy | Grøtavær Church | Grøtavær | 1915 |
| Lundenes Church | Lundenes | 1974 | |
| Harstad | Harstad Church | Harstad | 1958 |
| Kanebogen | Kanebogen Church | Kanebogen | 1999 |
| Sandtorg | Gausvik Church | Gausvik | 1979 |
| Sandtorg Church | Sørvika | 1932 | |
| Trondenes | Trondenes Church | Trondenes | 15th century |
| Elgsnes Chapel | Elgsnes | 1985 |
Military connections
Harstad traditionally has strong ties with the Norwegian Armed Forces. Kystjegerkommandoen (Coastal Ranger Command) has its home base at Trondenes, Harstad. Marinejegerkommandoen is based in Ramsund in Tjeldsund on the mainland south of Harstad. General Carl Gustav Fleischer led the field operations of the Norwegian Armed Forces in WW2, among them the 7,500 soldiers which from the north pushed the Nazi Germans back to Narvik and participated in retaking Narvik on 28 May 1940. A street in Harstad is named Gen. Fleischers Gate in his honour.
Operation Judgement, Kilbotn took place on 4 May 1945, when the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy attacked a U-boat base at Kilbotn, a village in the Harstad district, sinking two ships and a U-boat.
Harstad is also the hometown of the Norwegian army band "Forsvarets Musikkorps Nord Norge" with professional musicians.
Transportation

The towns airport is Harstad/Narvik Airport, Evenes, located on the mainland, 44 kilometres (27 mi) by road from the town center. The airport offers daily flights to Oslo, Trondheim, Bodø, Tromsø and Andenes.[64]
Every morning a northbound and a southbound Hurtigruten ship stop in Harstad.[65]
High-speed craft regularly go between Harstad and Tromsø, Finnsnes, Senja and other places.[66]
There are several ferries and buses in the district, and in Harstad there are local buses.[66]
The leading helicopter company in Northern Norway, Heli-Team, is located in Harstad.[67]
Local areas


- Villages north/west of the city
Alvestad, Aune, Elgsnes, Ervik, Grøtavær, Hagan, Kasfjord, Kilhus, Kjøtta, Lundenes, Mustaparta, Nergården, Røkenes, Steinnes, Stornes, Storvassbotn, Sørlia, Tennvassåsen, Tømmeråsen, Undlandet, Vika and Årnes.
- City neighbourhoods
Bergseng, Blåbærhaugen, Breivika, City Center, Eineberget, Gangsås, Grønnebakkan, Harstadbotn, Harstadåsen, Heggen, Holtet, Kanebogen, Kilbotn, Medkila, Ruggevika, Sama, Seljestad, Skaret, Stangnes, Trondenes and Åsby.
- Villages south of the city
Brokvik, Fauskevåg, Gausvik, Halsebø, Haukebø, Melvik, Nordvik, Sandtorg and Sørvika.
 Northeastern part of Harstad seen from Eineberget; 4 May 2008
Northeastern part of Harstad seen from Eineberget; 4 May 2008 View from Harstad towards the Vågsfjord and Andørja island; May 2008
View from Harstad towards the Vågsfjord and Andørja island; May 2008 Harstad university college
Harstad university college
Notable people
Public Service
.jpg.webp)

- Andrew V. Stoltenberg (1865 in Aarnes – 1921) a US Navy recipient of the Medal of Honor
- Hans Egede (1686–1758) a Dano-Norwegian Lutheran missionary, the Apostle of Greenland
- Anders Holte (1849 in Oldra – 1937) a Norwegian sea captain and navigator
- Rikard Kaarbø (1850–1901) businessman and politician, established the town of Harstad
- John Bernhard Rekstad (1852 in Trondenes – 1934) a geologist and amateur photographer
- Erland Frisvold (1877–1971) a Norwegian colonel, civil engineer and Mayor of Harstad
- Paal Frisvold (1908–1997) a Norwegian general, head of the Norwegian Army 1961 to 1966
- Sverre Holm (1910–1996) a librarian, novelist, resistance member and sociologist
- Bjarne Berg-Sæther (1919–2009) Mayor of Harstad 1963 to 1967 & county mayor
- Hanna Kvanmo (1926–2005) a controversial Norwegian politician; convicted for treason after WWII and later a member of the Norwegian Nobel Committee
- Ola Heide (born 1931 in Trondenes) a Norwegian botanist.
- Leif Arne Heløe (born 1932) a Norwegian politician & former Minister of Social Affairs
- Pål Spilling (1934–2018) a Norwegian Internet pioneer and academic
- Ola M. Steinholt (1934—2009) a Norwegian bishop of the Diocese of Nord-Hålogaland
- Unni Wikan (born 1944), professor of social anthropology
- Gerd Kristiansen (born 1955) a licensed practical nurse and leader of the Norwegian Confederation of Trade Unions from 2013 to 2017
- Kristin Clemet (born 1957) a Norwegian politician & former Minister of Education
- Elisabeth Aspaker (born 1962) a Norwegian politician & former Minister of Fisheries
- Jon Lech Johansen (born 1983) also known as DVD Jon, a Norwegian computer programmer
- Silje Lundberg (born 1988) a Norwegian environmentalist, grew up in Harstad


The Arts
- Ragnhild Kaarbø (1889–1949) a Norwegian painter
- Knut Andersen (1931-2019) film director [68]
- Reidar Thomassen (born 1936) a Norwegian writer and javelin thrower
- Jan Høiland (1939–2017) a Norwegian pop singer, who lived for many years in Harstad
- Odd Børre (born 1939) a former pop singer, sang at the 1968 Eurovision Song Contest
- Leif Erik Forberg (born 1950) a Norwegian television and radio presenter
- Kine Hellebust (born 1954) a singer, actress, children's writer and playwright [69]
- Ketil Stokkan (born 1956) a pop singer, sang at the 1986 and the 1990 Eurovision Song Contest
- Iren Reppen (born 1965) a Norwegian actress [70]
- Bodil Arnesen (born 1967) a Norwegian operatic soprano
- Kari Innerå (born 1982) a Norwegian gourmet chef
- Iselin Steiro (born 1985) a Norwegian model
- Sophie Elise, (Norwegian Wiki) (born 1994), blogger and singer
- Ruben Markussen (born 1995) a Norwegian singer / songwriter; grew up in Bjarkøy
- Thea Floer Kulseng, (Norwegian Wiki) (born 2003), winner of Melodi Grand Prix Junior 2015
Sport
- Trygve Bornø (born 1942) a retired footballer with 419 club caps and 43 for Norway
- Knut Frostad (born 1967) a yachtsman, competed in the 1988 & 1992 Summer Olympics
- Marianne Paulsen (born 1980) a Norwegian football defender
- Tom Høgli (born 1984) a former football defender with 300 club caps and 49 for Norway
- Eirik Lamøy (born 1984) a Norwegian football striker with 300 club caps
International relations

Twin towns – Sister cities
The twin towns of Harstad are:[71]
See also
References
- ↑ "Navn på steder og personer: Innbyggjarnamn" (in Norwegian). Språkrådet.
- ↑ "Forskrift om målvedtak i kommunar og fylkeskommunar" (in Norwegian). Lovdata.no.
- ↑ Bolstad, Erik; Thorsnæs, Geir, eds. (26 January 2023). "Kommunenummer". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget.
- 1 2 "Stadnamn og rettskriving" (in Norwegian). Kartverket. Retrieved 19 November 2023.
- ↑ Municipality second largest in Troms county, by population
- ↑ City second largest in Troms county; third largest in Northern Norway
- ↑ Statistisk sentralbyrå. "Table: 06913: Population 1 January and population changes during the calendar year (M)" (in Norwegian).
- ↑ Statistisk sentralbyrå. "09280: Area of land and fresh water (km²) (M)" (in Norwegian).
- ↑ "Sætertinden".
- ↑ "MSN". www.msn.com. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ↑ "Infoclimat Harstad averages".
- ↑ "Eklima/met.no". Norwegian Meteorological Institute – extremes and precipitation Harstad Stadion. Archived from the original on 30 November 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2019.
- ↑ Jukvam, Dag (1999). "Historisk oversikt over endringer i kommune- og fylkesinndelingen" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Statistisk sentralbyrå.
- ↑ "Fylkesinndelingen fra 2024" (in Norwegian). Regjeringen.no. 5 July 2022.
- ↑ "Bronze axe". Archived from the original on 11 March 2007.
- ↑ "Bronze collar".
- ↑ David Nikel. "Viking Trading Place Discovered In Norway By Student Archaeologist". Forbes.com. Retrieved 27 March 2022.
- 1 2 Rygh, Oluf (1911). Norske gaardnavne: Troms amt (in Norwegian) (17 ed.). Kristiania, Norge: W. C. Fabritius & sønners bogtrikkeri. p. 21.
- ↑ "Harstad fikk samisk navn". NRK Nord-Norge (in Norwegian). 6 February 2017.
- ↑ "Civic heraldry of Norway - Norske Kommunevåpen". Heraldry of the World. Retrieved 26 January 2023.
- ↑ "Harstad, Troms (Norway)". Flags of the World. Retrieved 26 January 2023.
- ↑ "Forskrift for bruk av byvåpen" (PDF). Harstad kommune (in Norwegian). 9 February 1988. Retrieved 26 January 2023.
- ↑ Hansen, Tore; Vabo, Signy Irene, eds. (20 September 2022). "kommunestyre". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Kunnskapsforlaget. Retrieved 14 October 2022.
- ↑ "Kommunestyrevalg 2023 - Troms Romsa". Valgdirektoratet. Retrieved 6 January 2024.
- ↑ "Tall for Norge: Kommunestyrevalg 2019 – Troms og Finnmark". Valg Direktoratet. Retrieved 26 October 2019.
- 1 2 3 4 "Table: 04813: Members of the local councils, by party/electoral list at the Municipal Council election (M)" (in Norwegian). Statistics Norway.
- ↑ "Tall for Norge: Kommunestyrevalg 2011 – Troms Romsa". Valg Direktoratet. Retrieved 26 October 2019.
- ↑ "Kommunestyrevalget 1995" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo-Kongsvinger: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1996. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunestyrevalget 1991" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo-Kongsvinger: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1993. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunestyrevalget 1987" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo-Kongsvinger: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1988. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunestyrevalget 1983" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo-Kongsvinger: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1984. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunestyrevalget 1979" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1979. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene 1975" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1977. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene 1972" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1973. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene 1967" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1967. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene 1963" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1964. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1959" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1960. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1955" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1957. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1951" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1952. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1947" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1948. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1945" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1947. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1937" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1938. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1934" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1935. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1931" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1932. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1928" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1929. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1925" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1926. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ "Kommunevalgene og Ordførervalgene 1922" (PDF) (in Norwegian). Oslo: Statistisk sentralbyrå. 1923. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑ Simensen, S (1953). Harstad gjennom femti år (in Norwegian). Harstad: Harstad kommune. pp. 27–33.
- ↑ "Ordførere i Harstad" (in Norwegian). LokalHistorieWiki.no. Retrieved 22 February 2023.
- ↑ "New operational area in Northern Norway". Archived from the original on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 2 April 2012.
- ↑ "DNV increases Arctic focus, acquires Norwegian Petro Services". Offshore-mag.com. 2 May 2012. Retrieved 27 March 2022.
- ↑ "Total.no - Organisation". Archived from the original on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ "Det norske oljeselskap ASA". Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ "Multi-billion six year contract on Draugen — Aibel". Archived from the original on 23 October 2015. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ "Harstad — Aibel". Archived from the original on 22 October 2015. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ "Kvaefjord". Destinationharstad.no. Archived from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 27 March 2022.
- ↑ http://www.skogoglandskap.no/filearchive/Rapport_02_98.pdf%5B%5D
- ↑ "Festspillene i Nord-Norge". Archived from the original on 13 October 2004.
- ↑ "Arctic Moving Image and Film Festival".
- ↑ "Harstad University College".
- ↑ "HIL" (in Norwegian).
- ↑ "Harstad Vikings" (in Norwegian). Archived from the original on 15 March 2018. Retrieved 10 March 2006.
- ↑ "Anna Rogde" (in Norwegian).
- ↑ "Harstad/Narvik Lufthavn Evenes". supersaver.no. Retrieved 11 June 2011.
- ↑ "Coastal Express". hurtigruten.com. Retrieved 14 October 2011.
- 1 2 "Troms fylkestrafikk". tromskortet.no. Retrieved 30 June 2011.
- ↑ "Heli-Team". heliteam.no.
- ↑ IMDb Database retrieved 2 October 2020
- ↑ IMDb Database retrieved 2 October 2020
- ↑ IMDb Database retrieved 2 October 2020
- ↑ "Twin towns". Choose English > Political info > Friendship cities
External links
 Harstad travel guide from Wikivoyage
Harstad travel guide from Wikivoyage- Information in English Harstad municipality
- Visit Harstad
- Culture
- Old history of Harstad
- Harstad pictures
- Green and black aurora over Harstad NASA astronomy picture of the day
- Particularly rare purple auroral corona over Harstad NASA astronomy picture of the day
- Web-cam Showing various parts of the town
- Photo presentation on YouTube
- The Adolf Cannon
- Art of the States: Frozen Horizon Musical work inspired by the Harstad landscape
- Harstad Tidende (Harstad Times) Newspaper for the district (in Norwegian)
- iHarstad.no Information portal (in Norwegian)
- Live weather station located in Harstad (in Norwegian)
- About Hinnøy (in Norwegian)
- Magnars garden at 69 degrees north (in Norwegian)

