| Branch of glossopharyngeal nerve to carotid sinus | |
|---|---|
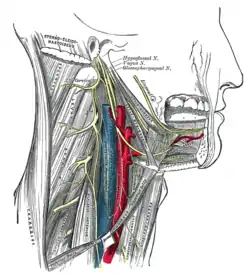 Hypoglossal nerve, cervical plexus and their branches (nerve not labeled, but region is visible) | |
| Details | |
| From | Glossopharyngeal nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Ramus sinus carotici nervi glossopharyngei |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.146 |
| TA2 | 6327 |
| FMA | 53488 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The carotid branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve (carotid sinus nerve or Hering's nerve) is a small branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX) that innervates the carotid sinus, and carotid body.
Anatomy
Course and relations
It runs downward anterior to the internal carotid artery. It communicates with the vagus nerve and sympathetic trunk before dividing in the angle of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery to innervate the carotid body, and carotid sinus.
Function
It conveys information from the baroreceptors of the carotid sinus to the vasomotor center in the brainstem (in order to mediate blood pressure homeostasis), and from chemoreceptors of the carotid body (mainly conveying information about partial pressures of blood oxygen, and carbon dioxide).
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 909 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 909 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (IX)
- "9-13". Cranial Nerves. Yale School of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03.