| Ophthalmic nerve | |
|---|---|
 Oblique section through the cavernous sinus. | |
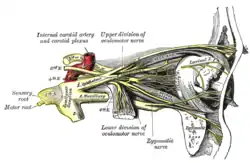 Nerves of the orbit, and the ciliary ganglion. Side view. | |
| Details | |
| From | trigeminal nerve |
| To | frontal nerve, lacrimal nerve, nasociliary nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | n. ophthalmicus |
| MeSH | D009882 |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.016 |
| TA2 | 6196 |
| FMA | 52621 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) is a sensory nerve of the head. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), a cranial nerve. It has three major branches which provide sensory innervation to the eye, and the skin of the upper face and anterior scalp, as well as other structures of the head.
Structure
It measures about 2.5 cm in length.
Origin
The ophthalmic nerve is the first branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), the first and smallest of its three divisions.[1] It arises from the superior part of the trigeminal ganglion.
Course
It passes anterior-ward along the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus inferior to the oculomotor nerve (CN III) and trochlear nerve (N IV).[1] It exits the skull into the orbit trough the superior orbital fissure.
Branches
Within the skull, the ophthalmic nerve produces:[1]
- meningeal branch (tentorial nerve)[1]
The ophthalmic nerve divides into three major branches which pass through the superior orbital fissure:[1]
Distribution
The ophthalmic nerve provides sensory innervation to the cornea, ciliary body, and iris; to the lacrimal gland and conjunctiva; to the part of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity; and to the skin of the eyelids, eyebrow, forehead and nose.
It carries sensory branches from the eyes, conjunctiva, lacrimal gland, nasal cavity, frontal sinus, ethmoidal cells, falx cerebri, dura mater in the anterior cranial fossa, superior parts of the tentorium cerebelli, upper eyelid, dorsum of the nose, and anterior part of the scalp.
Roughly speaking, the ophthalmic nerve supplies general somatic afferents to the upper face, head, and eye:
- Face: Upper eyelid and associated conjunctiva. Eyebrow, forehead, scalp all the way to the lambdoid suture.
- Skull: Roof of orbit, frontal, ethmoid, and possibly sphenoid sinuses.
- Eye: The eye itself (all the intraocular structures such as cornea) and the lacrimal gland and sac.
In comparison, the maxillary nerve (CN V2) provides general somatic afferents to the mid-face and mid-head.
Clinical significance
Damage to the ophthalmic nerve can cause loss of sensation of the structures it supplies in the face.[2] The corneal reflex may be lost, which can increase the risk of damage to the cornea.[2]
Additional images
 Nerves of the orbit. Seen from above.
Nerves of the orbit. Seen from above.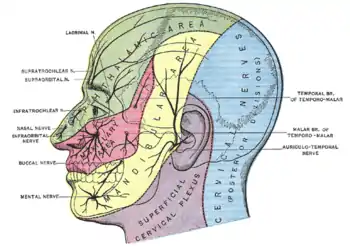 Dermatome distribution of the trigeminal nerve
Dermatome distribution of the trigeminal nerve Pathways in the ciliary ganglion.
Pathways in the ciliary ganglion. Ophthalmic nerve
Ophthalmic nerve Ophthalmic nerve
Ophthalmic nerve Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection. Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.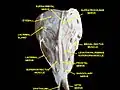 Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.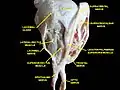 Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.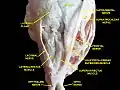 Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 887 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 887 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- 1 2 3 4 5 Essential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Head and Neck. Elsevier. 2016. pp. 58–59. doi:10.1016/c2014-0-05021-6. ISBN 978-0-12-803633-4.
- 1 2 Lin, Frank R.; Niparko, John K. (2009). "52 - Complications of Lateral Skull-Base Surgery". Complications in Head and Neck Surgery (2nd ed.). Mosby. pp. 689–701. doi:10.1016/B978-141604220-4.50056-0. ISBN 978-1-4160-4220-4.
External links
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb1.htm
- Atlas image: eye_33 at the University of Michigan Health System
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)