| History of Lebanon |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
|
|
The history of ancient Lebanon traces the course of events related to the geographic area in the Eastern Mediterranean of what is now known as Lebanon from the beginning of antiquity to the beginning of Arab rule.
Prehistoric times
The earliest known settlements in Lebanon date back to earlier than 5000 BC. In Byblos, which is considered to be the oldest continuously inhabited city in the world, archaeologists have discovered remnants of prehistoric huts with crushed limestone floors, primitive weapons, and burial jars which are evidence of the Neolithic and Chalcolithic fishing communities who lived on the shore of the Mediterranean Sea over 8,000 years ago.
Bronze Age
The area was first recorded in history around 4000 BC as a group of coastal cities and a heavily forested hinterland. It was inhabited by the Canaanites, a Semitic people, whom the Greeks called "Phoenicians" because of the purple (phoinikies) dye they sold. These early inhabitants referred to themselves as "men of Sidon" or the like, according to their city of origin. The Canaanites were city-state settlers, who established colonies throughout the Mediterranean (see: List of Phoenician cities) into a form of a Thalassocracy as opposed to an established empire with a designated capital city.
Each of the coastal cities was an independent city-state noted for the special activities of its inhabitants. Tyre and Sidon were important maritime and trade centers; Gubla (later known as Byblos; in Arabic, Jbeil) and Berytus (present-day Beirut) were trade and religious centers. Gubla was the first Canaanite city to trade actively with Egypt and the pharaohs of the Old Kingdom (2686-2181 BC), exporting cedar, olive oil, and wine, while importing gold and other products from the Nile Valley.
Before the end of the 17th century BC, Canaanite-Egyptian relations were interrupted when the Hyksos, a nomadic Semitic people, conquered Egypt. After about three decades of Hyksos rule (1600-1570 BC), Ahmose I (1570-1545 BC), Theban prince, launched the Egyptian liberation war. Opposition to the Hyksos increased, reaching a peak during the reign of the pharaoh Thutmose III (1490-1436 BC), who invaded the area now known as Syria, put an end to Hyksos domination, and incorporated Canaan into the Egyptian Empire.
Toward the end of the 14th century BC, the Egyptian Empire weakened, and the city-states were able to regain some of their autonomy by the beginning of the 12th century BC. The subsequent three centuries were a period of prosperity and freedom from foreign control during which the earlier Canaanite invention of the alphabet facilitated communications and trade. The Canaanites also excelled not only in producing textiles but also in carving ivory, in working with metal, and above all in making glass. Masters of the art of navigation, they founded colonies wherever they went in the Mediterranean Sea (specifically in Cyprus, Rhodes, Crete, and Carthage) and established trade routes to Europe and western Asia. These colonies and trade routes flourished until the invasion of the coastal areas by the Assyrians.
Middle Bronze
In the Middle Bronze IIA, the Beqa Valley was a high way for trade between the Kingdom of Qatna in the north and Kingdom of Hazor in the south. Hazor may have been subject to Qatna, meaning that the entire region was under influence of Qatna, with Kadesh facing the northern part of the valley. Trade routes went further to Mari on the Euphrates river. In the valley, Kamid el-Loz had a palace and temple, being a hub for trade routes going north-south and east-west. There were trade routes to Beirut, Sidon, Hazor, Damascus, Tell Hizzin and Baalbek.
Late Bronze
In the Late Bronze II, the Beqa Valley (Amqu) was controlled from Kamid el-Loz became the seat of an Egyptian governor. The northern part of the Beqa Valley consisted of pasture lands and functioned as a border region to Kadesh in the north. At first Syria was part of the Mitanni Empire, but following the military campaigns of Suppiluliuma I of Hatti (c. 1350 BC), Kadesh became a stronghold of the Hittite Empire facing the Egyptian Empire in the south. Literary evidence from this period is found in the Amarna Archive.
Iron Age II - Phoenicia
Assyrian Period
Assyrian rule (875-608 BC) deprived the Canaanite city-states of their independence and prosperity and brought repeated, unsuccessful rebellions. In the middle of the 8th century BC, Tyre and Byblos rebelled, but the Assyrian ruler, Tiglath-Pileser III, subdued the rebels and imposed heavy tributes. Oppression continued unabated, and Tyre rebelled again, this time against Sargon II (722-705 BC), who successfully besieged the city in 721 BC and punished its population. During the 7th century BC, the city of Sidon rebelled and was completely destroyed by Esarhaddon (681-668 BC); its inhabitants were enslaved. Esarhaddon built a new city on Sidon's ruins. By the end of the 7th century BC, the Assyrian Empire, weakened by the successive revolts, had been destroyed by the Median Empire.
Babylonian Period
As the Babylonians finally defeated the Assyrians at Carchemish, much of the region of Canaan was already in their hands, since much of it was seized from the collapsing Assyrian kingdom. In that time two Babylonian kings succeeded the throne, Nabopolassar who focused on ending Assyrian influence in the region, and his son Nebuchadnezzar II whose reign witnessed several regional rebellions, especially in Jerusalem. Revolts in Canaanite cities became more frequent during that period (685-636 BC, Tyre rebelled again and for thirteen years resisted a siege by the troops of Nebuchadnezzar 587-574 BC. After this long siege, the city capitulated; its king was dethroned, and its citizens were enslaved.
Persian Period - Achaemenid Empire
| Achaemenid Phoenicia | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of the Persian Empire | |||||||||||||
| c.538 BC–c.332 BC | |||||||||||||
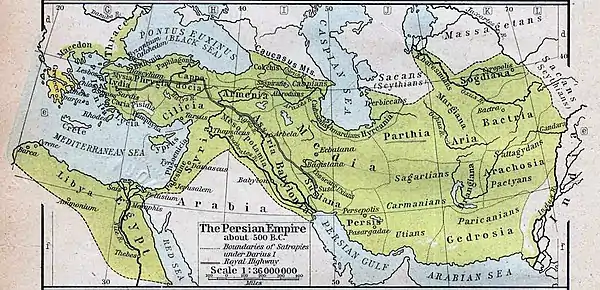 Phoenicia within The Achaemenid Empire, 500 BC. | |||||||||||||
| Historical era | Achaemenid Empire | ||||||||||||
| c.538 BC | |||||||||||||
| c.332 BC | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
The Babylonian province of Phoenicia and its neighbors passed to Achaemenid rule with the conquest of Babylon by Cyrus the Great in 539/8 BC. [1]
The Syro-Canaan coastal cities remained under Persian rule for the following two centuries. The Canaanite navy supported Persia during the Greco-Persian War (490-49 BC). But when the Canaanites were overburdened with heavy tributes imposed by the successors of Darius I (521-485 BC), revolts and rebellions resumed in the coastal city-states.
The Persian Empire, including the Canaan province, eventually fell to Alexander the Great, king of Macedonia in 4th century BC.
Main rulers under the Achaemenid Empire:

 The Lycian sarcophagus of Sidon, 430-420 BC.
The Lycian sarcophagus of Sidon, 430-420 BC.
Classical antiquity
Macedonian rule
The Persian Empire eventually fell to Alexander the Great, king of Macedon. He attacked Asia Minor, defeated the Persian troops in 333 BC, and advanced toward the eastern Mediterranean coast. Initially the Canaanite cities made no attempt to resist, and they recognized Alexander as suzerain. However, when Alexander tried to offer a sacrifice to Melqart, Tyre's god, the city resisted. Alexander besieged Tyre in retaliation in early 332 BC. After six months of resistance, the city fell, and its people were sold into slavery. Despite his early death in 323 BC, Alexander's conquest of the eastern Mediterranean Basin left a Greek imprint on the area. The Phoenicians, being a cosmopolitan people amenable to outside influences, adopted aspects of Greek civilization with ease.
The Seleucid Dynasty
After Alexander's death, his empire was divided among his Macedonian generals. The eastern part—Canaan, Asia Minor, northern Syria, and Mesopotamia fell to Seleucus I, founder of the Seleucid dynasty. The southern part of modern day Syria and modern day Egypt fell to Ptolemy, and the Balkan regions, including Macedonia, to Antigonus I. This settlement, however, failed to bring peace because Seleucus I and Ptolemy clashed repeatedly. A final victory of the Seleucids ended a forty-year period of conflict.
Roman rule
.JPG.webp)
The last century of Seleucid rule was marked by disorder and dynastic struggles. These ended in 64 BC, when the Roman general Pompey added Seleucid Syria and Canaan as a Roman province to the Roman Empire. Economic and intellectual activities flourished in Canaan during the Pax Romana. The inhabitants of the principal Canaanite city-states of Byblos, Sidon, and Tyre were granted Roman citizenship. These cities were centers of the pottery, glass, and purple dye industries; their harbors also served as warehouses for products imported from eastern regions such as Persia and India. They exported cedar, perfume, jewelry, wine, and fruit to Rome. Economic prosperity led to a revival in construction and urban development; temples and palaces were built throughout the country, as well as paved roads that linked the main cities like Heliopolis and Berytus.
Indeed, starting in the last quarter of the 1st century BCE (reign of Augustus) and over a period of two centuries (reign of Philip the Arab), the Romans built a huge temple complex in Heliopolis (actual Baalbek) on a pre-existing tell consisting of three temples: Jupiter, Bacchus and Venus. On a nearby hill, they built a fourth temple dedicated to Mercury.
Furthermore, the veterans of two Roman legions were established in the city of Berytus (actual Beirut): the fifth Macedonian and the third Gallic.[2] The city quickly became Romanized. Large public buildings and monuments were erected and Berytus enjoyed full status as a part of the empire.[3]
_19.jpg.webp)
Under the Romans, Berytus was enriched by the dynasty of Herod the Great, and was made a colonia, Colonia Iulia Augusta Felix Berytus, in 14 BC. Beirut's school of law was widely known at the time.[4] Two of Rome's most famous jurists, Papinian and Ulpian, both natives of Canaan, taught at the law school under the Severan emperors.
Furthermore, The city of Heliopolis was made a colonia by Septimius Severus in 193 AD, having been part of the territory of Berytus on the Canaanite coast since 15 BC. Work on the religious complex there lasted over a century and a half and was never completed. The dedication of the present temple ruins, the largest religious building in the entire Roman empire, dates from the reign of Septimus Severus, whose coins first show the two temples. The great courts of approach were not finished before the reigns of Caracalla (211-217 CE) and Philip the Arab (244-249 CE). In commemoration of the dedication of the new sanctuaries, Severus conferred the rights of the ius Italicum on the city. Today, only six Corinthian columns remain standing of this huge Jupiter temple.
Severus also separated the area of modern Lebanon and parts of Syria from the greater province of Syria Coele, and formed the new province of Phoenice.
Upon the death of Theodosius I in 395 AD, the Roman empire was ruled by 2 centres: the eastern or Eastern Roman part with its capital at Constantinople, and the western part with its capital at Rome. Under the Byzantine Empire, intellectual and economic activities in Beirut, Tyre, and Sidon continued to flourish for more than a century. However, in the late 6th century a series of earthquakes demolished the temples of Heliopolis and destroyed the Romanized city of Beirut, leveling its famous law school and killing nearly 30,000 inhabitants. To these natural disasters were added the abuses and corruptions prevailing at that time in the empire. Heavy tributes and religious dissension produced disorder and confusion. Furthermore, the ecumenical councils of the 5th and 6th centuries were unsuccessful in settling religious disagreements. This turbulent period weakened the empire and made it easy prey to the newly converted Muslim Arabs of the Arabian Peninsula that invaded the region in 642 AD.
See also
References
- ↑ http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+lb0015)
- ↑ Roman Berytus: a colony of legionaries
- ↑ About Beirut and Downtown Beirut, DownTownBeirut.com. Retrieved November 17, 2007.
- ↑ Beirut, Britannica.com
- This article is based on public-domain text from the Lebanon Country Study (1987) of the Library of Congress Country Studies project; specifically from Chapter 1: Historical Setting, by Afaf Sabeh McGowen.