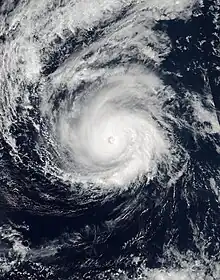
 Hurricane Madeline at peak intensity east of Hawaii on August 29 | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | August 26, 2016 |
| Dissipated | September 2, 2016 |
| Category 4 hurricane | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/NWS) | |
| Highest winds | 130 mph (215 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 950 mbar (hPa); 28.05 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | None |
| Damage | Minimal |
| Areas affected | Hawaii |
| IBTrACS / [1] | |
Part of the 2016 Pacific hurricane season | |
Hurricane Madeline was the first of two tropical cyclones that threatened to make a landfall on Hawaii as a hurricane in 2016, the other being Hurricane Lester. The fourteenth named storm, eighth hurricane and fifth major hurricane of the 2016 Pacific hurricane season, Madeline developed out of an area of low pressure that formed well to the south-southwest of Baja California. By August 26, the disturbance developed to a tropical depression, before becoming a tropical storm shortly afterwards. Wind shear initially inhibited development, however as the cyclone turned northwest, Madeline underwent rapid intensification as an eye feature developed within the storm on August 29. Madeline ultimately peaked as a Category 4 major hurricane the next day. The hurricane then began to weaken as wind shear began to increase as it approached Hawaii. By September 1, Madeline weakened to a tropical storm and passed just south of the Big Island of Hawaii, dumping heavy rainfall, surf, and gusty winds to the island. The cyclone eventually degenerated into a remnant low on September 2 before dissipating later that day.
In advance of both Madeline and Lester to its east, the state of Hawaii began to prepare for a potentially historic strike, possibly two, as the hurricanes approached. Hurricane warnings were issued for the Big Island in preparation for the imminent landfall. As Madeline approached, somewhat weaker than expected, a state of emergency was declared for the entire state of Hawaii still, with dozens of emergency shelters opening on the Big Island. Public schools were closed through September 1 due to the hurricane, and officials advised to stay off any roads and remain indoors if possible. Madeline brought less damage then expected, mainly due to its southward jog and missing the state as a tropical storm, however, areas of Hawaii still experienced heavy rainfall, flooding, storm surge and gusty winds at times.
Meteorological history
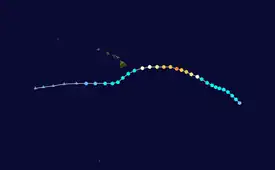
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
On August 22, the National Hurricane Center began to monitor a broad area of low pressure that formed about 1,000 mi (1,600 km) south-southwest of the southern tip of Baja California.[2] Over the next few days, the disturbance gradually organized as it tracked westward across the Pacific. Thunderstorm activity increased early on August 25,[3] and as the disturbance further coalesced into the following day, it is estimated that Tropical Depression Fourteen-E formed at 18:00 UTC on August 26, about 1,125 miles (1,811 km) east-southeast of the Big Island of Hawaii.[1] Convective banding features formed to the west of the cyclone, and the depression was later upgraded to Tropical Storm Madeline at 00:00 UTC on August 27. Moving northwestwards under the influence of being located at the southwestern periphery of a mid-level ridge, Madeline strengthened slowly in an environment of moderate wind shear, before crossing 140°W and entering the Central Pacific basin at 00:00 UTC on August 28, at which point the power of issuing advisories on tropical cyclone was transferred to the Central Pacific Hurricane Center.[1]

Once in the Central Pacific, Madeline changed little in intensity until 03:00 UTC on August 29, at which point Madeline began to undergo a period of rapid intensification as an eye feature developed in an organizing central dense overcast (CDO), and it was upgraded to a hurricane at 09:00 UTC that day.[4] Fueled by warm sea surface temperatures in excess of 27 °C (81 °F) and low wind shear, Madeline continued to rapidly strengthen, and by 21:00 UTC, it became a major hurricane – the fifth of the season.[5] The hurricane reached its peak intensity as a powerful Category 4 hurricane at 06:00 UTC the next day with winds of 130 mph (210 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 950 millibars (28 inHg).[1] By later that day, however, the cloud presentation of Madeline began to degrade as wind shear increased slightly due to an upper-level trough that was located near Hawaii, and by mid-day on August 30, as shown by an Air Force reconnaissance aircraft, the hurricane fell below major hurricane intensity by early on August 31 as it approached Hawaii.[6] Further weakening occurred and six hours later it had weakened to a Category 1 hurricane.[7] The eye later disappeared from satellite and reconnaissance data indicated that the low and mid-level centers were beginning to become elongated.[8] Later that day, the circulation became exposed from the convection as wind shear continued to impact the cyclone, and it eventually weakened to a tropical storm by early on September 1.[9] The deepest convection was pushed to the northeast of the center. Despite favorable sea surface temperatures, the wind shear continued to take its toll on Madeline, and although a new burst of convection over the center flared,[10] the tropical storm continued to further deteriorate in structure. Eventually, by late on September 2, Madeline opened up into a trough of low pressure south-southwest of Hawaii.[1]
Preparations and impact

As Madeline rapid intensified on August 29, posing a great threat to Hawaii, a hurricane watch was issued for Hawaii County.[11] A tropical storm warning and a tropical storm watch was issued for Hawaii County and Maui County respectively on the next day as Madeline moved closer to Hawaii.[12] The CPHC issued a hurricane warning for Hawaii County later that day, the first since Iselle in 2014.[13] The watches in Maui County was modified to tropical storm warning on August 31.[14] The hurricane warning was lowered to tropical storm warning later that day as Madeline weakened and failed to make a landfall in the state.[15] All warnings were discontinued on September 1 as Madeline weakened and moved away from the islands.[16]
Governor of Hawaii David Ige declared a state of emergency on August 30 as Madeline approached, subsequently citing that an emergency relief period be in effect from August 31 to September 9, in preparation of a possible impact from Hurricane Lester.[17][18] More than a dozen emergency shelters were opened by the American Red Cross of Hawaii to offer food, water and other essential supplies.[19] All public schools were closed on the Big Island through September 1 as Madeline approached.[20] Residents were also strongly advised to stay inside during the storm.[21] The Umauma Bridge (Route 19) was closed in both directions in anticipation of high winds impacting the bridge.[22]
Although Madeline did affect the Big Island, it did not make the major landfall that was anticipated by some meteorologists. Instead, a southwards jog of the system caused much less impacts then what were actually anticipated. Still, Madeline produced heavy rain and gusty winds on the Big Island. In multiple locations, wind gusts exceeded 40 mph (64 km/h), the highest reported being in Waimea, which recorded a peak gust of 60 mph (97 km/h).[23] Total rainfall accumulations amounted up to 5–11 inches (13–28 centimetres) across the Big Island. A few low-lying, flood-prone roads in Hilo were inundated briefly but no significant damages were reported.[24]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 John P. Cangialosi; Sam Houston; Tom Birchard (March 4, 2019). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Madeline" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Central Pacific Hurricane Center. Retrieved March 9, 2019.
- ↑ John Cangialosi (August 22, 2016). "NHC Graphical Outlook Archive". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 4, 2017.
- ↑ Michael Brennan (August 25, 2016). "NHC Graphical Outlook Archive". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 4, 2017.
- ↑ "Hurricane Madeline Discussion Number 11". Central Pacific Hurricane Center. August 29, 2016. Retrieved May 4, 2017.
- ↑ "Hurricane Madeline Discussion Number 13". Central Pacific Hurricane Center. August 29, 2016. Retrieved May 4, 2017.
- ↑ "Hurricane Madeline Discussion Number 18". Central Pacific Hurricane Center. August 30, 2016. Retrieved May 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Hurricane Madeline Special Discussion Number 19". Central Pacific Hurricane Center. August 31, 2016. Archived from the original on December 23, 2016. Retrieved May 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Hurricane Madeline Discussion Number 20". Central Pacific Hurricane Center. August 31, 2016. Archived from the original on December 23, 2016. Retrieved May 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Tropical Storm Madeline Discussion Number 23". Central Pacific Hurricane Center. September 1, 2016. Archived from the original on December 23, 2016. Retrieved May 5, 2017.
- ↑ "Tropical Storm Madeline Discussion Number 25". Central Pacific Hurricane Center. September 1, 2016. Archived from the original on December 23, 2016. Retrieved May 5, 2017.
- ↑ Tom Birchard (August 29, 2016). Hurricane Madeline Advisory Number 13. Central Pacific Hurricane Center (Report). Archived from the original on April 20, 2018. Retrieved April 20, 2018.
- ↑ Jeff Powell (August 30, 2016). Hurricane Madeline Advisory Number 16. Central Pacific Hurricane Center (Report). Archived from the original on April 21, 2018. Retrieved April 20, 2018.
- ↑ Derek Wroe (August 30, 2016). Hurricane Madeline Advisory Number 17. Central Pacific Hurricane Center (Report). Archived from the original on April 21, 2018. Retrieved April 20, 2018.
- ↑ Tom Birchard (August 31, 2016). Hurricane Madeline Advisory Number 21. Central Pacific Hurricane Center (Report). Archived from the original on April 20, 2018. Retrieved April 20, 2018.
- ↑ Derek Wroe (August 31, 2016). Hurricane Madeline Advisory Number 22. Central Pacific Hurricane Center (Report). Archived from the original on April 21, 2018. Retrieved April 20, 2018.
- ↑ Tom Birchard (September 1, 2016). Tropical Storm Madeline Advisory Number 25. Central Pacific Hurricane Center (Report). Archived from the original on April 21, 2018. Retrieved April 20, 2018.
- ↑ "Hawaii Governor Declares State of Emergency, Schools Close Ahead of Tropical Storm Madeline". weather.com. Archived from the original on 13 October 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
- ↑ David Ige (August 30, 2016). "OFFICE OF GOVERNOR STATE OF HAWAII" (PDF). Retrieved January 25, 2017.
- ↑ Staff, HNN. "Emergency shelters no longer open on the Big Island". hawaiinewsnow.com. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
- ↑ Staff, HNN. "LIST: Closures, changes due to Tropical Storm Madeline". hawaiinewsnow.com. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
- ↑ Arevalo, Elyssa; Namata, Brigette (29 August 2016). "Hawaii Island braces for effects of Hurricane Madeline". khon2.com. Archived from the original on 17 September 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
- ↑ "Department of Transportation - Umauma Bridge to temporarily close in anticipation of high winds". hidot.hawaii.gov. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
- ↑ Jonathan Belles (2 September 2016). "Hurricane Madeline Recap in the Pacific". Retrieved 15 June 2017.
- ↑ "August 2016 Precipitation Summary". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 8 September 2016. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
