
Skeletal formula of α-hydroxybutyric acid
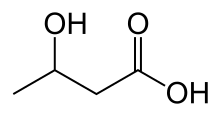
Skeletal formula of β-hydroxybutyric acid

Skeletal formula of γ-hydroxybutyric acid

Skeletal formula of 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid
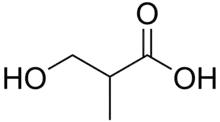
Skeletal formula of 3-hydroxyisobutyric acid
Hydroxybutyric acid is a group of four-carbon organic compounds that have both hydroxyl and carboxylic acid functional groups.[1] They can be viewed as derivatives of butyric acid. The carboxylate anion and the esters of hydroxybutyric acids are known as hydroxybutyrates. β-hydroxybutyric acid is relevant to human health as it is a member of a class of products of fatty acid oxidation referred to as ketone bodies.
The isomers are distinguished by the distance between the two functional groups and the branching.
- alpha-Hydroxybutyric acid (2-hydroxybutyric acid)
- beta-Hydroxybutyric acid (3-hydroxybutyric acid)
- gamma-Hydroxybutyric acid (4-hydroxybutyric acid, GHB)
- 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid
- 3-hydroxyisobutyric acid
See also
References
- ↑ Miltenberger, Karlheinz (2000). "Hydroxycarboxylic Acids, Aliphatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_507. ISBN 978-3527306732.
External links
- Hydroxybutyrates at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.