| IL1RAPL1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | IL1RAPL1, IL1R8, IL1RAPL, MRX10, MRX21, MRX34, OPHN4, TIGIRR-2, interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein like 1, IL-1RAPL-1, IL-1-RAPL-1, IL1RAPL-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 300206 MGI: 2687319 HomoloGene: 8609 GeneCards: IL1RAPL1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
X-linked interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein-like 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL1RAPL1 gene.[5][6][7] IL1RAPL1 is composed of 11 exons, about 1.37 Mb total.[8]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the interleukin-1 receptor family and is similar to the interleukin 1 accessory proteins. It is most closely related to interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein-like 2 (IL1RAPL2). [7]
Clinical significance
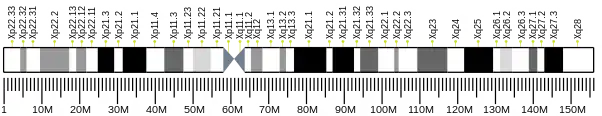
This gene and IL1RAPL2 are located at a region on chromosome X that is associated with X-linked non-syndromic mental retardation. Deletions and mutations in this gene were found in patients with mental retardation. This gene is expressed at a high level in post-natal brain structures involved in the hippocampal memory system, which suggests a specialized role in the physiological processes underlying memory and learning abilities.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000169306 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000052372 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Carrie A, Jun L, Bienvenu T, Vinet MC, McDonell N, Couvert P, Zemni R, Cardona A, Van Buggenhout G, Frints S, Hamel B, Moraine C, Ropers HH, Strom T, Howell GR, Whittaker A, Ross MT, Kahn A, Fryns JP, Beldjord C, Marynen P, Chelly J (Sep 1999). "A new member of the IL-1 receptor family highly expressed in hippocampus and involved in X-linked mental retardation". Nat Genet. 23 (1): 25–31. doi:10.1038/12623. PMID 10471494. S2CID 38236297.
- ↑ Jin H, Gardner RJ, Viswesvaraiah R, Muntoni F, Roberts RG (May 2000). "Two novel members of the interleukin-1 receptor gene family, one deleted in Xp22.1-Xp21.3 mental retardation". Eur J Hum Genet. 8 (2): 87–94. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200415. PMID 10757639. S2CID 22262168.
- 1 2 3 "Entrez Gene: IL1RAPL1 interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein-like 1".
- ↑ "OMIM Entry - * 300206 - INTERLEUKIN 1 RECEPTOR ACCESSORY PROTEIN-LIKE 1; IL1RAPL1". www.omim.org. Retrieved 2020-12-05.
Further reading
- Kozák L, Chiurazzi P, Genuardi M, et al. (1993). "Mapping of a gene for non-specific X linked mental retardation: evidence for linkage to chromosomal region Xp21.1-Xp22.3". J. Med. Genet. 30 (10): 866–9. doi:10.1136/jmg.30.10.866. PMC 1016571. PMID 8230164.
- Tranebjaerg L, Lubs HA, Borghgraef M, et al. (1996). "Seventh International Workshop on the Fragile X and X-linked Mental Retardation". Am. J. Med. Genet. 64 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960712)64:1<1::AID-AJMG1>3.0.CO;2-Z. PMID 8826442.
- Liu C, Chalmers D, Maki R, De Souza EB (1996). "Rat homolog of mouse interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein: cloning, localization and modulation studies". J. Neuroimmunol. 66 (1–2): 41–8. doi:10.1016/0165-5728(96)00016-1. PMID 8964912. S2CID 3797569.
- Born TL, Smith DE, Garka KE, et al. (2000). "Identification and characterization of two members of a novel class of the interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) family. Delineation of a new class of IL-1R-related proteins based on signaling". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (39): 29946–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004077200. PMID 10882729.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2001). "DNA Cloning Using In Vitro Site-Specific Recombination". Genome Res. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Kitano T, Schwarz C, Nickel B, Pääbo S (2004). "Gene diversity patterns at 10 X-chromosomal loci in humans and chimpanzees". Mol. Biol. Evol. 20 (8): 1281–9. doi:10.1093/molbev/msg134. PMID 12777533.
- Bahi N, Friocourt G, Carrié A, et al. (2004). "IL1 receptor accessory protein like, a protein involved in X-linked mental retardation, interacts with Neuronal Calcium Sensor-1 and regulates exocytosis". Hum. Mol. Genet. 12 (12): 1415–25. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddg147. PMID 12783849.
- Khan JA, Brint EK, O'Neill LA, Tong L (2004). "Crystal structure of the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain of human IL-1RAPL". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (30): 31664–70. doi:10.1074/jbc.M403434200. PMID 15123616.
- Zhang YH, Huang BL, Niakan KK, et al. (2005). "IL1RAPL1 is associated with mental retardation in patients with complex glycerol kinase deficiency who have deletions extending telomeric of DAX1". Hum. Mutat. 24 (3): 273. doi:10.1002/humu.9269. PMID 15300857. S2CID 7885220.
- Tabolacci E, Pomponi MG, Pietrobono R, et al. (2006). "A truncating mutation in the IL1RAPL1 gene is responsible for X-linked mental retardation in the MRX21 family". Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 140 (5): 482–7. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.31107. PMID 16470793. S2CID 23607874.