| ING3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | ING3, Eaf4, ING2, MEAF4, p47inhibitor of growth family member 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 607493 MGI: 1919027 HomoloGene: 6804 GeneCards: ING3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Inhibitor of growth protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ING3 gene.[5][6]
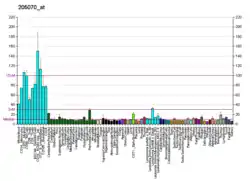
The protein encoded by this gene is similar to ING1, a tumor suppressor protein that can interact with TP53, inhibit cell growth, and induce apoptosis. This protein contains a PHD finger, which is a common motif in proteins involved in chromatin remodeling. This gene can activate p53 trans-activated promoters, including promoters of p21/waf1 and bax. Overexpression of this gene has been shown to inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis. Allelic loss and reduced expression of this gene were detected in head and neck cancers. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been observed.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000071243 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000029670 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Gunduz M, Ouchida M, Fukushima K, Ito S, Jitsumori Y, Nakashima T, Nagai N, Nishizaki K, Shimizu K (Jun 2002). "Allelic loss and reduced expression of the ING3, a candidate tumor suppressor gene at 7q31, in human head and neck cancers". Oncogene. 21 (28): 4462–70. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205540. PMID 12080476.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: ING3 inhibitor of growth family, member 3".
Further reading
- Doyon Y, Côté J (2004). "The highly conserved and multifunctional NuA4 HAT complex". Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 14 (2): 147–54. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2004.02.009. PMID 15196461.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Sanger Centre, The; Washington University Genome Sequencing Cente, The (1999). "Toward a complete human genome sequence". Genome Res. 8 (11): 1097–108. doi:10.1101/gr.8.11.1097. PMID 9847074.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Nagashima M, Shiseki M, Pedeux RM, et al. (2003). "A novel PHD-finger motif protein, p47ING3, modulates p53-mediated transcription, cell cycle control, and apoptosis". Oncogene. 22 (3): 343–50. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206115. PMID 12545155.
- Hillier LW, Fulton RS, Fulton LA, et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 7". Nature. 424 (6945): 157–64. Bibcode:2003Natur.424..157H. doi:10.1038/nature01782. PMID 12853948.
- Cai Y, Jin J, Tomomori-Sato C, et al. (2003). "Identification of new subunits of the multiprotein mammalian TRRAP/TIP60-containing histone acetyltransferase complex". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (44): 42733–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.C300389200. PMID 12963728.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Doyon Y, Selleck W, Lane WS, et al. (2004). "Structural and functional conservation of the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex from yeast to humans". Mol. Cell. Biol. 24 (5): 1884–96. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.5.1884-1896.2004. PMC 350560. PMID 14966270.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Cai Y, Jin J, Florens L, et al. (2005). "The mammalian YL1 protein is a shared subunit of the TRRAP/TIP60 histone acetyltransferase and SRCAP complexes". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (14): 13665–70. doi:10.1074/jbc.M500001200. PMID 15647280.
- Wang Y, Dai DL, Martinka M, Li G (2007). "Prognostic significance of nuclear ING3 expression in human cutaneous melanoma". Clin. Cancer Res. 13 (14): 4111–6. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0408. PMID 17634537.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.