Interleukin 7 (IL-7) is a protein[5] that in humans is encoded by the IL7 gene.[6][7][8]
IL-7 is a hematopoietic growth factor secreted by stromal cells in the bone marrow and thymus. It is also produced by keratinocytes,[9] dendritic cells,[10] hepatocytes,[11] neurons, and epithelial cells,[12] but is not produced by normal lymphocytes.[13] A study also demonstrated how the autocrine production of the IL-7 cytokine mediated by T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) can be involved in the oncogenic development of T-ALL and offer novel insights into T-ALL spreading. [14]
Structure
The three-dimensional structure of IL-7 in complex with the ectodomain of IL-7 receptor has been determined using X-ray diffraction.[15]
Function
Lymphocyte maturation
IL-7 stimulates the differentiation of multipotent (pluripotent) hematopoietic stem cells into lymphoid progenitor cells (as opposed to myeloid progenitor cells where differentiation is stimulated by IL-3). It also stimulates proliferation of all cells in the lymphoid lineage (B cells, T cells and NK cells). It is important for proliferation during certain stages of B-cell maturation, T and NK cell survival, development and homeostasis.
IL-7 is a cytokine important for B and T cell development. This cytokine and the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) form a heterodimer that functions as a pre-pro-B cell growth-stimulating factor. This cytokine is found to be a cofactor for V(D)J rearrangement of the T cell receptor beta (TCRß) during early T cell development.[16] This cytokine can be produced locally by intestinal epithelial and epithelial goblet cells, and may serve as a regulatory factor for intestinal mucosal lymphocytes. Knockout studies in mice suggested that this cytokine plays an essential role in lymphoid cell survival.[17]
IL-7 signaling
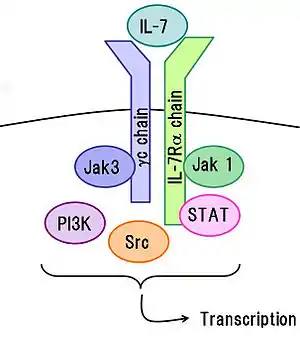
IL-7 binds to the IL-7 receptor, a heterodimer consisting of Interleukin-7 receptor alpha and common gamma chain receptor.[18] Binding results in a cascade of signals important for T-cell development within the thymus and survival within the periphery. Knockout mice which genetically lack IL-7 receptor exhibit thymic atrophy, arrest of T-cell development at the double positive stage, and severe lymphopenia. Administration of IL-7 to mice results in an increase in recent thymic emigrants, increases in B and T cells, and increased recovery of T cells after cyclophosphamide administration or after bone marrow transplantation.
Disease
Cancer
IL-7 promotes hematological malignancies (acute lymphoblastic leukemia, T cell lymphoma).[19]
Viral Infections
Elevated levels of IL-7 have also been detected in the plasma of HIV-infected patients.[20]
Clinical application
IL-7 as an immunotherapy agent has been examined in many pre-clinical animal studies and more recently in human clinical trials for various malignancies and during HIV infection.[13][21]
Cancer
Recombinant IL-7 has been safely administered to patients in several phase I and II clinical trials. A human study of IL-7 in patients with cancer demonstrated that administration of this cytokine can transiently disrupt the homeostasis of both CD8+ and CD4+ T cells with a commensurate decrease in the percentage of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T regulatory cells.[22] No objective cancer regression was observed, however a dose limiting toxicity (DLT) was not reached in this study due to the development of neutralizing antibodies against the recombinant cytokine.
HIV infection
Associated with antiretroviral therapy, IL-7 administration decreased local and systemic inflammations in patients that had incomplete T-cell reconstitution. These results suggest that IL-7 therapy can possibly improve the quality of life of those patients.[23]
Transplantation
IL-7 could also be beneficial in improving immune recovery after allogenic stem cell transplant.[24]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000104432 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000040329 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Namen AE, Lupton S, Hjerrild K, Wignall J, Mochizuki DY, Schmierer A, Mosley B, March CJ, Urdal D, Gillis S (June 1988). "Stimulation of B-cell progenitors by cloned murine interleukin-7". Nature. 333 (6173): 571–3. Bibcode:1988Natur.333..571N. doi:10.1038/333571a0. PMID 3259677. S2CID 4315541.
- ↑ Goodwin RG, Lupton S, Schmierer A, Hjerrild KJ, Jerzy R, Clevenger W, Gillis S, Cosman D, Namen AE (January 1989). "Human interleukin 7: molecular cloning and growth factor activity on human and murine B-lineage cells". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86 (1): 302–6. Bibcode:1989PNAS...86..302G. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.1.302. PMC 286452. PMID 2643102.
- ↑ Sutherland GR, Baker E, Fernandez KE, Callen DF, Goodwin RG, Lupton S, Namen AE, Shannon MF, Vadas MA (July 1989). "The gene for human interleukin 7 (IL7) is at 8q12-13". Hum. Genet. 82 (4): 371–2. doi:10.1007/BF00274000. PMID 2786840. S2CID 30870920.
- ↑ Lupton SD, Gimpel S, Jerzy R, et al. (1990). "Characterization of the human and murine IL-7 genes". J. Immunol. 144 (9): 3592–601. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.144.9.3592. PMID 2329282. S2CID 36007598.
- ↑ Heufler C, Topar G, Grasseger A, et al. (September 1993). "Interleukin 7 is produced by murine and human keratinocytes". J. Exp. Med. 178 (3): 1109–14. doi:10.1084/jem.178.3.1109. PMC 2191157. PMID 8350050.
- ↑ Kröncke R, Loppnow H, Flad HD, Gerdes J (October 1996). "Human follicular dendritic cells and vascular cells produce interleukin-7: a potential role for interleukin-7 in the germinal center reaction". Eur. J. Immunol. 26 (10): 2541–4. doi:10.1002/eji.1830261040. PMID 8898972. S2CID 20992591.
- ↑ Sawa Y, Arima Y, Ogura H, et al. (March 2009). "Hepatic interleukin-7 expression regulates T cell responses". Immunity. 30 (3): 447–57. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.01.007. PMID 19285437.
- ↑ Watanabe M, Ueno Y, Yajima T, et al. (1995). "Interleukin 7 is produced by human intestinal epithelial cells and regulates the proliferation of intestinal mucosal lymphocytes". J. Clin. Invest. 95 (6): 2945–53. doi:10.1172/JCI118002. PMC 295983. PMID 7769137.
- 1 2 Fry TJ, Mackall CL (June 2002). "Interleukin-7: from bench to clinic". Blood. 99 (11): 3892–904. doi:10.1182/blood.V99.11.3892. PMID 12010786.
- ↑ Buffière A, Uzan B, Aucagne R, Hermetet F, Mas M, Nassurdine S, Aznague A, Carmignac V, Tournier B, Bouchot O, Ballerini P, Barata JT, Bastie JN, Delva L, Pflumio F, Quéré R (November 2019). "T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia displays autocrine production of Interleukin-7". Oncogene. 38 (1): 7357–7365. doi:10.1038/s41388-019-0921-4. PMID 31417180. S2CID 199668368.
- ↑ McElroy CA, Dohm JA, Walsh ST (January 2009). "Structural and biophysical studies of the human IL-7/IL-7Ralpha complex". Structure. 17 (1): 54–65. doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.10.019. PMC 2654238. PMID 19141282.
- ↑ Muegge K, Vila MP, Durum SK (July 1993). "Interleukin-7: a cofactor for V(D)J rearrangement of the T cell receptor beta gene". Science. 261 (5117): 93–5. Bibcode:1993Sci...261...93M. doi:10.1126/science.7686307. PMID 7686307.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: IL7 interleukin 7".
- ↑ Noguchi M, Nakamura Y, Russell SM, et al. (1994). "Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain: a functional component of the interleukin-7 receptor". Science. 262 (5141): 1877–80. Bibcode:1993Sci...262.1877N. doi:10.1126/science.8266077. PMID 8266077.
- ↑ Or R, Abdul-Hai A, Ben-Yehuda A (December 1998). "Reviewing the potential utility of interleukin-7 as a promoter of thymopoiesis and immune recovery". Cytokines Cell. Mol. Ther. 4 (4): 287–94. PMID 10068062.
- ↑ Napolitano LA, Grant RM, Deeks SG, et al. (January 2001). "Increased production of IL-7 accompanies HIV-1-mediated T-cell depletion: implications for T-cell homeostasis". Nat. Med. 7 (1): 73–9. doi:10.1038/83381. PMID 11135619. S2CID 22536639.
- ↑ Fry TJ, Mackall CL (2003). "Interleukin-7 and immunorestoration in HIV: beyond the thymus". J. Hematother. Stem Cell Res. 11 (5): 803–7. doi:10.1089/152581602760404603. PMID 12427286.
- ↑ Rosenberg SA, Sportès C, Ahmadzadeh M, Fry TJ, Ngo LT, Schwarz SL, Stetler-Stevenson M, Morton KE, Mavroukakis SA, Morre M, Buffet R, Mackall CL, Gress RE (2006). "IL-7 administration to humans leads to expansion of CD8+ and CD4+ cells but a relative decrease of CD4+ T-regulatory cells". J. Immunother. 29 (3): 313–9. doi:10.1097/01.cji.0000210386.55951.c2. PMC 1473976. PMID 16699374.
- ↑ Sereti I, Estes JD, Thompson WL, Morcock DR, Fischl MA, et al. (2014). "Decreases in Colonic and Systemic Inflammation in Chronic HIV Infection after IL-7 Administration". PLOS Pathogens. 10 (1): e1003890. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003890. PMC 3907377. PMID 24497828.
- ↑ Snyder KM, Mackall CL, Fry TJ (July 2006). "IL-7 in allogeneic transplant: clinical promise and potential pitfalls". Leuk. Lymphoma. 47 (7): 1222–8. doi:10.1080/10428190600555876. PMID 16923550. S2CID 20531769.
Further reading
- Möller P, Böhm M, Czarnetszki BM, Schadendorf D (1997). "Interleukin-7. Biology and implications for dermatology". Exp. Dermatol. 5 (3): 129–37. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.1996.tb00107.x. PMID 8840152. S2CID 20874926.
- Appasamy PM (1999). "Biological and clinical implications of interleukin-7 and lymphopoiesis". Cytokines Cell. Mol. Ther. 5 (1): 25–39. PMID 10390077.
- Al-Rawi MA, Mansel RE, Jiang WG (2004). "Interleukin-7 (IL-7) and IL-7 receptor (IL-7R) signalling complex in human solid tumours". Histol. Histopathol. 18 (3): 911–23. PMID 12792903.
- Aspinall R, Henson S, Pido-Lopez J, Ngom PT (2004). "Interleukin-7: an interleukin for rejuvenating the immune system". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1019 (1): 116–22. Bibcode:2004NYASA1019..116A. doi:10.1196/annals.1297.021. PMID 15247003. S2CID 8931092.
- Sica D, Rayman P, Stanley J, et al. (1993). "Interleukin 7 enhances the proliferation and effector function of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from renal-cell carcinoma". Int. J. Cancer. 53 (6): 941–7. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910530613. PMID 8473051. S2CID 41223517.
- Kim JH, Loveland JE, Sitz KV, et al. (1997). "Expansion of restricted cellular immune responses to HIV-1 envelope by vaccination: IL-7 and IL-12 differentially augment cellular proliferative responses to HIV-1". Clin. Exp. Immunol. 108 (2): 243–50. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2249.1997.d01-1006.x. PMC 1904649. PMID 9158092.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.