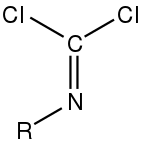
An isocyanide dichloride.
Isocyanide dichlorides are organic compounds containing the RN=CCl2 functional group. Classically they are obtained by chlorination of isocyanides. Phenylcarbylamine chloride is a well-characterized example.
Preparation and reactions
Chlorination of organic isothiocyanates is also well established:[1]
- RN=C=S + 2 Cl2 → RN=CCl2 + SCl2
Alkylisocyanates are chlorinated by phosphorus pentachloride:
- RN=C=O + PCl5 → RN=CCl2 + POCl3
Cyanogen chloride also chlorinates to give the isocyanide dichloride:[1]
- ClCN + Cl2 → ClN=CCl2
Reactions
Isocyanide dichlorides participate in Friedel-Crafts-like reactions, leading, after hydrolysis, to benzamides:
- RN=CCl2 + ArH → RN=C(Cl)Ar + HCl
- RN=C(Cl)Ar + H2O → R(H)NC(O)Ar + HCl
References
- 1 2 R. G. Guy (1977). "Syntheses and Preparative Applications of Thiocyanates". In Saul Patai (ed.). Cyanates and Their Thio Derivatives: Part 2, Volume 2. PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups. p. 619-818. doi:10.1002/9780470771532.ch2. ISBN 9780470771532.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.