James Mayer de Rothschild | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) Portrait by Jean-Hippolyte Flandrin | |
| Born | Jakob Mayer Rothschild 15 May 1792 |
| Died | 15 November 1868 (aged 76) |
| Known for | Rothschild banking family of France Château Lafite Rothschild |
| Spouse | |
| Children | Charlotte, Mayer Alphonse, Gustave Samuel, Salomon James, Edmond Benjamin |
| Parent(s) | Mayer Amschel Rothschild Guttle Schnapper |
| Awards | Baron of the Austrian Empire |
Baron James Mayer de Rothschild (born Jakob Mayer Rothschild; 15 May 1792 – 15 November 1868) was a German-French banker and the founder of the French branch of the prominent Rothschild family.[1][2]
Early life
He was born as Jakob Mayer Rothschild in Frankfurt am Main, then part of the Holy Roman Empire. He was the fifth son and youngest child of Mayer Amschel Rothschild (1744–1812) and his wife, Guttle Schnapper (1753–1849).[3]
Career
In 1812, he moved to Paris to co-ordinate the purchase of specie and bullion for his brother Nathan Mayer Rothschild (1777–1836), and in 1814 and 1815, he was the linchpin in Nathan's plan to furnish Wellington's armies with funds. In 1817, he expanded his family's banking empire to Paris, opening De Rothschild Frères. By 1823, the Parisian branch was firmly established as banker to the French government.
An adviser of ministers and kings, he became the most powerful banker in the country. Following the Napoleonic Wars, he played a major role in financing the construction of railroads and the mining business that helped make France an industrial power. Along the way, he added to his fortune with investments in such things as the importation of tea and the wine industry. A strong-willed and shrewd businessman, de Rothschild amassed a fortune that made him one of the richest men in the world.
In 1822, de Rothschild, along with his four brothers, was awarded the hereditary title of Freiherr (Baron) by Emperor Francis I of Austria. That same year, he was appointed consul-general of the Austrian Empire. In 1823, he was awarded the French Legion of Honour.
Following the July 1830 Revolution that saw King Louis Philippe come to power, de Rothschild put together a loan package to stabilize the finances of the new government, and in 1834 a second loan. In gratitude for his services to the French nation, Louis Philippe elevated him to the dignity of Grand Officer of the Legion of Honour.
King Louis Philippe was forced to abdicate after the outbreak of the French Revolution of 1848. Under Emperor Napoleon III, de Rothschild lost part of his political influence, however, despite some difficulties, the family business survived and prospered under the new regime. From 1852, he also had to defend the attacks of the bank Crédit Mobilier. The conflict between the Rothschilds and the rival company also spread to other countries. De Rothschild succeeded in maintaining the leading position of his house.
In addition to his banking business, de Rothschild purchased Château Lafite in 1868, one of France's most outstanding vineyards. Located in the Bordeaux region, it is a business that remains in the family to this day.
Personal life

On 11 July 1824, in Frankfurt, Germany, de Rothschild married his niece Betty von Rothschild (1805–1886), the daughter of his elder brother, Salomon Mayer von Rothschild (1774–1855). They had the following children:
- Charlotte de Rothschild (1825–1899), who married Nathaniel de Rothschild (1812–1870)
- Mayer Alphonse de Rothschild (1827–1905), who married Leonora de Rothschild (1837–1911), the daughter of Lionel de Rothschild of the English branch of the family.
- Gustave Samuel de Rothschild (1829–1911), who married Cécile Anspach
- Salomon James de Rothschild (1835–1864), who married Adèle von Rothschild (1843–1922), daughter of his cousin Mayer Carl von Rothschild
- Edmond Benjamin de Rothschild (1845–1934), who married Adelheid von Rothschild (1853–1935), daughter of Wilhelm Carl von Rothschild and Mathilde Hannah von Rothschild of the Naples branch of the Rothschild family
De Rothschild and his sophisticated Viennese wife were at the center of Parisian culture. The chef for their lavish receptions was Antonin Carême.[4] They patronized major personalities in the arts, including Gioacchino Rossini, Frédéric Chopin, Honoré de Balzac, Eugène Delacroix, and Heinrich Heine. As an acknowledgment of the many years of patronage extended by Baron James and his wife Betty, in 1847 Chopin dedicated his Valse Op. 64, N° 2 in C sharp minor to their daughter Charlotte. In 1848 Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres painted Betty de Rothschild's portrait.
Personality
After the death of Nathan in 1836, James took over the management of the family firm. His sons, brothers and nephews were in awe of his dynamic authority. Contemporaries remembered his quick wit, expressed in a heavy German accent, though the sharp tongue which went with it was not always benign. James was devoted to his extended family, but it was not beyond him to turn against any member whom he felt to have acted improperly. His response to the marriage of his niece, Hannah Mayer, displayed at once his demand for obedience and his faithfulness to the family's Jewish beliefs.
Residence
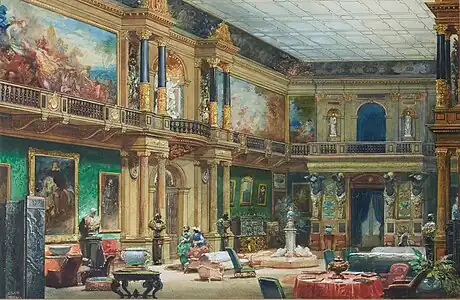
In 1817, de Rothschild purchased Château Rothschild in Boulogne-Billancourt, where his children were born and reared. In 1838, he purchased from Charles Maurice de Talleyrand a large residence in Paris, at 2 rue Saint-Florentin on the Place de la Concorde. It remained in the family until 1950, when it was sold to the United States government; today it serves as the consular section of the American Embassy.
In 1854, de Rothschild commissioned the famous architect Joseph Paxton to build the Château de Ferrières in Ferrières-en-Brie, some 35 kilometres (22 mi) east of Paris. Ferrières was inaugurated 16 December 1862 with a gala attended by Napoleon III. The property remained the home of his inheriting male descendants until 1975, when Guy de Rothschild gave it to the University of Paris. It was considered to be the largest and most luxurious 19th-century château in France.
Art collection
Beyond his business activities, de Rothschild was an avid collector of art, fuelled not only by a desire to show himself the equal in taste and possessions of any of the French aristocracy but by a genuine interest. The purchase of Greuze's painting, La Laitière, in 1818 formed the basis of a magnificent art collection which he supplemented often in frenzied buying sprees from the grand sales of the Paris hotels.
Horse racing
In 1835, Baron James de Rothschild created racing stables at his Ferrières estate. Still in existence, now relocated to Normandy, the Rothschild stables are one of the oldest in France. Ferrières was the perfect location, close to both Paris and Chantilly, which was the centre of the horse-racing world in France. Initially, the majority of horses belonging to Baron James raced under the colours of their trainer, Thomas Carter, in amber vest, lilac sleeves and grey cap. This was soon changed to the now famous blue vest and yellow cap, variations of which are still used by different members of the Rothschild family. The stables were successful in James's lifetime with victories in the Grand Prix Royal in 1844 won by Drummer, and the Prix du Jockey Club in 1846 won by Médon.
Philanthropy
De Rothschild also used his enormous wealth for philanthropic works and became a leader of the French Jewish community. His contributions to France, along with those of his offspring, can be found in many fields, including medicine and the arts. He was involved in many charities: anti-tuberculosis dispensaries, the first social housing in Paris, or aid provided to Assistance Publique.
Funeral

Baron James de Rothschild died in 1868, just three months after purchasing the Chateau Lafite vineyard. As Nathaniel de Rothschild reported, on his funeral, 4,000 guests waited in his drawing rooms, while another 6,000 guests waited in the courtyard. The streets of Paris, from the Rue Laffitte across to Père Lachaise Cemetery, were lined with unknown thousands of citizens, who paid tribute to the banker. De Rothschild had remained active in business throughout his life, expanding his railways, industries, factories, shipping, and mining interests so successfully that by the time of his death, the capital of the Paris house perhaps even exceeded some of his other prominent family members.
Sons Alphonse and Gustave took the reins of a vast French business empire, whose industrial interests spread as far afield as Africa and the South Sea Islands.
See also
References
- ↑ Niall Ferguson, The House of Rothschild (1999) p 87ff.
- ↑ Muhlstein (1983)
- ↑ "This day, May 15, in Jewish history". Cleveland Jewish News. Archived from the original on 2014-05-19. Retrieved 2014-05-18.
- ↑ Crème du Carême
In popular culture
- The House of Rothschild (1934) directed by Alfred L. Werker. He was played by Murray Kinnell.
- Die Rothschilds (1940) directed by Erich Waschneck. He was played by Albert Lippert.
- Sharpe's Rifles, the first episode of the TV miniseries, based on the novel of the same name by Bernard Cornwell. He was played by Kerry Shale.
Further reading
- Grunwald, Kurt. "Europe's Railways and Jewish Enterprise: German Jews as Pioneers of Railway Promotion." Leo Baeck Institute Yearbook 12.1 (1967): 163–209, on Rothschild and the Pereire brothers.
- Muhlstein, Anka (1983). Baron James: The Rise of the French Rothschilds. New York: Vendome Press. ISBN 978-0-86565-028-2.
External links
 Media related to James Mayer de Rothschild at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to James Mayer de Rothschild at Wikimedia Commons