
A total lunar eclipse took place on Sunday, June 3, 1928.
Visibility
It was completely visible over Asia, Australia and the Americas, seen rising over Asia and Australia and setting over the Americas.

Related lunar eclipses
Saros series
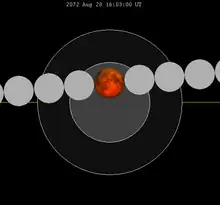
Lunar saros series 129, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, containing 71 events, has 11 total lunar eclipses. The first total lunar eclipse of this series was on May 24, 1910, and last will be on September 8, 2090. The longest occurrence of this series was on July 16, 2000 when totality lasted 106 minutes and 24.6 seconds.
| Greatest | First | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 The greatest eclipse of the series occurred on 2000 Jul 16, lasting 106 minutes. |
Penumbral | Partial | Total | Central |
| 1351 Jun 10 | 1513 Sep 15 | 1910 May 24 | 1946 Jun 14 | |
| Last | ||||
| Central | Total | Partial | Penumbral | |
| 2036 Aug 7 | 2090 Sep 8 | 2469 Apr 26 | 2613 Jul 24 | |
| 1910 May 24 | 1928 Jun 3 | 1946 Jun 14 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1964 Jun 25 | 1982 Jul 6 | 2000 Jul 16 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
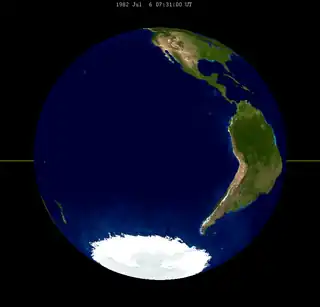
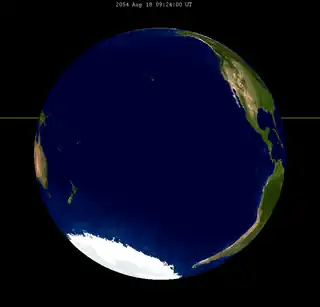
| 2018 Jul 27 | 2036 Aug 7 | 2054 Aug 18 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
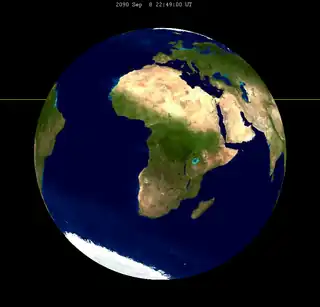
| 2072 Aug 28 | 2090 Sep 8 | ||||
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
It last occurred on May 24, 1910 and will next occur on June 14, 1946.
This is the 33rd member of Lunar Saros 129. The previous event was the May 1910 lunar eclipse. The next event is the June 1946 lunar eclipse. Lunar Saros 129 contains 11 total lunar eclipses between 1910 and 2090. Solar Saros 136 interleaves with this lunar saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series.
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[1] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 136.
| May 29, 1919 | June 8, 1937 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
See also
Notes
- ↑ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
- 1928 Jun 03 chart Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC

_(cropped).jpg.webp)
