| Laacher See | |
|---|---|
 View of the caldera volcano | |
 Laacher See Location in Germany  Laacher See Laacher See (Germany) | |
| Location | Ahrweiler, Rhineland-Palatinate |
| Coordinates | 50°24′45″N 07°16′12″E / 50.41250°N 7.27000°E |
| Type | Volcanic caldera lake |
| Primary inflows | None |
| Primary outflows | Fulbert-Stollen (canal) |
| Basin countries | Germany |
| Max. length | 1.964 km (1.220 mi) |
| Max. width | 1.186 km (0.737 mi) |
| Surface area | 3.31 km2 (1.28 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 31 m (102 ft) |
| Max. depth | 51 m (167 ft) |
| Water volume | 1.03 km3 (0.25 cu mi) |
| Shore length1 | 7.3 km (4.5 mi) |
| Surface elevation | 275 m (902 ft) |
| Islands | None |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
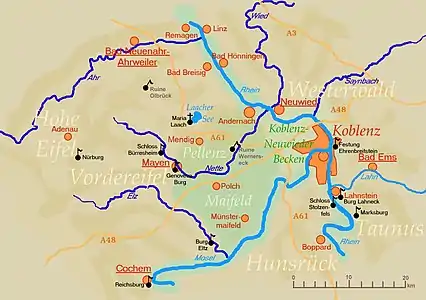
Laacher See (German pronunciation: [ˈlaːxɐ ˈzeː]), also known as Lake Laach or Laach Lake, is a volcanic caldera lake with a diameter of 2 km (1.2 mi) in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, about 24 km (15 mi) northwest of Koblenz, 37 km (23 mi) south of Bonn, and 8 km (5.0 mi) west of Andernach. It is in the Eifel mountain range, and is part of the East Eifel volcanic field within the larger Volcanic Eifel. The lake was formed by a Plinian eruption approximately 13,000 years BP with a Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 6, on the same scale as the Pinatubo eruption of 1991.[1][2][3][4][5] The volcanic discharge observable as mofettas on the southeastern shore of the lake are signs of dormant volcanism.
Description
The lake is oval in shape and surrounded by high banks. The lava was quarried for millstones from the Roman period until the introduction of iron rollers for grinding grain.[6]
On the western side lies the Benedictine Maria Laach Abbey (Abbatia Lacensis), founded in 1093 by Henry II of Laach of the House of Luxembourg, first Count Palatine of the Rhine, who had his castle opposite to the monastery above the eastern lakeside.
The lake has no natural outlet but is drained by a tunnel dug before 1170 and rebuilt several times since. It is named for Fulbert, abbot of the monastery from 1152–1177, who is believed to have built it.
The eruption
Volcanism in Germany can be traced back for millions of years, related to the development of the European Cenozoic Rift System, which was caused by the collision between the African and Eurasian plates. Yet, the Eifel volcanism, which started in the East Eifel volcanic field around 450,000 BC, is the result of a hotspot.
The initial blasts of Laacher See, which took place in late spring or early summer at around 11,000 BC, flattened trees up to four kilometres away. The magma opened a route to the surface that erupted for about ten hours, with the plume probably reaching a height of 35 kilometres. Activity continued for several weeks or months, producing pyroclastic currents that covered valleys up to ten kilometres away with sticky tephra. Near the crater, deposits reach over fifty metres in thickness, and even five kilometres away they are still ten metres thick. All plants and animals for a distance of about sixty kilometres to the northeast and forty kilometres to the southeast must have been wiped out.[7] An estimated 6 km3 (1.4 cu mi) of magma erupted,[8] producing around 16 km3 (3.8 cu mi) of tephra.[9] This 'huge' Plinian eruption thus had a Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 6.
Tephra deposits from the eruption dammed the Rhine, creating a 140 km2 (50 sq mi) lake. When the dam broke, an outburst flood swept downstream, leaving deposits as far away as Bonn.[8] The fallout has been identified in an area of more than 300,000 square kilometres, stretching from central France to northern Italy and from southern Sweden to Poland, making it an invaluable tool for chronological correlation of archaeological and palaeoenvironmental layers across the area.[10]


Aftermath of the eruption

The wider effects of the eruption were limited, amounting to several years of cold summers and up to two decades of environmental disruption in Germany. However, the lives of the local population, known as the Federmesser culture, were disrupted. Before the eruption, they were a sparsely distributed people who subsisted by foraging and hunting, using both spears and bows and arrows. According to archaeologist Felix Riede, after the eruption the area most affected by the fallout, the Thuringian Basin occupied by the Federmesser, appears to have been largely depopulated, whereas populations in southwest Germany and France increased. Two new cultures, the Bromme of southern Scandinavia and the Perstunian of northeast Europe emerged. These cultures had a lower level of toolmaking skills than the Federmesser, particularly the Bromme who appear to have lost the bow and arrow technology. In Riede's view the decline was a result from the disruption caused by the Laacher See volcano.[11]
The eruption was discussed as a possible cause for the Younger Dryas, a period of global cooling near the end of the last glacial maximum that appeared to coincide with the time of the Laacher See eruption.[12][13] A new radiocarbon date for the eruption, published in 2021, suggested that the Younger Dryas began about 130 years after the eruption,[14] though this new date was challenged as having perhaps been affected by radiocarbon dead magmatic carbon, which was not accounted for and would have made the date appear too old.[15] The current best estimates for the age of the Laacher See eruption are 12,880 ± 40 years BP[16] or 13,006 ± 9 calibrated years before present,[14] depending on if the radiocarbon date was affected by magmatic carbon dioxide. If the date was affected by magmatic carbon dioxide, the Laacher See eruption would then have occurred immediately before the onset of the Younger Dryas Event, and could have acted a trigger. If the radiocarbon-derived date of 13,006 calibrated years before present is correct, the Laacher See eruption may have still affected climate as part of a large cluster of volcanic events happening in the 130 years immediately before the event,[17] though would not have immediately preceded the event.
See also
References
- ↑ Oppenheimer, Clive (2011). Eruptions that Shook the World. Cambridge University Press. pp. 216–217. ISBN 978-0-521-64112-8.
- ↑ de Klerk, Pim; et al. (2008). "Environmental impact of the Laacher See eruption at a large distance from the volcano: Integrated palaeoecological studies from Vorpommern (NE Germany)". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 270 (1–2): 196–214. Bibcode:2008PPP...270..196D. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.09.013.
- ↑ Bogaard, Paul van den (1995). "40Ar/39Ar ages of sanidine phenocrysts from Laacher See Tephra (12,900 yr BP): Chronostratigraphic and petrological significance". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 133 (1–2): 163–174. Bibcode:1995E&PSL.133..163V. doi:10.1016/0012-821X(95)00066-L.
- ↑ "Geo-Education and Geopark Implementation in the Vulkaneifel European Geopark/Vulkanland Eifel National Geopark". The Geological Society of America. 2011. Archived from the original on 13 January 2019. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- ↑ Reinig, Frederick; Wacker, Lukas; Jöris, Olaf; Oppenheimer, Clive; Guidobaldi, Giulia; Nievergelt, Daniel; et al. (30 June 2021). "Precise date for the Laacher See eruption synchronizes the Younger Dryas". Nature. 595 (7865): 66–69. Bibcode:2021Natur.595...66R. doi:10.1038/S41586-021-03608-X. ISSN 1476-4687. Wikidata Q107389873.
[Measurements] firmly date the [Laacher See eruption] to 13,006 ± 9 calibrated years before present (BP; taken as AD 1950), which is more than a century earlier than previously accepted.
- ↑ Hull, Edward (1892). Volcanoes: Past and Present (2010 ed.). Echo Library. pp. 73–74. ISBN 9781406868180. Archived from the original on 28 April 2022. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ↑ Oppenheimer, pp. 216–218
- 1 2 Schmincke, Hans-Ulrich; Park, Cornelia; Harms, Eduard (1999). "Evolution and environmental impacts of the eruption of Laacher See Volcano (Germany) 12,900 a BP". Quaternary International. 61 (1): 61–72. Bibcode:1999QuInt..61...61S. doi:10.1016/S1040-6182(99)00017-8.
- ↑ P.v.d. Bogaard, H.-U. Schmincke, A. Freundt and C. Park (1989). Evolution of Complex Plinian Eruptions: the Late Quarternary (sic) Laacher See Case History Archived 19 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine, "Thera and the Aegean World III", Volume Two: "Earth Sciences", Proceedings of the Third International Congress, Santorini, Greece, 3–9 September 1989. pp. 463–485.
- ↑ Oppenheimer, p. 218.
- ↑ Oppenheimer, pp. 217–222
- ↑ Baales, Michael; Jöris, Olaf; Street, Martin; Bittmann, Felix; et al. (November 2002). "Impact of the Late Glacial Eruption of the Laacher See Volcano, Central Rhineland, Germany". Quaternary Research. 58 (3): 273–288. Bibcode:2002QuRes..58..273B. doi:10.1006/qres.2002.2379. ISSN 0033-5894. S2CID 53973827.
- ↑ Baldini, James U. L.; Brown, Richard J.; Mawdsley, Natasha (4 July 2018). "Evaluating the link between the sulfur-rich Laacher See volcanic eruption and the Younger Dryas climate anomaly". Climate of the Past. 14 (7): 969–990. doi:10.5194/cp-14-969-2018. ISSN 1814-9332.
- 1 2 Reinig, Frederick; Wacker, Lukas; Jöris, Olaf; Oppenheimer, Clive; et al. (30 June 2021). "Precise date for the Laacher See eruption synchronizes the Younger Dryas". Nature. 595 (7865): 66–69. Bibcode:2021Natur.595...66R. doi:10.1038/S41586-021-03608-X. ISSN 1476-4687. Wikidata Q107389873.
- ↑ Baldini, James U. L.; Brown, Richard J.; Wadsworth, Fabian B.; Paine, Alice R.; Campbell, Jack W.; Green, Charlotte E.; Mawdsley, Natasha; Baldini, Lisa M. (5 July 2023). "Possible magmatic CO2 influence on the Laacher See eruption date". Nature. 619 (7968): E1–E2. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-05965-1. ISSN 0028-0836.
- ↑ Brauer, Achim; Endres, Christoph; Günter, Christina; Litt, Thomas; Stebich, Martina; Negendank, Jörg F.W. (March 1999). "High resolution sediment and vegetation responses to Younger Dryas climate change in varved lake sediments from Meerfelder Maar, Germany". Quaternary Science Reviews. 18 (3): 321–329. doi:10.1016/s0277-3791(98)00084-5. ISSN 0277-3791.
- ↑ Abbott, P.M.; Niemeier, U.; Timmreck, C.; Riede, F.; McConnell, J.R.; Severi, M.; Fischer, H.; Svensson, A.; Toohey, M.; Reinig, F.; Sigl, M. (December 2021). "Volcanic climate forcing preceding the inception of the Younger Dryas: Implications for tracing the Laacher See eruption". Quaternary Science Reviews. 274: 107260. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2021.107260. hdl:2158/1256642. ISSN 0277-3791.
Further reading
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 16 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 1.
- Ginibre, Catherine; Wörner, Gerhard; Kronz, Andreas (2004). "Structure and Dynamics of the Laacher See Magma Chamber (Eifel, Germany) from Major and Trace Element Zoning in Sanidine: a Cathodoluminescence and Electron Microprobe Study". Journal of Petrology. 45 (11): 2197–2223. Bibcode:2004JPet...45.2197G. doi:10.1093/petrology/egh053.
- Park, Cornelia; Schmincke, Hans-Ulrich (1997). "Lake Formation and Catastrophic Dam Burst during the Late Pleistocene Laacher See Eruption (Germany)". Naturwissenschaften. 84 (12): 521–525. Bibcode:1997NW.....84..521P. doi:10.1007/s001140050438. S2CID 36411187.
- Riede, Felix (2008). "The Laacher See-eruption (12,920 BP) and material culture change at the end of the Allerød in Northern Europe". Journal of Archaeological Science. 35 (3): 591–599. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2007.05.007.
- Hensch, Martin; Dahm, Torsten; Ritter, Joachim; Heimann, Sebastian; Schmidt, Bernd; Stange, Stefan; Lehmann, Klaus (2019). "Deep low-frequency earthquakes reveal ongoing magmatic recharge beneath Laacher See Volcano (Eifel, Germany)". Geophysical Journal International. 216 (3): 2025–2036. Bibcode:2019GeoJI.216.2025H. doi:10.1093/gji/ggy532.
External links
- Continuous event display of the 10 most recent registered seismic activities measured from the Laacher See
- Nixdorf, B.; et al. (2004), "Laacher See", Dokumentation von Zustand und Entwicklung der wichtigsten Seen Deutschlands (in German), Berlin: Umweltbundesamt, p. 28
- Apokalypse im Rheintal (Cornelia Park und Hans-Ulrich Schmincke)
- Martin Hensch, etal.: Deep low-frequency earthquakes reveal ongoing magmatic recharge beneath Laacher See Volcano (Eifel, Germany). Geophys. J. Int. (2019) 216, 2025–2036 doi:10.1093/gji/ggy532
- Michael W. Förster, Frank Sirocko: Volcanic activity in the Eifel during the last 500,000 years: The ELSA-Tephra-Stack .Global and Planetary Change (2016) (PDF)