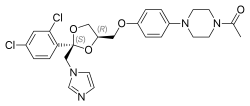 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Recorlev |
| Other names | COR-003; (2S,4R)-ketoconazole; NormoCort |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H28Cl2N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 531.43 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Levoketoconazole, sold under the brand name Recorlev, is a steroidogenesis inhibitor that is used for the treatment of Cushing's syndrome.[3][4][5][6] Levoketoconazole was approved for medical use in the United States in December 2021.[7][8]
Levoketoconazole is the levorotatory or (2S,4R) enantiomer of ketoconazole,[4][5][6] and it is an inhibitor of the enzymes CYP11B1 (11β-hydroxylase), CYP17A1 (17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase), and CYP21A2 (21-hydroxylase).[3][4][6] It inhibits glucocorticoid biosynthesis and hence circulating levels of glucocorticoids, thereby treating Cushing's syndrome.[3][6] In addition to its increased potency, the drug is 12-fold less potent than racemic ketoconazole in inhibiting CYP7A1 (cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase), theoretically resulting in further reduced interference with bile acid production and metabolite elimination and therefore less risk of hepatotoxicity.[6] Levoketoconazole has also been found to inhibit CYP11A1 (cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme) and CYP51A1 (lanosterol-14α-demethylase), similarly but more potently relative to ketoconazole.[9]
References
- ↑ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ↑ "Recorlev- levoketoconazole tablet". DailyMed. 12 January 2022. Retrieved 20 February 2022.
- 1 2 3 "Levoketoconazole - Strongbridge Biopharma". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
- 1 2 3 Laws Jr ER, Pace L (11 November 2016). Cushing's Disease: An Often Misdiagnosed and Not So Rare Disorder. Elsevier Science. pp. 113–. ISBN 978-0-12-804390-5.
- 1 2 Geer EB (1 December 2016). The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis in Health and Disease: Cushing's Syndrome and Beyond. Springer. pp. 170–. ISBN 978-3-319-45950-9.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Cuevas-Ramos D, Lim DS, Fleseriu M (2016). "Update on medical treatment for Cushing's disease". Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology. 2 (1): 16. doi:10.1186/s40842-016-0033-9. PMC 5471955. PMID 28702250.
- ↑ "Levoketoconazole: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ "Xeris Biopharma Announces U.S. FDA Approval of Recorlev (levoketoconazole) for the Treatment of Endogenous Hypercortisolemia in Adult Patients With Cushing's Syndrome" (Press release). Xeris Biopharma. 30 December 2021. Retrieved 3 January 2022 – via Business Wire.
- ↑ Thieroff-Ekerdt R, Lavin P, Abou-Gharbia M, France N (October 2016). Pharmacology of COR-003 (levoketoconazole), an investigational treatment for endogenous Cushing's syndrome (PDF). Pituitary disorders—it’s not the anterior pituitary (posters). Endocrine Society. pp. SAT-547–SAT-547. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
External links
- "Levoketoconazole". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Clinical trial number NCT03277690 for "A Study to Assess the Safety and Efficacy of Levoketoconazole in the Treatment of Endogenous Cushing's Syndrome" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT01838551 for "Treatment for Endogenous Cushing's Syndrome (SONICS)" at ClinicalTrials.gov