The Lewitz is a protected landscape in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, a land of broad, flat pastures and farmland, fish ponds and occasional woodlands.
Geography




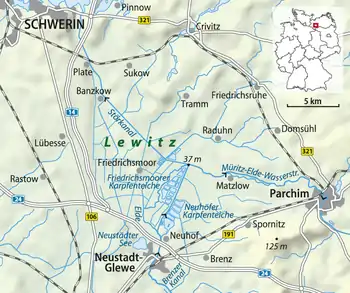
The terrain of the Lewitz lies in the southwest of Mecklenburg, south of Schwerin between the settlements of Crivitz, Parchim, Neustadt-Glewe and Banzkow. Its area is about 16,800 hectares.[1] The landscape is crossed by the River Elde, whose original river bed survives in places, its canalised course, the Müritz-Elde Waterway (MEW), the Stör Canal, which empties here into the MEW, the New Canal and the Brenz Canal. The Lewitz, which is a protected landscape, is also dissected by numerous drainage ditches. Amongst the standing waterbodies are the protected,[2] extensive Friedrichsmoor Carp Ponds and Neuhof Carp Ponds north of Neustadt-Glewe and the Neustädter See.
Within the Lewitz are the nature reserves of Klinker Plage, Fischteiche in der Lewitz, Friedrichsmoor und Töpferberg.
Origin of the name
The origin of the name has various theories. One common one is the belief that the word Lewitz comes from the Slavic lowit which means "gathering", "hunting" or "game-rich region".[3] Another possible derivation is lowej (Bohemian for "wood" or "woodland").[4] It is also possibly related to the Old Slavic li-, liv-, lijati meaning "to water" or "rain", the Russian lyva or liva meaning "swamp wood" or the Bulgarian/Serbian livada meaning "pasture".[5]
History
The Lewitz was formed, like the whole of Mecklenburg, in the last ice age. When the glacier melted it filled the Lewitz and the Stör valley with meltwater which scoured out a basin, 12,000 hectares in area. A 16 metre deep lake was formed. Later it suddenly emptied southwards. The lake became marshy and turned into peat over the course of the following millennia. Shallow waterbodies and fens (Niedermoore). In the Middle Stone Age its island-like hills, small lakes and woods offered hunters, gatherers and fishers suitable places to settle. Likewise the dried out, sandy moorlands were suitable for the arable farmers and cattle breeders of the New Stone Age. During that time several Funnelbeaker culture earthworks were constructed.
In the 13th century the Lewitz depression was still covered by oak, beech, black alder and birch. The expanding towns during the Hanseatic period obtained their wood from the Lewitz and other areas. From the early 16th century to the 18th century Neustadt-Glewe was one of the centres of bog iron ore smelting. The iron was surface-mined. The Lewitz was well suited to this wood-hungry industry with its river system and extensive woodlands. Charcoal was made from the wood and this in turn became fuel for the smelting ovens. In 1577 alone, 6,300 tonnes of coal and 8,300 cubic metres of wood were needed. In addition, so-called Holzdeputanten ("wood deputies") of the princely house and court, "wood taxes" paid to the surrounding towns and a flourishing timber trade led to a shrinkage of the stocks of timber. By the 17th century these stood at only 25% of their original size. In 1620 the last beech and oak trees were felled in Tuckhude for the construction of Kraaker Castle. The timber industry was unsustainable, with the result that the last iron smeltery in Neustadt closed in 1717 due to a lack of wood. At that time the forests of the surrounding area were almost entirely gone and in their place boggy pastures emerged that were harvested for hay. The Friedrichsmoor Forest Office (Forstamt Friedrichsmoor) that was established in the 18th century managed the reforestation of small areas of land in the years that followed. However, a complete restoration of the original forests was not carried out, because as early as the end of the 1820s, people expected that income from the management of pasture would exceed that of the timber industry.
In 1862/63 the Brenz Canal was constructed in order to drain the land northwest of Brenz and enable it to be used for agriculture. In 1862 the head office for the administrative department of the ducal court in the Lewitz was established in Tuckhude. It was responsible for the maintenance of the ditches, paths, bridges, control of irrigation and drainage, monitoring the water levels and ensuring the harvest.
By 1938 parts of the Lewitz were already being placed under conservation orders due to their importance as breeding areas for waders. Breeding species here include the curlew, redshank, black-tailed godwit and ruff. During the GDR period, from 1958 to 1962 and 1976 to 1980, with the introduction of industrial agricultural production methods, complex, large-scale land improvement work was carried out in order to create grassland for cattle breeding. Many animal and plant species disappeared, as did the population of breeding birds on the pasture land.
In the Neustadt village of Hohes Feld horses were bred for riding at the Lewitz VEG along with cattle breeding. Since 1971 there has been a new breed of horse, the Lewitzer or Lewitzschecken from its piebald (gescheckt) colour.[6] The Lewitz estate has been run since the Wende by German show jumper and businessman, Paul Schockemöhle.
Since 1990 land improvement measures have been partially reversed. Wet biotopes with wet meadows and bogs have been recreated out of pasture and arable land. As a result, several threatened species of plant and animal have established themselves here. osprey, falcon, otter, great crested newt and grass snake have been seen once more. The Lewitz is a popular stopover for wild geese, crane and other migratory birds. Amongst the rare plants in the Lewitz are orchids, Pasqueflower, common tormentil and marsh gentian. The Lewitz is today both a protected area and nature reserve. Parts of the landscape were also designated as a European Bird Reserve at the end of the 20th century.[7]
Tourism

There are attempts to market the Lewitz as a destination for sustainable tourism. Brown tourist signs to "The Lewitz", with outlines of Neustadt Castle and the countryside, have been installed on the A 24 motorway. The aim is to attract especially nature lovers and water explorers. Also worth seeing are the Friedrichsmoor hunting lodge, the preserve of former dukes, the Tuckhude Land Office (Wiesenmeisterei) and the Banzkow Mill.
References
- ↑ List of the protected landscapes in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern at http://www.lung.mv-regierung.de/
- ↑ List of the nature reserves in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern at http://www.lung.mv-regierung.de/
- ↑ Landesportal MV Archived 2012-01-19 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ LISCH/WEDEMEIER: Friedrichsmoor. Grossherzogliches Jagdhaus im Domanial-Amt Neustadt. Archived 2007-10-26 at the Wayback Machine at lexikus.de
- ↑ Paul Kühnel, Die slavischen Ortsnamen in Meklenburg in Jahrbücher des Vereins für Mecklenburgische Geschichte und Altertumskunde. - Bd. 46 (1881), p. 83 Archived 2012-02-10 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Steckbrief der Pferderasse "Lewitzer" auf lewitz-partner.de". Archived from the original on 2012-04-26. Retrieved 2011-12-14.
- ↑ Standarddatenbogen EU-Vogelschutzgebiet Lewitz
Literature
- Ralf Ottmann, Europäisches Vogelschutzgebiet Lewitz, Naturperle in Mecklenburg., 2011, ISBN 978-3-00-034947-8
- Burkhard Fellner, Faszination Lewitz. Ein Naturparadies in Mecklenburg., 2006, ISBN 3-9811338-0-3
- ders., Ansichten aus der Lewitz, Mecklenburg-Magazin 2004 No. 5 p. 7, No. 6 p. 7, No. p S. 9, No. 11 p. 7 f., No. 15 p. 3f. and No. 20 p. 7 f., 2005 No. 9 p. 9 f., No. 20 p. 1 f.
- Georg Christian Friedrich Lisch, Friedrich Wedemeier: Album Mecklenburgischer Schlösser und Landgüter. 1860-62
- Frank Löser, Sagen und Geschichten der Kulturlandschaft Lewitz , Verlag Rockstuhl, Bad Langensalza, 2009, ISBN 978-3-86777-101-6
- Hans Mulsow, Entstehung und Entwicklung der Lewitz, Diss. Rostock 1941 (masch.schr.) nebst Bildanlage hierzu